Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):619-624
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200004
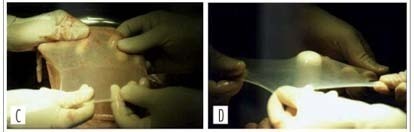
PURPOSE: to evaluate the results of neovaginoplasty with the use of a human amniotic graft in patients with the Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. METHODS: the study was a retrospective analysis of a series of 28 patients with the MRKH syndrome conducted from 1990 to 2003. The patients were attended and treated at the Ambulatório de Ginecologia Infanto-Puberal (AGIP) of the Hospital Universitário of the Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto of the Universidade de São Paulo (FMRP-USP), being submitted to neovaginoplasty by the technique of McIndoe and Bannister, modified by the use of a human amniotic membrane graft. Epithelization, amplitude and depth of the neovaginas were evaluated 7 and 40 days after the procedure. Patient satisfaction was determined during the late postoperative period in terms of the presence of discomfort and dyspareunia during sexual relations. RESULTS: postoperatively, seven patients (25%) presented vaginal stenosis and six of them were submitted to a new surgical intervention, one had shortening of the neovagina, corrected with the use of exercises with a vaginal mold, three (10.7%) developed a rectovaginal fistula, one (3.6%) a uterovesical fistula, and one (3.6%) excess skin in the vaginal introitus - all successfully corrected with surgery. Four patients (14.3%) presented urinary tract infection. Two months after surgery, 11/19 patients (57.8%) presented satisfactory sexual activity and 42% dyspareunia, and within a maximum period of four years, 20/21 patients (95.2%) had satisfactory sexual activity and 4.8% dyspareunia. CONCLUSIONS: an amniotic membrane graft is a good option for the treatment of vaginal agenesis. Perioperative follow-up involves educational guidance regarding the use of the mold and regarding patient sexuality in order to reduce the complaints of dysfunctional coitus in the presence of a favorable surgical evolution and a neovagina of adequate aspect.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):625-632
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200005
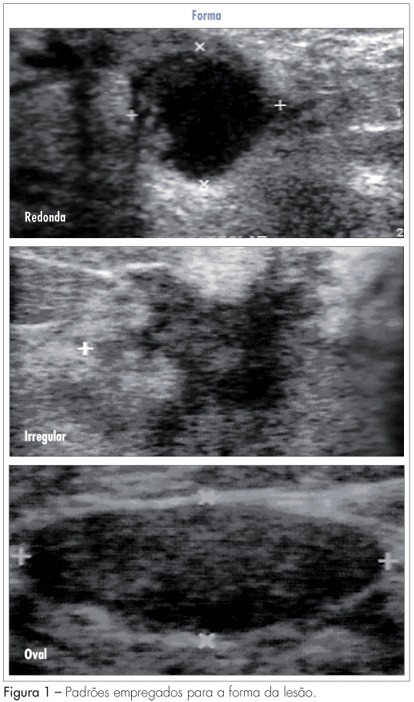
PURPOSE: to analyze which characteristics proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound have the greatest impact on distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions. METHODS: ultrasonography features from the third edition of the BIRADS were studied in 384 nodes submitted to percutaneous biopsy from February 2003 to December 2006, at the Medical School of Botucatu. For the ultrasonography, the equipment Logic 5 with a 7.5-12 MHz multifrequential linear transducer was used. The ultrasonography analysis of the node considered the features proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound. The data were submitted to statistical analysis by the logistic regression model. RESULTS: the benign lesions represented 42.4% and the malignant, 57.6%. The logistic regression analysis found an odds ratio (OR) for cancer of 7.69 times when the surrounding tissue was altered, of 6.25 times when there were microcalcifications in the lesions interior, of 1.95 when the acoustic effect is shadowing, of 25.0 times when there was the echogenic halo, and of 7.14 times when the orientation was non-parallel. CONCLUSIONS: among the features studied, the lesion limit, represented by the presence or not of the halogenic halo, is the most important differentiator of the benign from the malignant masses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):633-638
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200006
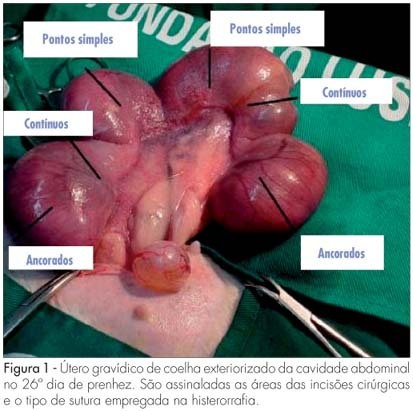
