Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):345-351
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600005
PURPOSE: to evaluate association between CD4+ cell count and cervical intraepithelial lesion severity in HIV-infected women. METHODS: cross-sectional study of 87 HIV-infected patients which were confirmed by previous serologic examinations. All had cervical HPV diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). All patients underwent anamnesis, physical examinations and colposcopy. Cervix biopsy was performed when indicated by colposcopical examination. Histopathological results followed Richart's classification, adapted by Wright, and CD4+ cell count and cervical intraepithelial lesion severity association was analysed by comparison of means using analysis using analysis of variance (ANOVA). RESULTS: among 60 biopsied women 24 were found (40.0%) with CIN I, eight (13.3%) with CIN II, three (5%) with CIN III, 14 (23.3%) with chronic cervicitis and 11 with cytopathic effect of HPV, without cell polarity loss. This corresponds to 35 (58.3%) women with intraepithelial lesion of low grade (CIN I + HPV) and 11 (18.3%) with intraepithelial lesion of high grade (CIN II + CIN III). There was no significant association between CD4+ cell count mean and cervical intraepithelial lesion severity (p=0.901). CONCLUSIONS: there was no association between CD4+ cell count and cervical intraepithelial lesion severity diagnosed by histopathological examination.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):352-357
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600006
PURPOSE: to analyze the impact of urinary incontinence on women's quality of life, submitted or not to surgical treatment. METHODS: sixty women with urinary incontinence during stress were interviewed and divided into two groups classified as: S-CIR group, including 30 women not yet submitted to specific surgical treatment for urinary incontinence, and C-CIR group, including 30 women who had already undergone surgery. The scores obtained after the addition of values attributed to each question of the questionnaires were compared between the two groups. The number of patients who showed any impairment on quality of life due to specific symptoms of incontinence was also compared between groups. Data were analyzed by the variance test and the chi-square test, when applicable. RESULTS: symptoms, limitations and concerns related to urinary incontinence exhibited a strong negative impact on quality of life in patients from the S-CIR group. Impairment during physical exercises, domestic activities and daily working activities was the most important affected aspect in patients of the S-CIR group. Furtherimore, patients of the S-CIR group reported more fatigue, embarrassment, and excessive nervousness. Urine loss during stress followed by urgency were also significantly relevant aspects when groups were compared. CONCLUSIONS: the study allowed the identification and quantification of the derangements of quality of life due to urinary incontinence and demonstrated that these derangements either become less important or even disappear in women submitted to surgery.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):358-364
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600007
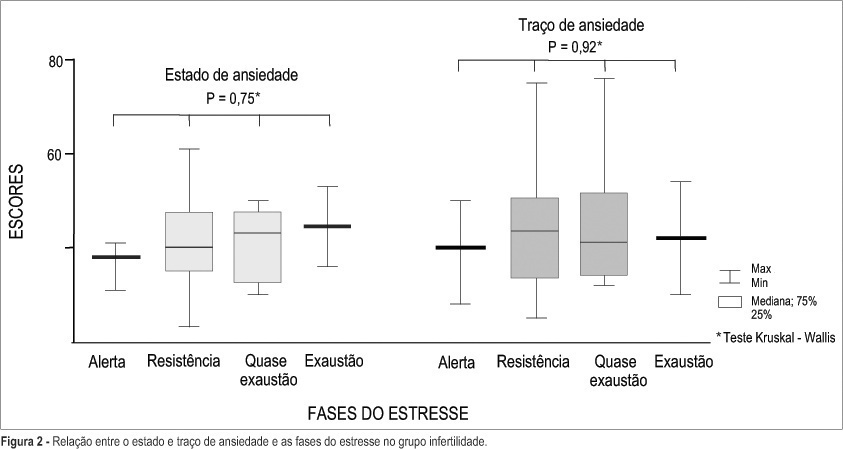
PURPOSE: to assess the frequency of stress and anxiety levels in infertile women, in order to obtain data for specific psychological intervention. METHODS: a cross-sectional study involving 152 infertile (mean age 30.3±5.4 years), and 150 healthy control women (25.7±7.9 years). All patients were evaluated with the Lipp's Inventory of Stress Symptoms and the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Considered dependent variables were: stress frequency and anxiety scores (state and trait). Statistical analysis was performed by the chi2 and Mann-Whitney tests, and logistical regression to test associations between response variables and considered risk factors. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05. RESULTS: the stress was more frequent in the infertile group than in the control group (61.8 and 36.0%, respectively); however, no significant differences were observed between groups in relation to stress phases and predominant symptoms. With respect to anxiety, there were no significant differences between infertile and control groups as to median state scores (39.5 and 41.0, respectively) and anxiety trait scores (44.0 and 42.0, respectively). Factors significantly associated with greater risk for high anxiety scores in the infertile group were: unawareness of the causal factor, diagnostic phase investigation, and lack of children from other marriages. CONCLUSIONS: it can be concluded that infertile women are more vulnerable to stress; however, they are capable of adapting themselves to stressful events without serious physical or psychological compromise.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):271-277
