- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
04-11-1998
A FEBRASGO e as ações voltadas para a promoção da saúde
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):301-301
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
Abstract
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300011
Views108Avaliação Longitudinal de Aspectos Imunológicos e Virológicos Durante a Gravidez e Puerpério em Mulheres Portadoras do Vírus da Imunodeficiência Humana Tipo 1 (HIV-1)[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
Abstract
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300010
Views83A Dopplervelocimetria com Mapeamento em Cores dos Ramos Intramiometriais da Artéria Uterina de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa, com e sem Carcinoma de Endométrio[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
Abstract
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300009
Views80Avaliação da Esteroidogênese das Supra-Renais em Mulheres Normais por Meio dos Testes de ACTH Simples de Depósito[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Recurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
Abstract
Case ReportRecurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300008
Views93See moreHELLP syndrome is a severe complication of preeclampsia that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Two cases of recurrent HELLP syndrome are described, maternal death occurring in one of the cases. This study is a warning about the increased risk of HELLP syndrome in the next pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Fetal reanimation: a case report
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Wladimir Correa Taborda,
- Anna Maria Bertini,
- Jorge Francisco Kuhn dos Santos
Abstract
Case ReportFetal reanimation: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):161-163
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300007
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Wladimir Correa Taborda,
- Anna Maria Bertini,
- Jorge Francisco Kuhn dos Santos
Views93See moreA tocolytic treatment is described with the use of terbutaline in a case of cardiotocographic prolonged deceleration of fetal heart rate with successful outcome.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Equipments and Methods04-10-1998
A new catheter in the treatment of fetal obstructive uropathies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):155-159
Abstract
Equipments and MethodsA new catheter in the treatment of fetal obstructive uropathies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):155-159
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300006
Views83See moreManagement of prenatally diagnosed uropathies is controversial, mainly because the prognosis for these fetuses is quite different. However pioneering studies have shown that prenatal drainage of obstructed urinary tract can improve the outcome of selected fetuses. The aim of this study is to describe the experience of the Service with the treatment of fetal obstrutive uropathy with the catheter developed by the Centro de Medicina Fetal do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG. A total of 25 fetuses with obstructive uropathy received the catheter. Three fetuses required more than one insertion. Ten of 25 (40%) shunted fetuses survived with good postnatal renal and pulmonary function. Complications occurred in 12/25 (48%) cases including: 06/25 (24%) inadequate shunt drainage or migration; 01/25 (04%) urinary ascitis; 01/25 (04%) DPP, 01/25 (04%) premature rupture of membranes, 02/25 (08%) premature labor, 01/25 (04%) scarring and fibrosis of the renal parenchyma. Three of 25 (12%) fetuses died intra-utero and 12 (48%) died during the neonatal period. In conclusion, the drainage of the obstructed urinary tract with this catheter proved to be technically feasible and safe for both mother and fetus, with a survival rate of 40%.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-10-1998
Prevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300005
Views120See moreA retrospective study examining medical records of female prostitutes attending the STD/AIDS Reference Center in Vitória, Brazil from January/93 to December/96 was conducted. During this period, 180 women received medical and psychological care in this clinic. Mean age was 25.9 year (SD=6.8). Out of 180, 140 agreed to be tested for HIV, of whom 12 (8.6%) had a positive result. Among 157 women who agreed to be tested for syphilis, 144 (91.7%) had a negative result, while 13 (8.3%) had a positive one. According to the educational degree, 6 (3.3%) women were illiterate, 114 (63.3%) attended elementary school, 37 (20.6%) attended secondary school, 7 (3.9%) went to college and 16 gave no information. One hundred and forty-one patients (78.3%) were single, 17 (9.4%) married, 10 (5,5%) divorced and 4 (2.2%) widows. The frequency of condom use was: always, 56 (31.3%), sometimes, 93 (52.0%), and 30 (16.8%) never used condoms. Other STDs were reported by 89 (49.4%) women and 9 (5.0%) reported intravenous (IV) drug use. There was a significant difference between the HIV positive and the negative group only regarding IV drug abuse (p=0.031) and syphilis infection (p=0.014). The present study showed prevalence rates of HIV infection among prostitutes in Vitória much higher than those found in the general population. There is a pressing need to improve medical assistance and educational campaigns especially designed to reach this population of women, and focusing the importance of regular condom use and the risks associated with IV drug abuse.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-01-2019
Increasing the Chances of Natural Conception: Opinion Statement from the the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations – FEBRASGO Committee of Gynecological Endocrinology
- Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
 ,
, - Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos,
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros,
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Daniela Angerame Yela, [ … ],
- Laura Olinda Bregieiro Fernandes Costa
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTIncreasing the Chances of Natural Conception: Opinion Statement from the the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations – FEBRASGO Committee of Gynecological Endocrinology
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):183-190
- Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
 ,
, - Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos,
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros,
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- Andrea Prestes Nácul,
- Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel,
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa e Silva,
- Laura Olinda Bregieiro Fernandes Costa
Views467See moreAbstract
Considering that myths and misconceptions regarding natural procreation spread rapidly in the era of easy access to information and to social networks, adequate counseling about natural fertility and spontaneous conception should be encouraged in any kind of health assistance. Despite the fact that there is no strong-powered evidence about any of the aspects related to natural fertility, literature on how to increase the chances of a spontaneous pregnancy is available. In the present article, the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO, in the Portuguese acronym) Committee on Endocrine Gynecology provides suggestions to optimize counseling for non-infertile people attempting spontaneous conception.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Do Food Intake and Food Cravings Change during the Menstrual Cycle of Young Women?
