Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):142-148
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000004
PURPOSE: to compare the intra and interobserver reproducibility of the total thickness measurement of the inferior uterine segment (IUS), through the abdominal route, and of the muscle layer measurement, through the vaginal route, using bi and tridimensional ultrasonography. METHODS: the IUS thickness measurement of 30 women, between the 36th and 39th weeks of gestation with previous caesarean section, done by two observers, was studied. Abdominal ultrasonography with the patient in both supine and lithotomy position was performed. In the sagittal section, the IUS was identified and four bidimensional images and two tridimensional blocks of the total thickness were collected through the abdominal route, and the same for the muscle layer, through the vaginal route. Tridimensional acquisitions were manipulated in the multiplanar mode. The time was measured with a chronometer. Reproducibility was evaluated by the computation of the absolute difference between measurements, the ratio of differences smaller than 1 mm, the intraclass coefficient (ICC), and the Bland and Altman's concordance limits. RESULTS: the average bidimensional measurement of IUS thickness was 7.4 mm through the abdominal and 2.7 mm through the vaginal route, and the tridimensional measurement was 6.9 mm through the abdominal and 5.1 mm through the vaginal route. Intra- and interobserver reproducibility of vaginal versus abdominal route: smaller absolute difference (0.2-0.4 mm versus 0.8-1.5 mm), greater ratio of differences (85.8-97.8% versus 48.7-72,8%), with p<0,0001, higher ICC (0.8-0.9 versus 0.6-0.8) and lower concordance limits (-0.9 to 1.5 versus -3.8 to 4 mm) for the vaginal route. Tri versus bidimensional ultrasonography: lower absolute difference (0.2-1.4 versus 0.4-1.5 mm), higher ratio of differences (57.7-97.8% versus 48.7-91.7%) with p>0.05[A1] and similar lower concordance limits (-38 to 3.4 versus -3.6 to 4 mm) for tridimensional ultrasonography and ICC (0.6-0.9 versus 0.7-0.9). CONCLUSIONS: from the above, we came to the conclusion that the measurement of the IUS muscle layer, through the vaginal route using tridimensional ultrasonography is more reproducible. Nevertheless, our results do not indicate that this measurement shows any clinical evidence to predict uterine tear, as that was not the aim of this study. The only work that has correlated the UIS thickness with risk of uterine tear, without interfering in the obstetrician behavior or anticipating delivery, was done by bidimensional abdominal measurements of the total thickness.
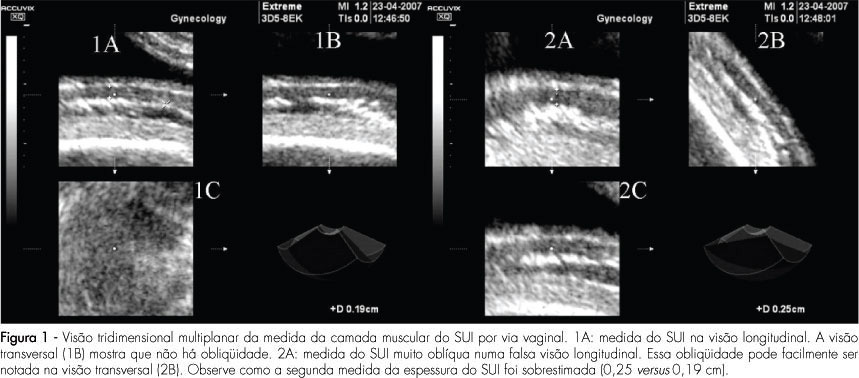
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):555-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100002
PURPOSE: to identify the factors related to successful gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) management with glyburide and to evaluate perinatal outcomes. METHODS: prospective longitudinal study including 50 pregnant women with GDM who required complementary treatment to diet and physical activity, whose fetus presented normal abdominal circumference (AC) to ultrasound (pct<75). Study period was August 2005 to July 2006. Ultrasonography was carried out monthly. Glyburide was used until delivery, as long as glucose control was obtained and fetal AC was normal, being thus considered therapeutically successful. In case there was no glucose control or alteration in AC, management was switched to insulin therapy, being thus considered therapeutically unsuccessful. Pregnant women were divided into two groups: one therapeutically successful (n=29) and another therapeutically unsuccessful (n=21). The results evaluated were: therapeutic success, maternal characteristics and perinatal outcome. RESULTS: fifty-eight percent of the cases were successfully managed with glyburide. No difference was found (p>0.05) in either group, with regards to maternal age, glucose values at OGTT75g, maternal body mass index (BMI), number of pre-natal consultations, number of previous pregnancies. According to the logistic model of regression used, therapeutically successful pregnant patients had had a later diagnosis (p=0.02) and lower weight gain during gestation (p<0.01). Perinatal outcome did not differ in either group. CONCLUSIONS: patients with later diagnosis and lower weight gain are more likely to have successful GDM management with glyburide. Unsuccessful management with glyburide did not alter the perinatal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):561-567
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100003