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the contraceptive methods adopted by the public health system of Maringá County, Paraná, regarding the orientations for using them, indications, contraindications and reasons for interrupting these methods, as well as the profile of the female users. METHODS: transversal descriptive study, performed through 284 home interviews with women selected from the 62 groups of the Family Health Program, after their free and informed consent, and after the questionnaire had been approved by the Ethics in Research Committee involving human beings of the State University of Maringá (Universidade Estadual de Maringá - UEM). Before applying the questionnaires, they were pretested, focusing on the following sections: characterization of the interviewee, socioeconomical factors and contraceptive methods. Results were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software 12.0 version. RESULTS: most women were white, married, between 35 and 49 years old, with high school education, working without salary, and from D and E economical classes. Of them, 22.5% were smokers and 4.9% alcohol users. Contraceptive pills were adopted by 50.3% of the women; condom by 28.1% and tubal ligature by 32%, following, in general, the health professional orientation. Reasons for interrupting the contraceptive methods were the wish to get pregnant, preference for a permanent method, and also because of the side effects of the pill. Smoking was the most prevalent risk factor for pill use. Only 35.9% of the interviewed women started using the pill after a previous medical visit, and almost in the same proportion, 33.6%, without visit before starting to use it. CONCLUSIONS: it was observed that the indications of the contraceptive method to be used, and the orientations accomplished by the health professionals were satisfactory, despite the high levels of tubal ligature and the detection of relative contraindications for pill users with more than 5 years of use.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):278-284
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500003
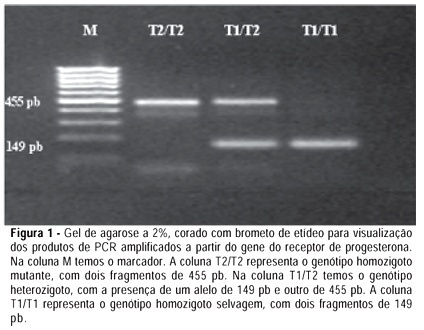
PURPOSE: to analyze race, parity and presence of the progesterone receptor polymorphism, named PROGINS, as factors related to uterine leiomyoma occurrence in Brazilian women. METHODS: we carried out a case-control study, composed of 122 patients with the diagnosis of uterine fibroid and 125 women without the disease. After recording the clinical data, we collected biological material for DNA extraction, polymerase chain reaction and agarose gel electrophoresis in order to identify the presence of PROGINS polymorphism. Statistical analysis was performed using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test or the chi2 test, depending on the studied variable. The risk for the occurrence of the disease was calculated by the logistic regression model, providing the odds ratio (OR). The adopted significance level was 5% (p<0.05) and the confidence interval was 95% (95% CI). RESULTS: we observed a higher prevalence of "non-white"women - mulatto and black - (50 vs 22.4%) and nulliparas (23.8 vs 11.2%) in the cases, while the progesterone receptor genotype was more often PROGINS positive - heterozygous or mutant homozygous - among the controls (21.6 vs 10.7%). The OR indicated an elevated risk for leiomyoma related to the "non-white"race (OR=3.46; 95% CI: 2.0-6.0) and the nulliparity (OR=3.30; 95% CI: 1.9-5.6), with reduction in the presence of PROGINS-positive genotypes (OR=0.43; 95% CI: 0.2-0.9). CONCLUSIONS: the "non-white"race and nulliparity were considered risk factors for the occurrence of uterine fibroid in the studied population, while PROGINS polymorphism showed to be a protective factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):285-291
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500004
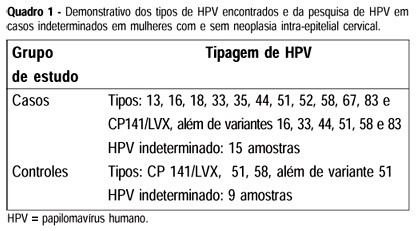