- Luciana Bronzi de Souza,
- Karine Anusca Martins,
- Mariana Morais Cordeiro,
- Ymárdila de Souza Rodrigues,
- Bruna Paola Murino Rafacho, [ … ],
- Rafael Aiello Bomfim
Abstract
Original ArticleDo Food Intake and Food Cravings Change during the Menstrual Cycle of Young Women?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):686-692
- Luciana Bronzi de Souza,
- Karine Anusca Martins,
- Mariana Morais Cordeiro,
- Ymárdila de Souza Rodrigues,
- Bruna Paola Murino Rafacho,
- Rafael Aiello Bomfim
Views434Abstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to assess the anthropometric measures, food intake and food cravings during the menstrual cycle of undergraduate students of the faculty of nutrition.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed with 27 students from a public university in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, who had their food intake evaluated through a 24-hour food recall, their nutritional status evaluated based on anthropometric measures, and food cravings evaluated using the Food Desire Questionnaire. Data were collected during an evaluation in the follicular phase (between the 5th and the 9th day of the menstrual cycle) and another in the luteal phase (LP) (between the 20th and the 25th day of the menstrual cycle). For food intake variables, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used, followed by the Tukey test. The Mann-Whitney test was used for the analysis of food cravings, considering a significance level of 5% (p< 0.05).
Results
The desire for foods rich in sugar, salt, and fat, such as chocolate, pastries, snacks and desserts were higher (p< 0.05) during the premenstrual period, although it did not reflect neither a higher energy intake nor an alteration in the distribution of macronutrients. A higher intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, and calcium was observed during the LP; however, without statistical difference between the groups. There were no differences either in the intake of any food group or in the anthropometric measurements (p> 0.05).
Conclusion
Food cravings of nutrition students differed between the phases of the menstrual cycle; however, with no difference in food intake and in anthropometric measures.
Key-words Feeding behaviorfollicular phasefood intakeluteal phaseMenstrual cycleNutrition assessmentSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 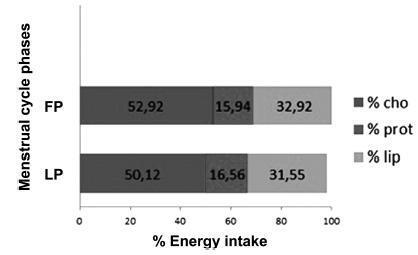
-
Review Article01-11-2023
Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
 ,
, - Moema Alves Guerra de Araujo
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Zimmermann Simões
 ,
, - Ronnier de Oliveira
 ,
, - Kleyton Santos de Medeiros
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):808-817
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
 ,
, - Moema Alves Guerra de Araujo
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Zimmermann Simões
 ,
, - Ronnier de Oliveira
 ,
, - Kleyton Santos de Medeiros
 ,
, - Ayane Cristine Sarmento
 ,
, - Robinson Dias de Medeiros
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views431See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of misoprostol in the treatment of incomplete miscarriage.
Data sources
The PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases (clinicaltrials.gov) were searched for the relevant articles, and search strategies were developed using a combination of thematic Medical Subject Headings terms and text words. The last search was conducted on July 4, 2022. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection of studies
Randomized clinical trials with patients of gestational age up to 6/7 weeks with a diagnosis of incomplete abortion and who were managed with at least 1 of the 3 types of treatment studied were included. A total of 8,087 studies were screened.
Data collection
Data were synthesized using the statistical package Review Manager V.5.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). For dichotomous outcomes, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were derived for each study. Heterogeneity between the trial results was evaluated using the standard test, I2 statistic.
