Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):460-466
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800004
PURPOSE: to assess the performance of lamellar body count compared to the shake (Clements) test in the prediction of fetal lung maturity in diabetics. METHODS: prospective study of 62 patients who underwent amniocentesis between the 26th and 39th week of pregnancy. Immediately after collection, the amniotic fluid sample was submitted to the shake test and lamellar body count. Deliveries occurred within three days of amniocentesis. Immature test results (absence of a complete bubble ring in the third tube for the shake test and less than 50,000 lamellar bodies) were confronted with the occurrence of pulmonary immaturity in the neonate (respiratory distress syndrome). The performance of both tests was compared using the chi2 test and p<0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: seven infants had respiratory distress syndrome (11.3%). The lamellar body count and shake test were similar regarding sensitivity (100 vs 71.4%, respectively) and negative predictive value (100 vs 93.5%). Lamellar body count was superior as regards specificity (87.3 vs 52.7%, p=0.0001), positive predictive value (50 vs 16.1%, p=0.017), and accuracy (88.7 vs 54.8%, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: lamellar body count is a simple and accurate method of assessing fetal lung maturity. It performs slightly better than the shake test in terms of specificity, positive predictive value and accuracy, with the advantage of not requiring manipulation or reagents. Similar to the shake test, lamellar body count has a high-negative predictive value: mature results (50,000 or more) indicate thar the infant will not have hyaline membrane.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):467-472
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800005
PURPOSE: to assess human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) seroprevalence among pregnant women attended at Public Health Units in Goiânia-Goiás and some epidemiologic characteristics of the studied group. METHODS: from September/2003 to December/2004, 15,485 pregnant women were submitted to enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assays (ELISA), to screen HTLV-I, using filter paper - dried blood in, and to confirm the infection, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of whole blood was performed. The epidemiologic factors evaluated were: average age, age of 30 years and above, schooling less than nine years, marital status and number of pregnancies. The factors average age, age of 30 years and above, and schooling less than nine years were compared between the infected and non-infected pregnant group. Statistical analysis used Fisher's exact test and Student's t test. RESULTS: the found prevalence was 0.1%. The average age among the infected pregnant group was 26.4 years, 43.7% of them being 30 years old and above, and 62.5% with schooling less than nine years. The non-infected group showed an average age of 24.4 years, 15.4% of them being ³ 30 years old and above, and only 41.5% with schooling less than nine years. Significant statistical difference was noticed only regarding age of 30 years and above and schooling less than nine years. CONCLUSION: the study shows that HTLV-I seroprevalence among pregnant women in Goiânia during the studied period was 0.1%. It occurred more among pregnant women who were 30 years old and above and those with schooling of less than nine years.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):473-478
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800006