PURPOSE: to compare macro and microscopically, surgical uterine sutures in female rabbits, after caesarean section utilizing separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture stitches. METHODS: three New Zealand female rabbits in their first pregnancy were used. The caesarean section was carried out at the 26th day of gestation and three incisions were performed in each uterus. The hysterorrhaphy was performed with a 00 Vicryl® thread, and a different suture technique was employed for each incision. Total hysterectomy and adnexectomy were done at the 60th day post-delivery with the preservation of eventual adhesions for the evaluation of the surgical scars. The extent of scar retraction, amount of fibrin deposit and the suture integrity were evaluated through macroscopy. For the evaluation through microscopy, hematoxylin eosin technique was used for cellular colorimetry, and Masson's trichrom to evidence collagen. The statistical non-parametric Friedman's test was employed for the matching hypothesis, and Fisher's exact test to verify the homogeneity of the techniques (level of significance: 5%). RESULTS: a total of 18 scars were obtained (six scars per suture). The following mean values were obtained for the longitudinal (0.5/0.4/0.5, p=0.069) and transversal retraction degrees (0.3/0.4/0.3, p=0.143) respectively for separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture techniques. All sutures presented regular fibrin deposit, no adhesions and integral absorption of the stitches. The mean value of the blood vessels (158.5/139.3/172.1; p=0.293), fibroblasts (351.6/345.8/354.3; p=0.311) and of collagen percentage (44.0/45.5/48.5; p=0.422) were calculated through microscopy, respectively for separate, continuous and continuous anchored suture techniques. CONCLUSIONS: the type of hysterorrhaphy technique of caesarean section in female rabbits did not generate any significant statistical difference in the macroscopic and microscopic parameters evaluated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):639-646
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200007
PURPOSE: to compare the effectiveness of low doses of vaginal misoprostol (12.5 versus 25 µg) for induction of labor. METHODS: a double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial was performed in Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Sobral, from May 2005 to April 2006. Sixty-two term pregnant women, with intact membranes and with indication for labor induction, were included. They randomly received 25 µg (32) or 12.5 µg (30) of vaginal misoprostol each four hours, until the maximum of eight doses. Mode of delivery, time between induction and delivery, perinatal complications, and maternal side effects were studied. The control variables were maternal and gestational ages, parity and Bishop score. The statistical tests used were average calculations, shunting line-standards and Student t-test (numerical continuous variables), chi2 (categorical variables) and Mann-Whitney test (discrete variables). RESULTS: the two groups, 12.5 and 25 µg, did not differ in relation to the interval of time between the induction onset and delivery (1524 versus 1212 min, p=0.333), in the frequency of vaginal delivery (70 versus 71.8%, p=0.720), Apgar scores below seven at the fifth minute (3,3 versus 6,25%, p=0.533) and tachysystole frequency (3.3 versus 9.3%, p=0.533). The average of total dose administered was significantly higher in the 25 µg group (40 versus 61.2 µg, p=0.03). CONCLUSIONS: vaginal misoprostol in the dose of 12.5 µg was efficient, with collateral effects similar, to the 25 µg of vaginal misoprostol, for induction of labor at term.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000005
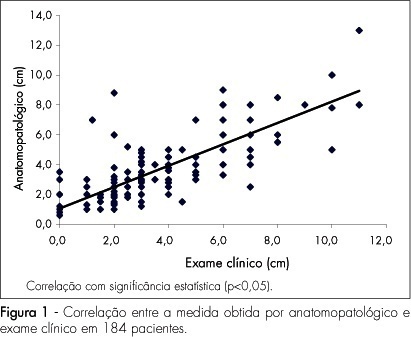
PURPOSE: to evaluate which method is the best to determine pre-surgically the size of breast cancer: clinical examination, mammography or ultrasonography, using as a reference the anatomopathological exam. METHODS: this study has included 184 patients with palpable-or-not breast lesions, detected by mammography and ultrasonography, that were submitted to surgical resection of the tumor, with histopathological diagnosis of breast cancer. The same examiner evaluated clinically the largest tumoral diameter, through clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography, and the measurements obtained by each method were correlated with the maximum diameter obtained by the anatomopathological exam. The comparative analysis has been done by Pearson's correlation coefficient (r). RESULTS: Pearson's correlation coefficient between the anatomopathological and the clinical exams was 0.8; between