Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):12-18
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100003
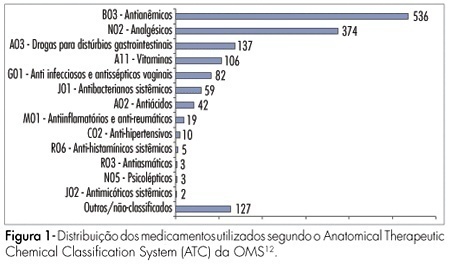
PURPOSE: to study the use of medicines by pregnant women during prenatal care in clinics of the national public health system in the city of Natal, Brazil. METHODS: a total of 610 pregnant women between the first and the third trimesters of pregnancy were interviewed in the public clinics of the four sanitary districts of Natal, from May to July 2006. The data were collected by a structured questionnaire, based in use-oriented and medicine-oriented questions. The drugs were classified according to the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC), in agreement with the gestation risk criteria from the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA). The statistical analysis was made by the chi2 test. RESULTS: a total of 1,505 drugs were used, with an average of 2.4 medications per woman. The use of at least one drug was found in 86.6% of the women. The most frequently used drugs were anti-anemics (35.6%), analgesics (24.9%), drugs for gastrointestinal disorders (9.1%) and vitamins (7%). According to the FDA classification, 42.7% belonged to category A risk, 27.1% to category B, 29.3% to category C, 0.3% to category D and none to category X. The use of medicines during the first trimester of pregnancy amounted to 43.6%. The rate of drug use increased with higher schooling level and family income. Self-medication was found in 12.2% of the drug intake and this rate was higher in the first trimester of gestation and with women with low education level and previous gestations. CONCLUSIONS: pregnant women from Natal are being exposed to a variety of medicines with uncertain safety in pregnancy. Therefore, more careful prescription is needed, to avoid possible fetal damage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):31-35
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100006
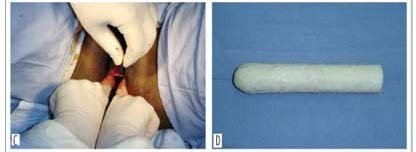
PURPOSE: to evaluate the use of natural latex mold (Hevea brasiliensis) as a modification of McIndoe and Bannister neovaginoplasty in patients presenting Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MKRH) syndrome. METHODS: we retrospectively included nine patients presenting MKRH syndrome, who had been submitted to McIndoe and Bannister neovaginoplasty modified by the use of natural latex mold. Neovaginal epithelization and depth, coitus occurrence and satisfaction, and surgical complications were evaluated. RESULTS: five weeks after the procedure, eight patients presented an epithelized 7 to 12 cm deep neovagina. There was one case of complete neovaginal stenosis, because of incorrect use of the mold. After at least one year, the others maintained 4 to 8 cm deep neovaginas and capacity for intercourse, with 66.7% satisfaction. One woman presented precocious rectovaginal fistula and late episodes of uretrovaginal fistulae. Two patients presented distal neovaginal stenosis in long-term follow-up. One of these and the patient with fistulae were submitted to a new procedure. CONCLUSIONS: the use of natural latex mold as a modification of classic neovaginoplasty technique allows the creation of neovaginas morphologically and functionally similar to the normal vagina in patients with vaginal agenesis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):36-41
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100007
PURPOSE: to establish whether there is a predictive relationship between the antral follicle count (AFC) on the second day of the cycle and the response pattern in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). METHODS: a prospective study developed from May 2004 to May 2005, in which 51 patients aged <37 years old were submitted to assisted reproduction/ICSI in ovarian hyperstimulation protocol with gonadotropin recombinant and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist. A transvaginal ultrasonography was performed on the second day of the cycle, to count the number of follicles measuring 2 to 10 mm, at the beginning of stimulus, data compared with the number of follicles with >15 mm on the day of ovulation triggering, the total number of oocytes retrieved and in metaphases II, the number of good quality embryos transferred and pregnancy rate. The statistical analysis was performed by the t-Student test and the Mann-Whitney test, with statistical significance of 5% (p<0.05). RESULTS: the mean age in the study group was 32.4 years. The AFC average was 7.1, minimum of 1 and maximum of 16. Considering AFC as a main variable, a significant direct correlation was observed with the number of follicles >15 mm on the day of ovulation triggering (p=0.0001), the total number of oocytes retrieved (p=0.0001) and those in metaphases II (p=0.0001). Such correlation between AFC and pregnancy was not observed (p=0.43). There was no significant correlation between AFC and the number of good quality embryos transferred (p=0.081). CONCLUSIONS: AFC on the second day of the stimulated cycle can be used to predict the quality of ovarian stimulation, the number of oocytes retrieved and the number of mature oocytes in in vitro fertilization cycles using GnRH antagonist.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):19-24