PURPOSE: to verify the effects of intrauterine levonorgestrel device (IUD) in women with adenomyosis, with implantation failure in previous in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. METHODS: eighty infertile women with ages up to 38 years, who had adenomyosis diagnosed by ultrasonography and MRI were selected. All the women presented antecedents of one or more tormer IVF attempts without success due to implantation failure. The women were subdivided into IUD Group, composed of 40 women with an IUD that released 20 µg of levonorgestrel/day during six months, preceding a new IVF cycle, and IVF Group, also composed of 40 women, who were directly submitted to a new IVF cycle without previous adenomyosis treatment. In the IUD Group the uterine volume, thickness and hypersignal foci of the junctional zone were assessed before and after treatment, as well as the pregnancy rates in the new IVF cycle, compared to the data obtained with the IVF Group. Statistical analyses were performed adopting the significance level of 5% (p<0,05), using the Mann-Whitney and Sudent's t tests. RESULTS: after treatment, there was a reduction of 77.7% in the cases of focal adenomyosis, in addition to a significant reduction of the uterine volume and of the mean thickness of the junctional zone from 128.8 to 93.6 ml and from 12.3 to 11.3 mm, respectively. In the IUD Group, pregnancy rate reached 30%, which was higher than, but not significantly different from that of the IVF group, which was 17.5%. CONCLUSION: the use of an IUD with levonorgestrel may be administered prior to IVF cycles in patients with adenomyosis who suffered previous implantation failure.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):479-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800007
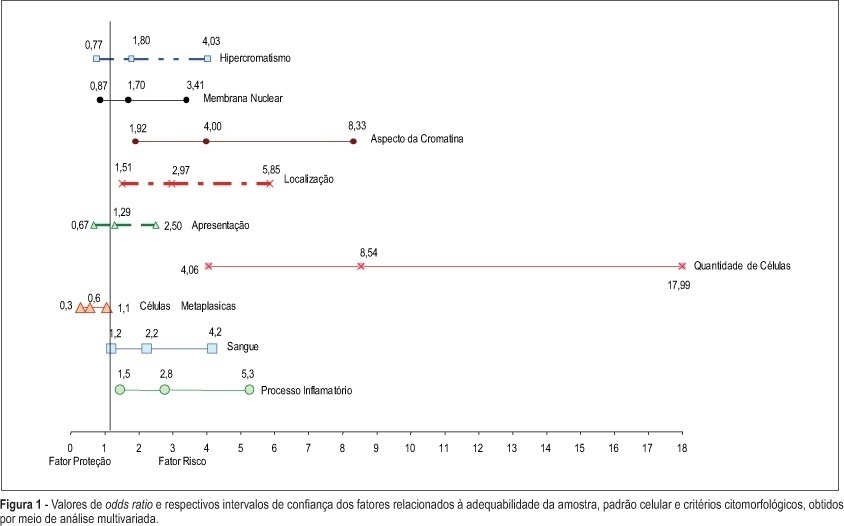
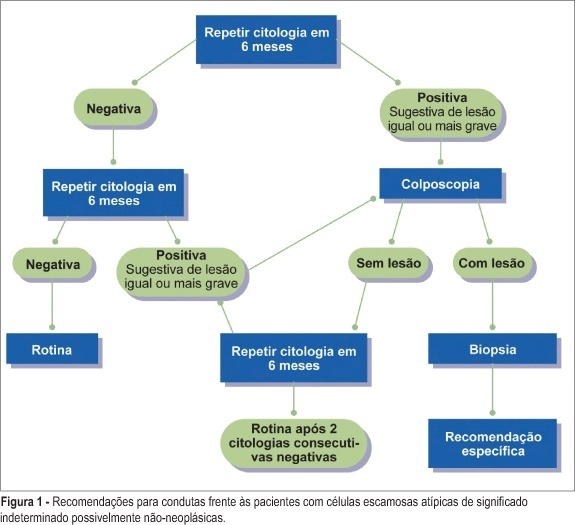
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether factors related to the adequacy of the sample, cell pattern and cytomorphological criteria are associated with false-negative (FN) results of cervical cytopathology during routine examinations. METHODS: this is a case-control study in which the study group included 100 cytopathologic smears with FN results detected during systematic internal quality control consisting of 100% rapid review. For each FN result detected, two smears with a true-positive diagnosis were identified by the same cytotechnician and these constituted the control group, making a total sample size of 300 smears. The variables were established in accordance with the criteria defined for the analysis of sample adequacy, cell pattern and cytomorphological analyzed criteria. The results were evaluated using bivariate analysis and logistic regression with stepwise variable selection criteria expressed in OR (95%). RESULTS: the number of atypical cells, the appearance of nuclear chromatin, and the distribution and presentation of atypical cells in the smear were the variables that showed the greatest risk for FN results with OR of 9.6, 4.2, 4.4, and 3.6, respectively. Inflammatory processes and the presence of blood in the smear were also identified as variables that influence the risk of FN results. CONCLUSIONS: the majority of the factors associated with FN results are dependent on the conditions and techniques of sample collection, since in the majority of cases, the lesion may not be adequately represented in the smear. Confounding factors such as blood and inflammatory processes may also impair analysis. With respect to cytomorphological alterations, thin chromatin strand was the variable that indicated the greatest risk of FN results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):486-504
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):324-330
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600002
PURPOSE: to compare the maternal factors, clinical aspects and perinatal results in placental abruption during two periods. METHODS: retrospective analysis of placental abruption cases that occurred from January 1, 1994 through December 31, 1997 (period 94-97), and from April 4, 2001 through March 3, 2005 (period 01-05), in singleton delivery with birthweight higher than 500 g and after 20 weeks of gestation. The following factors were analyzed: maternal age, previous obstetric history, prenatal care, premature rupture of membranes, obstetric and/or clinical intercurrent events, vaginal bleeding, uterine tonus, fetal anomaly, mode of delivery, hemoamnion and maternal complication (hysterectomy, uterine atony, disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute renal failure, and maternal death), and the perinatal results. RESULTS: the rate of placental abruption