PURPOSE: to identify risk factors for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and human papillomavirus (HPV) types among women with CIN, and to compare with HPV types among patients with normal cervix. METHODS: a total of 228 patients were studied, of whom 132 with CIN (cases) and 96 with normal cervix (controls). In the two groups consisting of women selected among outpatients attended in the same hospital, living near the place of the research, mean ages were similar (34.0±8.3 years) and there was a predominance of married women. Possible risk factors for CIN were investigated with the application of a questionnaire surveying age, marital status, level of schooling, age at first coitus, number of pregnancies, number of sexual partners, method of used contraception, reference of previously sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and smoking habits, with a comparison between the studied groups. Samples were collected for oncologic colpocytology and HPV search through polymerase chain reaction (PCR), using MY09/MY11 primers; then colposcopic and histopathological examinations were performed. For statistical analysis of the association between risk factors and CIN, odds ratio with 95% confidence interval and chi2 and Fisher tests were used at a significance level of 0.05. The logistic regression method with the significance expressed by the p value with maximum likelihood was also applied. RESULTS: the following variables remained in the logistic regression model: HPV infection of high oncogenic risk (OR=12.32; CI 95%: 3.79-40.08), reference of previous STDs (OR=8.23; CI 95%: 2.82-24.04), early age at first coitus (OR=4.00; CI 95%: 1.70-9.39) and smoking habit (OR=3.94; CI 95%: 1.73-8.98). PCR was positive in 48.5 and 14.6% in the case and control groups, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: the main risk factor for CIN was oncogenic HPV infection, with types 16, 18, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58, and 83. Among patients with a high-degree lesion, there was a predominance of HPV-16 or type 16 variant. In patients with normal cervix oncogenic, HPV types 51, 58, and 51 variant were also identified.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):292-297
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500005
PURPOSE: to verify if there is a relationship between the clinical periodontal parameters and estrogen levels and bone mineral density (BMD). METHODS: forty-six post-menopausal women aged 44 to 68 years (52.2±4.8) and 15 women aged 35 to 54 years (44.7±7.5) were evaluated. Periodontal parameters like probing depth (PD), clinical attachment loss (CAL), and missing teeth (MT) were compared with estrogen levels (sufficient and insufficient) and BMD (normal, osteopenic and osteoporotic). Data of the mean difference between the groups were compared by the Aspin-Welch test. RESULTS: the means of PD, CAL and MT, when associated with the normal (2.1±0.5; 2.9±1.4 and 10.6±5.0), osteopenic (2.3±0.7; 3.0±1.1 and 12.8±5.1) and osteoporotic BMD (2.4±0.6; 2.7±0.9 and 14.3±5.7), did not show statistical difference (p>0.05). A significant difference was found between the control group and postmenopausal women for CAL and MT. When compared with the estrogen levels the results did not show a difference regarding the periodontal parameters. CONCLUSION: although some studies showed a positive correlation with osteoporosis and estrogen level, in this population of menopausal women these findings were not confirmed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):298-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500006
PURPOSE: to assess p53 protein expression in infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma and to analyze its association with histological and nuclear grade. METHODS: sixty-five consecutive females who were diagnosed with primary infiltrating ductal breast tumor from July 1999 to July 2001 were included in the present study. Mean patient age at diagnosis was 69.2 years (range 41 - 90). All patients were first treated with surgical therapy, conservative surgery or mastectomy. None of the patients received any preoperative adjuvant therapy. Resected breast tumor specimens were fixed in 10% formalin, paraffin embedded, and conserved for immunohistochemical analysis. p53 protein expression was evaluated. Primary monoclonal anti-human p53 antibody DO-7 (DAKO) was used. Frequency distributions were tested by the chi2 test. A level of p<0,05 was considered significant. RESULTS: p53 expression was detected in 24 (36,9%) of 65 carcinomas. Of the cases with protein expression, 13 (54,2%) were high or histological grade III, 8 (33,3%), were grade II, 3 (12,5%) were grade I. On nuclear grade analysis, of the cases with protein expression, 13 (4,2%) were nuclear grade III, 9 (37,5%) were grade II and 2 (8,3%) were grade I. p53 expression was frequent in carcinomas with high histological and nuclear grades. CONCLUSIONS: p53 expression was significantly associated with the histological grade. On the other hand, nuclear grade was not significantly related to p53 expression.