Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):232-240
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500005
PURPOSE: to determine caffeine consumption in pregnant women and to evaluate its association with demographic, socioeconomic, reproductive, lifestyle and maternal nutritional status. METHODS: it is a cross-sectional study performed between 2005 and 2007. The present analysis refers to the period among the 8th and 13th gestational week and included 255 pregnant women from 18 to 40 years, clients of a municipal health center in Rio de Janeiro. The outcome variable was caffeine consumption, quantified by a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, which count with a list containing 81 items and eight options of consumption frequencies; besides it being previously validated in a sample of employees of the State University of Rio de Janeiro. The caffeine intake was quantified starting from the consumption of: powdered chocolate, chocolate bar or chocolate, soft drink, coffee and mate tea. The statistical analysis was performed by means of fitting a multivariate linear regression. RESULTS: the median and the mean caffeine consumption were, respectively, 97.5 and 121.1 mg (standard deviation, sd = 128.4). The high caffeine consumption (> 300 mg/day) was observed in 8.3% of pregnant women. It was observed in the multivariate model that women with earlier menarche (β = -0.15), with more household partners (b = 0.17) and who didn’t make use of medicines (β = -0.24) presented larger tendency to high caffeine consumption association that was statistically significant (p <0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the caffeine consumption for most of the pregnant women was inferior to the limit of 300 mg/day as commited in other studies. Tendency was observed toward higher consumption of caffeine in pregnant women with earlier menarche, with more household partners and who didn’t make use of medicines.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):241-247
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and with male factor and/or tubal infertility (Control Group) and compare in vitro maturation (IVM) rates between the groups analyzed. METHODS: five infertile patients with PCOS and eight controls, submitted to stimulated cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection, were selected prospectively and consecutively, and respectively assigned to the study group and the Control Group. Immature oocytes (21 and 29, respectively, from PCOS and Control Group) were submitted to IVM. After IVM, oocytes with first polar body extruded were fixed and submitted to immunostaining and fluorescence microscopy for morphological evaluation of the spindle and of chromosome distribution. Statistical analysis was performed by the Fisher test with significance, when p<0.05. RESULTS: IVM rates were similar between groups (47.6 e 44.8%, respectively, for PCOS and Control Group). Six of the ten oocytes (60%) from the study group and four of the 12 oocytes (33.3%) from the Control Group presented meiotic anomalies of the spindle and/or anomalous chromosome distribution, without statistical difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: data from the present study did not demonstrate significant difference neither in IVM rates nor in the proportions of meiotic anomalies between in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles from PCOS patients and control ones.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):248-255
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500007
PURPOSE: to describe the socio-demographic characteristics of deaths caused by uterine cervix cancer in women living in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, from 2000 to 2004. METHODS: a transversal populational study, including 323 deaths by uterine cervix cancer, among which 261 were recorded in the Information System about Mortality and 62 were identified after investigation on deaths by cancer at non-specified sites of the uterus. Mortality rate for all the variables was obtained and statistics for central tendency and variance were calculated. The χ2 test was performed to obtain the mortality coefficient concerning the living place and age range of the patients. RESULTS: death among women under 60 (54.7%), black (60.5%), single (67.6%), housewives (71.2%) and the ones living in poor neighborhood (53.3%) preponderated. Most of deaths occurred in hospitals (85.1%) and 90.2% of them occurred inside national health system hospitals. The mortality coefficient varied from 0.3 (among women under 30) to 54.9/100.00 (among women over 80). Significant statistical differences (p<0.05) were evidenced when death linked to age range and sanitary district was compared to characteristics of the female population living in the city. CONCLUSIONS: in Recife, death by cervix cancer are more frequent among adult, black, single, housewives, women living in poor neighborhoods and attended to at national health system hospitals, with differences in death risk among age ranges and living place.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400003
PURPOSE: the propose of this study was to analyze the clinical and laboratorial parameters of patients submitted to human assisted reproduction techniques with association of sperm processing techniques, in order to remove virus particles from semen samples of couples in which men was infected by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). METHODS: it was assessed 11 intracytoplasmatic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles from couples whose men were HIV seropositive (HIV Group), and 35 cycles in which semen donors' samples were used in ICSI procedures (Control Group). Semen samples from Control Group were submitted to routine semen analysis, sperm wash and cryopreservation. The man from HIV Group received previous antibiotic therapy; the semen samples were analyzed routinely and prepared by sperm wash and density gradient method before cryopreservation. Those samples were evaluated to viral load and ICSI was performed when no HIV was detected. RESULTS: regards to semen analysis the groups were similar to sperm concentration and