was 0.78% (60 cases) in the period 94-97 (n=7692 deliveries), and 0.59% (51 cases) in the period 01-05 (n=8644 deliveries), without significant difference. A significant difference was observed between the periods 94-97 and 01-05 regarding mean number of previous gestations (3.5±2.4 and 2.6±1.8, p=0.04), patients without prenatal care (13.3 and 2.0%, p=0.03) and maternal intercurrences (38.3 and 64.7%, p=0.01). No significant difference was observed related to vaginal bleeding, tonus abnormalities and perinatal results, between the periods, but a higher proportion of hemoamnion in 94-97 was found when compared to 01-05 (28.3 and 11.8%, p=0.03). CONCLUSIONS: in spite of obstetrical advances, maternal complications and perinatal results were similar in the analyzed periods. The severity and the unexpected results emphasize the importance of prevention and adequate control of associated factors, when this pathology is approached.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):331-339
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of supplementary ferrous sulfate and dietary counseling on hemoglobin levels in pregnant women. METHODS: a total of 197 pregnant women were evaluated during antenatal care at a health center. The treatment group consisted of 105 women who were prescribed 60 mg dietary iron per day, received dietary counseling and had hemoglobin measured by a portable photometer between the 14th and 20th week of pregnancy. The treatment group was reevaluated according to hemoglobin levels and food intake by a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire after the 34th week of pregnancy. The control group consisted of 92 women in a cross-sectional study, at no less than 34 weeks of pregnancy. Hemoglobin was analyzed by a portable photometer and anemia was defined concentrations of less than 11 g/dL. All pregnant women had their weight and height measured. Hierarchical logistic regression model was developed for the multivariate analysis. RESULTS: prevalence of anemia at the end of the third trimester was 31.6% in the treatment group and 26.1% in the control group (p=0.43). Use of the prescribed supplement was reported by 65% of women in the treatment group, of which 67.7% interrupted the treatment at some point. Principal reasons for interrupting treatment were forgetting (43.2%) and nausea or vomiting (27.2%). Risk of anemia in the third trimester was three times higher in women with less than 8 years of schooling. CONCLUSIONS: use of ferrous sulfate was not shown to be associated with lower prevalence of anemia. The results suggest that structural changes in socioeconomic conditions are needed in order to alter the current situation regarding iron deficiency anemia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(6):340-344
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000600004
PURPOSE: the study the effects of maternal cigarette smoking during pregnancy on placental maturation (calcifications) and the placental-uterine circulation, evaluated through umbilical and uterine Doppler. METHODS: prospective cohort study involving 244 pregnant women, 210 of them non-smokers and 34 smokers. Participants were submitted to four serial sonograms. The first was performed up to the 16th week of pregnancy to determine gestational age, and the other three at 28, 32 and 36 weeks for fetal biometry, evaluation of placental texture and Doppler studies of the uterine and umbilical arteries. Premature placental calcification was defined as grade III before 36 weeks. The chi2 and Fisher exact tests were used to compare placental grading, and the Mann-Whitney test to evaluate the resistance index of uterine and umbilical arteries. RESULTS: the frequency of grade III placenta and the resistance of the uterine arteries did not differ significantly between smokers and non-smokers, at all gestational ages. Umbilical artery Doppler was significantly higher in smokers than in non-smokers at 32 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: no association was found between cigarette smoking and premature placental calcification. Smoking was associated with increased umbilical artery resistance at 32 weeks.