PURPOSE: to verify the association of abortion, recurrent fetal loss, miscarriage and severe pre-eclampsia with the presence of hereditary thrombophilias and antiphospholipid antibodies in pregnant women. METHODS: observational and transverse study of 48 pregnant women with past medical record of miscarriage, repeated abortion and fetal loss story (AB Group) and severe pre-eclampsia (PE Group), attended to in the High Risk Pregnancy Ambulatory of the Faculdade de Medicina (Famed) from the Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul (UFMS) from November 2006 to July 2007. The pregnant women of both groups were screened for the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, lupic anticoagulant and anti-beta2-glycoprotein I) and hereditary thrombophilias (protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin deficiency, hyperhomocysteinemia and factor V Leiden mutation). The laboratorial screening was performed during the pregnancy. The parametric data (maternal age and parity) were analyzed with Student’s tau test. The non-parametric data (presence/absence of hereditary thrombophilias and antiphospholipid antibodies, presence/absence of pre-eclampsia, fetal loss, miscarriage and repeated abortion) were analyzed with Fisher’s exact test in contingency tables. It was considered significant the association with p value <0.05. RESULTS: out of the 48 pregnant women, 31 (65%) were included in AB Group and 17 (35%) in PE Group. There was no significant difference between maternal age and parity within the groups. There was significant statistical association between recurrent fetal loss, recurrent abortions and previous miscarriages and maternal hereditary thrombophilias (p<0.05). There was no statistical association between the AB Group and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. Neither there were associations of the PE Group with maternal hereditary thrombophilias and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. CONCLUSIONS: the data obtained suggest routine laboratorial investigation for hereditary thrombophilias in pregnant women with previous obstetrical story of recurrent fetal loss, repeated abortion and miscarriage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):568-574
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the histological differentiation pattern in superficial peritoneum lesions and in deeply infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) in utero-sacral ligament, bowel (rectum and sigmoid colon) and rectovaginal septum. METHODS: this prospective non-randomized study included 139 patients. Of the total, 234 biopsies were obtained (179 with DIE - Deeply Group - and 55 superficial endometriosis - Superficial Group). From the 179 DIE lesions (Depply Group), 15 were obtained from rectovaginal septum, 72 from rectosigmoid nodules and 92 from utero-sacral ligament. Biopsies were classified in well-differentiated glandular pattern, undifferentiated glandular, mixed glandular differentiation and pure stromal disease, based on specific morphological classification. RESULTS: in the Depply Group (DIE), 33.5% of the biopsies showed undifferentiated glandular pattern and 46.9% mixed glandular pattern. In the Superficial Group, there was the predominance of the well-differentiated glandular pattern (41.8%). Comparing specifically the different localizations of the biopsies of DIE lesions (Deeply Group), a predominance of mixed pattern in bowel nodules (61.1%) was noted. CONCLUSIONS: it was possible to conclude that there is a predominance of well-differentiated glandular pattern in superficial endometriosis, a predominance of mixed undifferentiated in deeply pelvic endometriosis and, specifically studying endometriosis from the rectum and sigmoid colon, there was a predominance of the mixed pattern.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):575-579
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100005
PURPOSE: the villoglandular adenocarcinoma (VGA) of the cervix has been identified as a variant of cervical adenocarcinoma that occurs in young women, which has an excellent prognosis. Considering the scarcity of studies related to the subject, we report six cases of VGA of the cervix. METHODS: we followed the development of six cases of VGA in the period from 1995 to 2006 at Hospital São Lucas of Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul (PUC-RS). We collected clinical and histologic information of the patients and submitted all the surgical specimens to histological review. RESULTS: mean age at diagnosis was 43.5 years (range 27-61 years). Four patients were submitted to Wertheim-Meigs radical hysterectomy and bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy, one to conization and subsequent radiotherapy and one to pelvic lymphadenectomy followed by radiotherapy. All the patients were alive and well at the time of this writing, without evidence of recurrence. CONCLUSIONS: the implications of therapy are discussed. We propose here the inclusion of the study of the pattern of lymphovascular involvement in determining the diagnosis of VGA. Thus, in referring to this diagnosis, we will be able to opt, with caution, for conservative therapy, except for particularities of each case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100006