the anatomopathological exam and the mammography, 0.7; and between anatomopathological exam and ultrasonography 0.7 (p<0.05). Pearson's correlation coefficients among the methods evaluated were also calculated and r=0.7 was obtained between clinical exam and mammography, r=0.8 between clinical examination and utrasonograhy, and r=0.8 between mammography and ultrasonography (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography have presented high correlation with the anatomopathological measures, besides high correlations among themselves, what seems to show that they may be used as equivalent methods in the pre-surgical evaluation of the breast tumoral size. Nevertheless, due to specific limitations of each method, clinical examination, mammography and ultrasonography should be seen as complementary to each other, in order to obtain a more accurate measurement of the breast cancer tumor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):113-120
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000001
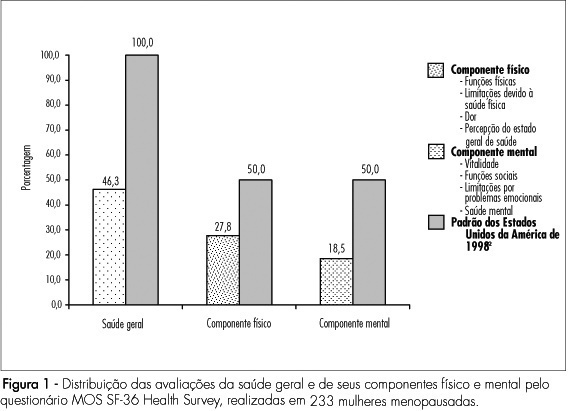
PURPOSE: to evaluate quality of life of climacteric women attended at a school hospital in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, adopting the Medical Outcome Study 36-item Short Form Health Survey (MOS SF-36 Health Survey) and the Women's Health Questionnaire (WHQ), as well as the modified Blatt-Kupperman index. METHODS: according to a descriptive, transversal study, 233 women, assisted from February to June 2006, were evaluated. Within a convenience sample, the inclusion criteria were age from 40 to 65 years old and agreement in participating of the research, excluding previous history of bilateral oophorectomy, hormonal therapy in the last semester and uncontrolled illnesses. The sample size was calculated admitting a prevalence of climacteric symptoms of 4% and a precision of 2.5%. The variables were: general health and physical and mental components based on the MOS SF-36 Health Survey; quality of health based on the WHQ and climacteric symptoms according to the modified Blatt-Kupperman index. Data were analyzed by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 13.0 software. RESULTS: the quality of life was classified as bad. Based on the MOS SF-36 Health Survey, there was more damage in the mental component (18.53 versus 27.77% for physical components), higher losses in social functions (80.28%) and limitations for emotional problems (78.61%). According to WHQ, there were limitations due to sleep disturbances (69.77%), somatic (69.15%) and vasomotor symptoms (68.80%), considering regular sexual function and menstrual symptoms. Estrogenic deficiency symptoms were found in 53% of the women. The increase of hypoestrogenism symptoms were followed by worsening of general and menopausal health. CONCLUSIONS: it seemed reasonable to assume that menopause, for the researched women, was really configured as a biopsychosocial event, more than organic, derived predominantly from estrogenic deficiency.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):121-126
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000002
PURPOSE: to compare the frequency of vulvovaginitis in women infected with human imunnodeficiency virus (HIV) with the frequency in non-infected women. METHODS: a transversal study including 64 HIV infected women and 76 non-infected ones. The frequencies of bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and trichomoniasis, diagnosed by Amsel's criteria, culture and fresh exam, respectively, were calculated. Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test and multiple regressions to verify the independence of associations were used to analyze the data. RESULTS: the vaginal infection was more prevalent in HIV infected patients, as compared to the control group (59.4 versus 28.9%, p<0,001; Odds Ratio=2.7, IC95%=1.33-5.83, p=0.007). Bacterial vaginosis occurred in 26.6% of the positive-HIV women; vaginal candidiasis, in 29.7% and trichomoniasis, in 12.5% of them. All the infections were significantly more frequent in the group of HIV infected women (p=0.04, 0.02 e 0.04, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: vulvovaginitis is more frequent in HIV infected women.