-
Artigos Originais
Factors associated with false diagnosis of fetal growth restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):264-268
06-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFactors associated with false diagnosis of fetal growth restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):264-268
06-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004935
Views119PURPOSE:
The aim of this study was to analize and describe some characteristics related to a false diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
METHODS:
We retrospectively included 48 pregnant women referred to our service with a suspected diagnosis of IUGR that was not confirmed after birth and we compared them to another group with confirmed IUGR. We then analyzed the characteristics of the false-positive results. The results of the study were divided into continuous and categorical variables for analysis. The χ2test or Fisher exact test was applied to compare proportions. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 for all tests.
RESULTS:
In our sample, pregnant women with a false diagnosis of IUGR had the following characteristics: they were referred earlier (mean gestational age of 32.8 weeks); were submitted to 2 to 6 ultrasound examinations before been registered in our service; in 25% of cases ultrasound examination was performed before 12 weeks; in 66.7% of cases the symphysis-fundal height measurement was normal; in 52.1% of cases they had at least 1 sonographic exam above the 10th percentile; on average, the last ultrasound examination (performed on average at 36 weeks) was above the 18th percentile; the women were submitted to a mean number of 5 ultrasound examinations and to a mean number of 4.6 vitality exams.
CONCLUSION:
The false diagnosis of IUGR involves high hospital costs and higher demand for specialists. The symphysis-fundal height measurement must be valued, and the diagnosis of IUGR must be confirmed with ultrasonography in the last weeks of pregnancy before any obstetric management is taken.
Key-words Diagnostic errorsDiagnostic techniques, obstetrical and gynecologicalFetal growth retardationFetal monitoringFetal weightPlacental function testsUltrasonography, prenatalSee more -
Artigos Originais
Pregnant Cards information and medical records of primary care on prenatal care
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):269-275
06-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisPregnant Cards information and medical records of primary care on prenatal care
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):269-275
06-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004907
Views74See morePURPOSE:
To determine the agreement between the information on pregnant cards and on primary care medical records about prenatal assistance in the city of Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil.
METHODS:
A population study of 360 puerperal women living in this city was interviewed at three hospitals where the cards were copied. Prenatal care data were collected by reviewing the medical records at the city health unit. The information was collected, processed, and submitted to Kappa, Adjusted Kappa, and McNemar tests to check agreement and tendency to disagreement between the cards and the medical records.
RESULTS:
The levels of agreement within prenatal care were predominantly moderate (Kappa=0.4-0.6). There was a higher tendency to keep records of appointments on the cards (McNemar=22.3; p-value<0.01). Records of supplementation with folic acid and ferrous sulphate were kept more often on the medical records (McNemar=70.8 and 69.8, respectively; p-value<0.01). The tetanus vaccination coverage was about 50%. Clinical and obstetric procedures and laboratory tests were primarily recorded on the card.
CONCLUSION:
The medical records of primary care were underused as a tool for communication among health professionals, highlighting a precarious record keeping. The results suggest that thought be given to guarantee that the minimum procedures established by the Guidelines of Maternal and Infant Health are followed, and also to the importance of clinical record keeping in health services, since there is variation depending on the source of information.
-
Artigos Originais
Why does the prevalence of cytopathological results of cervical cancer screening can vary significantly between two regions of Brazil?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):192-197
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisWhy does the prevalence of cytopathological results of cervical cancer screening can vary significantly between two regions of Brazil?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):192-197
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050002
Views55See morePURPOSE:
To analyze the prevalence of cervical cytopathological results for the screening of cervical cancer with regard to women's age and time since the last examination in Maceió and Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, among those assisted by the Brazilian Unified Health System.
METHODS:
Cervical cytopathological results available in the Information System of Cervical Cancer Screening for the year 2011 were analyzed, corresponding to 206,550 for Rio de Janeiro and 45,243 for Maceió.
RESULTS:
In Rio de Janeiro, examination at one and two year intervals predominated, while in Maceió examination at one and three year intervals had a higher predominance. Women who underwent cervical smear screening in Maceió were older than those in Rio de Janeiro. The prevalence of invasive squamous cell carcinoma was similar for the two cities, but all the other results presented a higher prevalence in Rio de Janeiro: ASCUS (PR=5.32; 95%CI 4.66-6.07); ASCH (PR=4.27; 95%CI 3.15-5.78); atypical glandular cells (PR=10.02; 95%CI 5.66-17.76); low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (PR=6.10; 95%CI 5.27-7.07); high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (PR=8.90; 95%CI 6.50-12.18) and adenocarcinoma (PR=3.00; 95%CI 1.21-7.44). The rate of unsatisfactory cervical samples was two times higher in Maceió and that of rejected samples for analysis was five times higher in Maceió when compared to Rio de Janeiro.