PURPOSE: to investigate women’s age at their first sexual intercourse and its correlation with their present age, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and cytological abnormalities at Pap smear. METHODS: women from the general population were invited to be screened for cervical cancer and pre-malignant lesions. After answering a behavior questionnaire, they were submitted to screening with cervical cytology and high-risk HPV testing with Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2). This report is part of the Latin American Screening (LAMS) study, that comprises centers from Brazil and Argentina, and the data presented herein refer to the Brazilian women evaluated at the cities of Porto Alegre, São Paulo and Campinas. RESULTS: from 8,649 women that answered the questionnaire, 8,641 reported previous sexual activity and were included in this analysis. The mean age at the interview was 38.1±11.0 years and the mean age at the first sexual intercourse was 18.5±4.0 years. The age at the first sexual intercourse increased along with the age at the interview, i.e., younger women reported they had begun their sexual life earlier than older women (p<0.001). From the total of women who had already begun having sexual intercourse, 3,643 patients were tested for high-risk HPV infection and 17.3% of them had positive results. In all the centers, it became clear that the women with the first sexual intercourse at ages below the mean age of all the population interviewed presented higher rates of HPV infection (20.2%) than the women with the first sexual intercourse at ages above the mean (12.5%) - Odds Ratio (OR) 1.8 (IC95% 1.5-2.2;p<0,001). According to the cytology, the women with first sexual intercourse at ages under the mean, presented higher percentage of abnormal cytology > or = ASC-US (6.7%) than the women with the first sexual intercourse at ages above the mean (4.3%) - OR 1.6 (IC95% 1.3-2.;p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: the high-risk HPV infection and cytological abnormalities identified during the asymptomatic population screening were significantly associated to the women’s age at the first sexual intercourse. Additionally, we have also identified that the women’s age at the first sexual intercourse has decreased during the last decades, suggesting an important contribution to the increase of HPV infection and the subsequent cervical lesions.
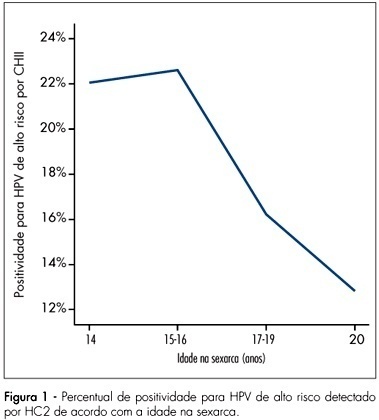
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(10):511-518
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000004
PURPOSE: to analyze the association between maternal pre-gestational nutritional status and maternal outcomes - hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, vitamin A deficiency, and anemia - and the newborn outcome - low birth weight. METHODS: cross-sectional study, with 433 adult puerperal women (> 20 years old) and their newborns, attending the Maternidade Escola of Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ). Data was collected through interviews and access to their medical records. Maternal pre-gestational nutritional status was established through pre-gestational body mass index according to the cut-offs for adult women defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 1995. The association between gestational outcomes and pre-gestational nutritional status was estimated through odds ratio (OR) and a 95% confidence interval (95%CI). RESULTS: frequency of pre-gestational weight deviation (low weight, overweight and obesity) was 31.6%. Considering the pre-gestational nutritional status, overweight and obese women presented a lower weight gain than eutrophic and low-weight women (p<0.05). Women with pre-gestational obesity presented a higher risk of developing hypertensive disordens of pregnancy (OR=6.3; 95%CI=1.9-20.5) and those with low pre-gestational weight were more likely to give birth to low birth weigh infants (OR=7.1; 95%CI=1.9-27.5). There was no evidence of the association between pre-gestational nutritional status and the development of anemia, vitamin A deficiency and gestational diabetes. The mean weight gain among overweight and obese pregnant women was significantly lower when compared to eutrophic and low-weight pregnant women (p=0.002, p=0.049, p=0.002, p=0.009). CONCLUSIONS: the high number of women with pre-gestational weight deviation reinforces the importance of a nutritional guidance that favors a good nutritional state and reduces the risks of maternal and newborn adverse outcomes.