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100004
PURPOSE: The aim of this article is to evaluate the use of nevirapine HIV-infected pregnant women in our service. METHODS: a retrospective study was performed between January 2003 and December 2006 analysing all women prescribed nevirapine in pregnancy. Exclusion criteria included: (1) women who started nevirapine before pregnancy, (2) patients with abnormal baseline liver enzymes, and (3) women with incomplete liver biochemistry data. Evaluated parameters included age, weeks of exposure to nevirapine, gestational age in the begginning of medication, weeks of follow-up, viral load, CD4 cells count and serum aminotransferase levels. The incidence of adverse hepatic and/or cutaneous effects was determined and correlated to the CD4 cells count. Statistical analysis were performed using Fisher’s exact test and t-Student test when appropriate, with a statistical significance level of p<0,05. RESULTS: one hundred fifty-seven women met the inclusion criteria. Thirty-one (19.7%) presented cutaneous and/or hepatic toxicity. Skin rash accounted for 77.4% of toxicities and liver function abnormalities were noted in 22.6% of women exhibiting toxicities. Grade 1, 2 and 3 hepatotoxicities were observed in 0.6, 2.5 and 1.3%, respectively. Baseline CD4 counts, viral loads and transaminases were similar in pregnant women with nevirapine adverse effects and those without reaction. Median absolute CD4 cell counts were 465.4 and 416.6 cells/µL in women with and without side effects, respectively (p=0.3). All patients who experienced hepatotoxicity had pretreatment CD4 counts superior to 250 cells/µL. CONCLUSIONS: The incidence of adverse events with nevirapine in our study was high, but most of them were cutaneous. There was no correlation between high CD4 counts and adverse events when analysing both cutaneous and hepatic reactions; nevertheless, hepatotoxicity occurred only in pregnant women with CD4 counts >250 cells/µL.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):25-30
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100005
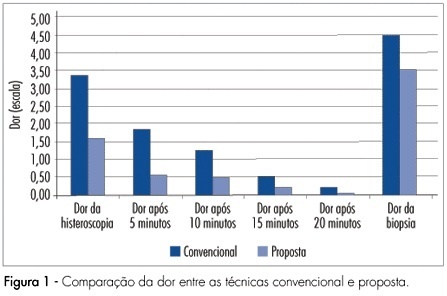
PURPOSE: to compare diagnostic hysteroscopy through vaginoscopy, using warm saline solution, with traditional technique, regarding to pain, patient satisfaction and feasibility of the procedure. METHODS: randomized clinical trial, involving 184 women, referred for diagnostic hysteroscopy, between May and December of 2006. Participants were randomized to be submitted to hysteroscopy by the proposed technique, which consisted of access through vaginoscopy using normal saline at 36ºC as distension medium, no speculum or cervical grasping, or by the traditional technique with CO2. In both techniques, a 2.7 mm hysteroscope was used. Pain was assessed by the analogical visual scale, during the procedure and every five minutes after it. RESULTS: the mean pain score was 1.60 in the proposed technique and 3.39 in the traditional technique (p<0.01). Lower pain scores were also observed after 5, 10 and 15 minutes (p<0,01) as well as after 20 minutes (p=0.056). In the proposed technique, 82.4% of the procedures were feasible, while, in the traditional technique, 84.9% were so (p=0.64). Satisfaction with the procedure was referred by 88.7% of women submitted to the proposed technique and by 76.3% of women submitted to the traditional technique (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: diagnostic hysteroscopy by the proposed technique resulted in less pain, same feasibility and greater satisfaction of patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):5-11
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100002
PURPOSE: to study the value of Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus, between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, associated to the nuchal translucency thickness measurement, in the detection of adverse fetal outcome. METHODS: a transversal and prospective study in which a total of 1,268 fetuses were studied consecutively. In 56 cases, a cytogenetic study was performed on material obtained from a biopsy of the chorionic villus and, in 1,181 cases, the postnatal phenotype was used as a basis for the result. In addition to the routine ultrasonographic examination, all the fetuses were submitted to measurement of the nuchal translucency thickness and to Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus. Aiming at prevalence and accuracy indices, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, probability of false-positive, probability of false-negative, reason of positive probability and reason of negative probability were calculated and analyzed. RESULTS: from the total of 1,268 fetuses, 1,183 cases were selected for analysis. From this