CONCLUSIONS:
The prevalence rates of altered cervical cytopathological results was significantly higher in Rio de Janeiro than in Maceió. There is no objective information that may justify this difference. One hypothesis is that there may be a difference in the diagnostic performance of the cervical cancer screening, which could be related to the quality of the Pap smear. Thus, these findings suggest that it would be necessary to perform this evaluation at national level, with emphasis on the performance of cervical cancer screening in order to improve the effectiveness of cervical cancer control.
-
Artigos Originais
Adherence to cervical cancer screening among woman from communities assisted by the Family Health Strategy at the Baixada Fluminense, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):198-204
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisAdherence to cervical cancer screening among woman from communities assisted by the Family Health Strategy at the Baixada Fluminense, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):198-204
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050003
Views45PURPOSE:
To assess the adherence to a cervical cancer screening program and to identify reported reasons for inadequate screening in women receiving care as part of the Family Health Strategy.
METHODS:
A selective prevalence study on cervical cancer screening in women receiving care as part of the Family Health Strategy in the cities of Duque de Caxias and Nova Iguaçu in the state of Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil, nine years after they participated in a previous study of the Brazilian National Cancer Institute. Only those women who were not diagnosed with CIN II or more severe lesions by histopathology, did not undergo hysterectomy during the study period and still resided in the communities were eligible to participate in the study. Information on exam sites, test results and schedules, sociodemographic characteristics and reported reasons of non-adherence was obtained. Data were collected through interviews and medical record review. The prevalence of adherence to screening was estimated, and the chi-square test was used to compare proportions between the variables studied and their relationship with the reported reasons of non-adherence to screening.
RESULTS:
A total of 764 women were interviewed, 70.7% of whom received adequate cervical cancer screening. The reported reasons for inadequate screening included: no risk perception (44.6%), social barriers (26.3%), perceived barriers to action (22.3%) and institutional barriers (21.4%). These reasons were proportionately higher among residents of Nova Iguaçu than among residents of Duque de Caxias (p<0.01), except for institutional barriers (p=0.19).
CONCLUSIONS:
Although difficulties and barriers were reported, there was good adherence to cervical cancer screening among the women studied. Health providers should receive proper training for complying with the Brazilian Ministry of Health guidelines of regular testing and to facilitate access to screening.
Key-words Family health Women's healthMass screeningUterine cervical neoplasms/ prevention & controlSee more -
Artigos Originais
PTEN expression in patients with carcinoma of the cervix and its association with p53, Ki-67 and CD31
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):205-210
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisPTEN expression in patients with carcinoma of the cervix and its association with p53, Ki-67 and CD31
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):205-210