progressive motility. Nevertheless, the percentage of sperm with normal morphology were higher on Control Group (14.3%) than HIV (5.8%; p=0.002). On embryo parameters assessment, the normal fertilization (CT: 74.7% and HIV: 71.7; p=0.838, respectively) and good embryos rate (CT: 42.4% and HIV: 65.1%; p=0.312, respectively) were comparable. On the other hand, the Control Group presented better clinic results than HIV Group (ongoing pregnancy rate: 52.9% versus 12.5%; p=0.054, and implantation rate: 42.6 versus 10.4%; p=0.059, respectively), however the differences were not statistically significant. After delivery, no seroconversion was observed on mother and child. CONCLUSIONS: the association of sperm processing techniques in order to remove HIV from semen samples does not influence in laboratorial parameters of assisted reproduction techniques cycles. On the other hand, it has been demonstrated excellent results getting safety gametes to serodiscordant couples.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):177-181
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400004
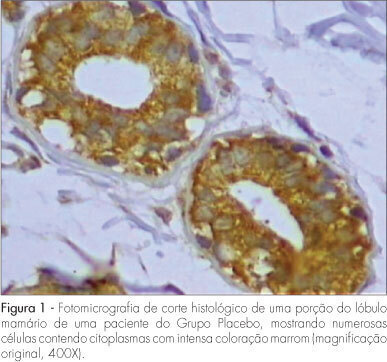
PURPOSE: to evaluate the expression of Bax antigen in the normal mammary epithelium of premenopausal women treated with raloxifene. METHODS: a randomized double-blind study was conducted in 33 ovulatory premenopausal women with fibroadenoma. Patients were divided into two groups: Placebo, (n=18) and Raloxifene 60 mg, (n=15). The medication was used for 22 days, beginning on the first day of the menstrual cycle. An excisional biopsy was carried out on the 23rd day of the menstrual cycle and a sample of normal breast tissue adjacent to the fibroadenoma was collected and submitted to immunohistochemical study using anti-Bax polyclonal antibody to evaluate the expression of Bax protein. Immunoreaction for Bax was evaluated taking into consideration intensity and fraction of stained cells, whose combination resulted in a final score ranging from 0 to 6. Cases with a final score >3 were classified as positive for Bax. The c2 test was used for statistical analysis (p<0.05). RESULTS: the percentage of positivity of Bax protein expression was 66.7 and 73.3% in Groups A and B, respectively. There was no significant difference in Bax expression between the two groups (p=0.678). CONCLUSIONS: raloxifene, administered for 22 days in the dose of 60 mg/day, did not alter the expression of Bax protein in the breast normal tissue of premenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):182-189
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the anthropometric measures as predictors of cardiovascular and metabolic risk in non-transmissible chronic diseases in postmenopausal women. METHODS: a clinical and sectional study enrolling 120 sedentary postmenopausal women (amenorrhea for at least 12 months, age 45 to 70 years was conducted). Exclusion criteria included insulin-dependent diabetes and use of statins or hormone therapy within the preceding six months. Anthropometric indicators included: weight, height, body mass index (BMI=weight/height²), and waist circumference (WC). Metabolic profiles as total cholesterol (TC), HDL, LDL, triglycerides (TG), glycemia, and insulin were measured and the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) and Homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were calculated. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Odds Ratio (OR) were used in the statistical analysis. RESULTS: subjects were classified on average as overweight and showed central fat distribution. Overweight and obesity were observed in 76% and abdominal obesity in 87.3% of the patients. On average, TC, LDL and TG levels were higher than recommended in 67.8, 55.9 and 45.8% of the women, respectively, and HDL was low in 40.7%. Values of WC >88 cm were observed in 14.8% of women with normal weight, 62.5% overweight and 100% obesity p>0.05). On average, the values of AIP, TG, and HOMA-IR increased significantly along with values of BMI and WC, while decreased HDL (p<0.05). Among women with WC >88 cm, a risk association was observed with low HDL (OR=5.86; 95%CI=2.31-14.82), with higher TG (OR=2.61; 95%CI=1.18-5.78), with higher AIP (OR=3.42; 95%CI=1.19-9.78) and with IR (OR=3.63; 95%CI=1.27-10.36). There was a risk of low HDL (OR=3.1; 95%CI=1.44-6.85) with increased obesity (BMI>30 kg/m²). CONCLUSIONS: in the postmenopausal women, the simple measure of WC can predict cardiovascular and metabolic risk of non-transmissible chronic diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):190-195
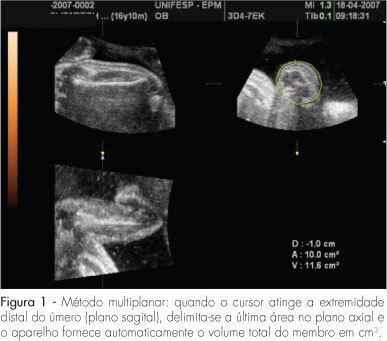
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of fetal upper arm volume, using three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS), in the prediction of birth weight. METHODS: this prospective cross-sectional study involved 25 pregnancies without structural or chromosomal anomalies. Bidimensional parameters (biparietal diameter, abdominal circumference and femur length) and the 3DUS fetal upper arm volume were obtained in the last 48 hours before delivery. The multiplanar method, using multiple sequential planes with 5.0-mm intervals, was used to calculate fetal upper arm volume. Polynomial regressions were used to determine the best equation in the prediction of fetal weight. The accuracy of this new formula was compared with Shepard's and Hadlock's formulas. RESULTS: fetal upper arm volume was strongly correlated to birth weight (r=0.83; p<0.005). Linear regression was the best equation [birth weight=681.59 + 43.23 x fetal upper arm volume]. The fetal upper arm volume mean error (0 g), mean absolute error (196.6 g) and mean percent absolute error (6.5%) were lower than using Shepard's formula; however, the difference did not reach significance (p>0.05). Birth weight predicted by fetal upper arm volume had a mean error lower than Hadlock's formula, but this difference was not statistically significant (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the accuracy of fetal upper arm volume obtained through 3DUS is similar to the accuracy of bidimensional ultrasound in the prediction of birth weight. These findings need to be confirmed by larger studies.