number, 1,170 fetuses were normal (98.9%) and 13 fetuses presented adverse outcome at birth (1.1%), including fetal death (trisomy 21 and 22) in two cases; genetic syndrome (Nooman) in one case; two cases of polymalformed fetuses; cardiopathy in three cases; and other structural defects in five cases. The prevalence of the modified ductus venosus (wave A zero/reverse) in the studied population was of 14 cases (1.2%), with a false-positive rate of 0.7%. CONCLUSIONS: there is a significant correlation between the alteration of the ductus venosus Doppler velocimetry and the thickness of the nuchal translucency as an ultrasonographic marker for the first trimester of gestation, in the detection of adverse fetal outcome, especially serious malformations. The ductus venosus was able to diminish the false-positive result in comparison to the isolated use of the nuchal translucency thickness, improving considerably the positive predictive value of the test.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):614-618
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200003
PURPOSE: to determine the variation of the number of ovarian follicles during fetal life. METHODS: twelve ovaries donated for research were included in our study, nine from fetuses and three from newborn babies who died in the first hour after being delivered with 39 weeks of pregnancy. Fetal age was confirmed both by the last menstrual period of the woman and by ultrasonography. Ovaries were fixed in formaldehyde, included in paraffin and serially sliced at 7 mm. At every 50 cuts, the obtained material was haematoxilin-eosin stained and evaluated with an optical microscope (400 X). The follicles were counted in ten different regions of the ovarian cortex, each region with an area of 625 mm². The presence of a nucleus was considered the parameter for counting. Follicular density, per 1 mm³ was calculated using the formula Nt=(No x St x t)/do, where Nt is the number of follicles; No is the mean number of follicles in 1 mm²; St is the total number of slices in 1 mm³; t is the slice thickness and do is the nuclei mean diameter. RESULTS: the gestational age of fetuses ranged from 24 to 39 weeks. The number of follicles per 0.25 mm² ranged from 10.9 ± 4.8 in a newborn to 34.7 ± 10.6 in another newborn. Among the fetuses, the least value was obtained in a 36 week-old fetus (11.1 ± 6.2) and the highest in a 28 week-old fetus (25.3 ± 9.6). The total number of slices per ovary ranged from six to 13, corresponding to follicles counted in areas from 15 to 32.5 mm². The total number of follicles ranged from 500,000 at the age of 22 weeks to > 1,000,000 at the age of 39 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: our results demonstrate different (increasing) densities of ovarian follicles along the gestational period, providing more knowledge about this still not well-known subject.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):608-613
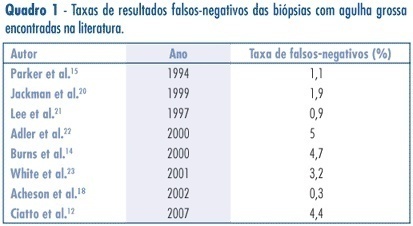
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200002
PURPOSE: to assess the accuracy (rate of correct predictions) of stereotactic core needle biopsy (CNB) of risk category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions. METHODS: a retrospective analysis of category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions that had been submitted to a stereotactic core-needle biopsy from June 1998 to June 2003. Patients with histological benign results consistent with the radiographic image were referred to mammographic follow-up. Patients with malign diagnosis and papillary lesions were submitted to standard specific treatment. Excisional biopsies were performed when results were benign, but in disagreement with the mammographic image. It was considered as a gold-standard attendance: (1) the mammographic follow-up of low suspicion lesions with benign results at CNB, which stayed unchanged for, at least, three years, and (2) surgical resection when specimen results were malign or benign, but with a high suspicion on mammography. Sensitivity (S) specificity (E) and overall accuracy of stereotactic CNB were statistically analyzed. RESULTS: among the 118 non-palpable lesions of category BI-RADS® 4 submitted to CNB, the results obtained were: 27 malign cases, 81 benign, and ten lesions with atypical or papillary lesions. The statistical analysis comprised 108 patients (atypical and papillary lesions were excluded). CNB sensitivity was 87.1% and specificity 100%. The positive predictive value was 100% and the negative, 95.1%. False negatives occurred in 3.7% (4/108) of cases. The prevalence of malign diagnostics in the BI-RADS® 4 lesions of this sample was 29.7 (31/118).The accuracy of this method in this casuistic was 96.3%. CONCLUSIONS: these results support stereotactic CNB as an extremely reliable alternative to open biopsy, in the diagnosis and definition of breast lesions. In positive results, it is possible to indicate the appropriate therapy, and, in negative (when mammography shows low suspicion), it allows a follow up.