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050004
Views122See morePURPOSE:
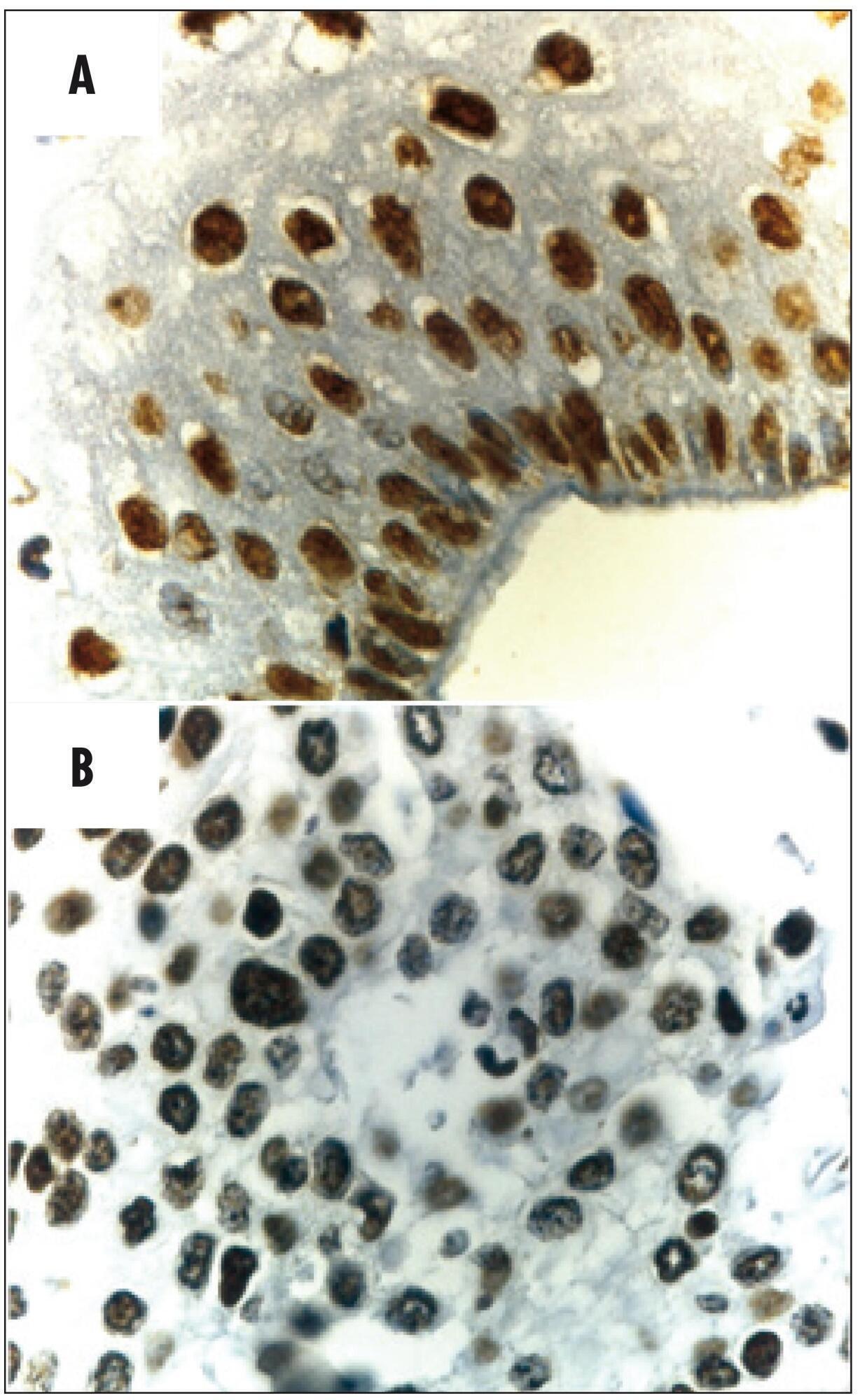
To investigate protein expression and mutations in phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in patients with stage IB cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) and the association with clinical-pathologic features, tumor p53 expression, cell proliferation and angiogenesis.
METHODS:
Women with stage IB CSCC (n=20 - Study Group) and uterine myoma (n=20 - Control Group), aged 49.1±1.7 years (mean±standard deviation, range 27-78 years), were prospectively evaluated. Patients with cervical cancer were submitted to Piver-Rutledge class III radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy and patients in the Control Group underwent vaginal hysterectomy. Tissue samples from the procedures were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation. Protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry. Staining for PTEN, p53, Ki-67 and CD31 was evaluated. The intensity of PTEN immunostaining was estimated by computer-assisted image analysis, based on previously reported protocols. Data were analyzed using the Student's t-test to evaluate significant differences between the groups. Level of significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTS:
The PTEN expression intensity was lower in the CSCC group than in the Control (benign cervix) samples (150.5±5.2 versus 204.2±2.6; p<0.001). Our study did not identify any mutations after sequencing all nine PTEN exons. PTEN expression was not associated with tumor expression of p53 (p=0.9), CD31 (p=0.8) or Ki-67 (p=0.3) or clinical-pathologic features in patients with invasive carcinoma of the cervix.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings demonstrate that the PTEN protein expression is significantly diminished in CSCC.
-
Artigos Originais
Correlation between antenatal corticosteroid therapy, resuscitation and mortality in very low birth weight infants
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):211-215
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCorrelation between antenatal corticosteroid therapy, resuscitation and mortality in very low birth weight infants
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):211-215
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050005
Views85PURPOSE:
To evaluate the correlation between the use of antenatal corticosteroid therapy (AC), the frequency of resuscitation in delivery room and mortality of newborn infants under 1,500 g and gestational age less than or equal to 34 weeks.
METHODS:
A cohort study was conducted on all newborn infants under 1,500 g and with a gestational age less than or equal to 34 weeks admitted at the neonatal ICU between January 2006 and December 2011. Newborns who had congenital anomalies, genetic syndromes, congenital infections and those who were transferred to or came from other institutions were excluded. The studied infants were divided into 2 groups: those who received (n=182) and those who did not receive (n=38) AC. The main outcomes studied were the necessity of neonatal resuscitation, the presence of the main neonatal diseases and mortality during hospitalization. The means of the variables were compared using Student's t-test or non-parametric test and frequencies were compared by χ2test with Fisher's correction. The variables that presented difference between groups were assessed by logistic regression. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) 16.0 was used and the significance level was set at 0.05.
RESULTS:
In this study, 220 patients were evaluated. The groups were similar concerning birth weight, gestational age and the presence of the main neonatal morbidity during hospitalization. The infants who received antenatal corticosteroids showed lower mortality (OR=3.0; 95%CI 1.4-6.5) and required less resuscitation (OR=2.4; 95%CI 1.1-5.0). Besides, they required less advanced resuscitation procedures, such as tracheal cannula (OR=3.7; 95%CI 1.7-7.6), cardiac massage (OR=5.7; 95%CI 2.0-16.5) and medications (OR=8.9; 95%CI 2.0-39.4).
CONCLUSIONS:
The use of antenatal corticosteroids reduced the need for resuscitation in delivery room, especially advanced procedures, and reduced the mortality in the studied groups.
Key-words Adrenal cortex hormonesCardiopulmonary resuscitationInfant, premature/mortalityInfant, very low birth weight/mortalitySee more -
Artigos Originais
Effects of physical exercise on the fetal hemodynamic parameters
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):216-221
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEffects of physical exercise on the fetal hemodynamic parameters
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):216-221
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050006
Views111See morePURPOSE:
To assess the effects of aerobic physical exercise on the Doppler velocimetry of fetal vessels in pregnant women with no clinical or obstetrical complications.
METHODS:
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 10 healthy low-risk pregnant women at 2 different gestational times: between the 26th and 29th week and 6 days, and at the end of pregnancy, between the 30th and 35th week. The patients were submitted to aerobic physical exercise on a treadmill until reaching fatigue. Ultrasonographic data were obtained at rest and after physical exercise (Doppler velocimetry indices for the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, ductus venosus, and uterine arteries). Data were analyzed statistically by the paired and independent Student's t-test using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) package, version 21.0.
RESULTS:
A change in the pulsatility index was observed, with an indication of vasodilatation, with a median value of 1.1±0.1 before exercise and of 1.0±0.1 after exercise; the median value of the resistance index was 0.7±0.04 before exercise and 0.6±0.07 after exercise. The median systole/diastole ratio of the umbilical artery was 3.1±0.4 before exercise and 2.9±0.2 (p=0.03) after exercise at the beginning of pregnancy. No changes in the Doppler velocimetry parameters were observed for the uterine arteries, the middle cerebral artery or the ductus venosus after physical activity at either testing time. Paired analysis of pre- and post-activity data showed a reduction of resistance from the first to the second period (p<0.04).
CONCLUSIONS:
Physical exercise does not lead to changes in systemic blood flow or fetal-placental flow in healthy pregnant women, confirming that exercises of mild to moderate intensity can be prescribed.
-
Artigos Originais
Risk factors associated with weight retention in postpartum period
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):222-227
05-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisRisk factors associated with weight retention in postpartum period
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):222-227
05-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050007
Views94See morePURPOSE:
To identify risk factors for weight retention in women after childbirth.
METHODS:
This was a prospective observational study that followed for six months adult women who delivered at a tertiary center. Were applied a structured questionnaire before hospital discharge and at six weeks and six months after childbirth, through home visits. The outcome was weight retention after childbirth (if risk >7.5 kg). The variables analyzed were: age, skin color, working during pregnancy, income, education, marital status, age at menarche, maternal age at first birth, parity, mode of delivery, birth interval, pre-pregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, percent body fat, and nutritional status. Data were first analyzed by bivariate analysis between prevalence of weight retention at six months and several covariates (p<0.2). We then calculated the Odds Ratio (OR) and their respective gross confidence intervals of 95% (95%CI) and finally performed multivariate logistic regression to control for confounding factors and to estimate the OR and 95%CI.
RESULTS:
The frequency of weight retention >7.5 kg by 6 months after delivery was 15%. In bivariate analysis, weight retention was associated with the following variables: age at menarche <12 years (OR=3.7; 95%CI1.1-13.2), gestational weight gain ≥16 kg (OR=5.8; 95%CI 1.8-18.6), percent body fat at baseline >30% (OR=5.0; 95%CI 1.1-23.6), and nutritional status by 6 weeks postpartum >25 kg/m2 (OR=7.7; 95%CI1.6-36.1). In multivariate analysis, only excessive gestational weight gain (OR=74.1; 95%CI 9.0-609.6) remained as a risk factor.
CONCLUSION:
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy should receive special attention in prenatal care in view of its association with weight retention and excess weight in women after childbirth.