Data synthesis
When comparing misoprostol with medical vacuum aspiration (MVA), the rate of complete abortion was higher in the MVA group (OR = 0.16; 95%CI = 0.07–0.36). Hemorrhage or heavy bleeding was more common in the misoprostol group (OR = 3.00; 95%CI = 1.96–4.59), but pain after treatment was more common in patients treated with MVA (OR = 0.65; 95%CI = 0.52–0.80). No statistically significant differences were observed in the general acceptability of the treatments.
Conclusion
Misoprostol has been determined as a safe option with good acceptance by patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 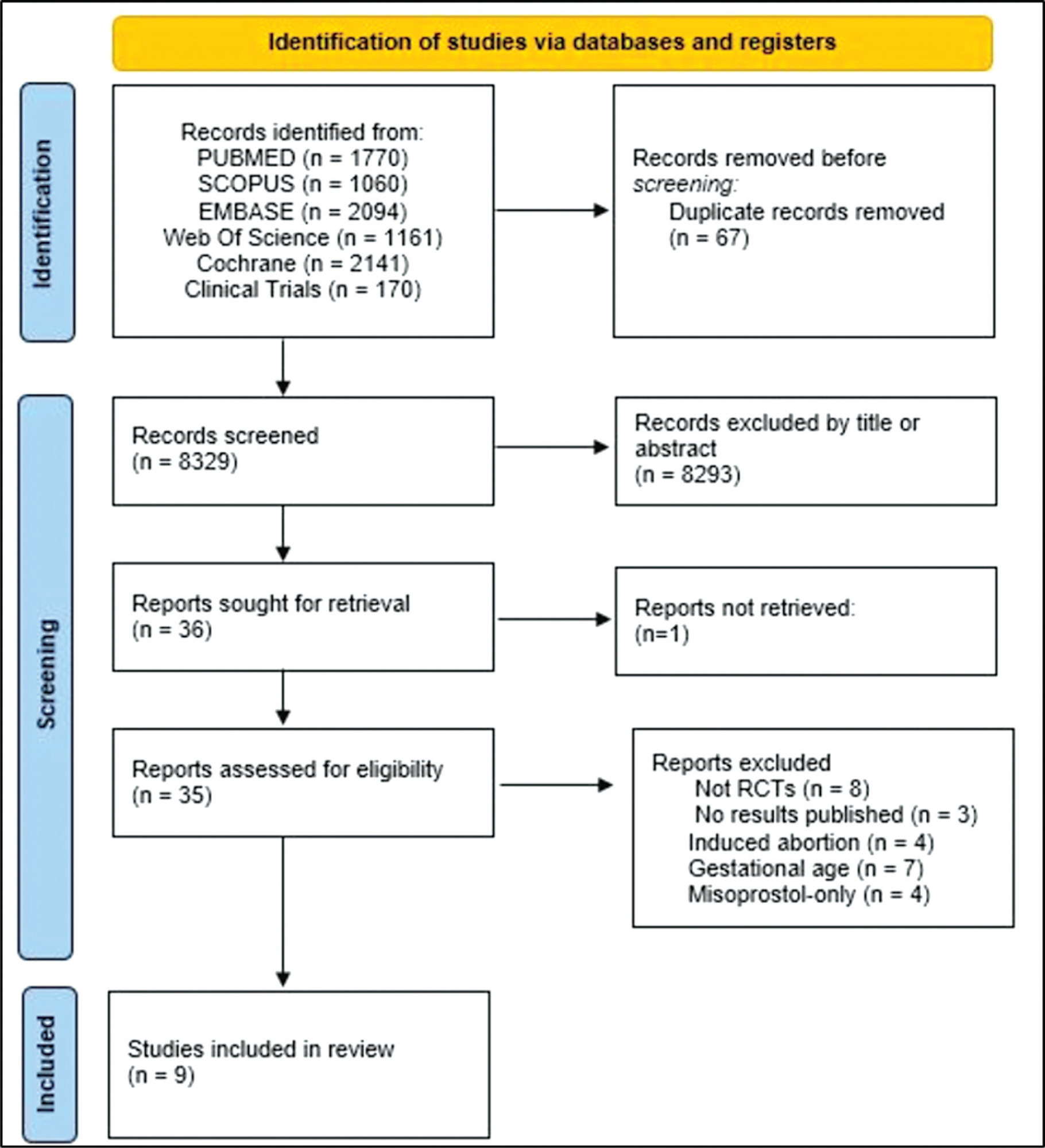
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
-
Review Article02-28-2022
Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Claudia Vargas

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 ,
, - Elsa Maria Vásquez-Trespalacios
 ,
, - Claudia Vargas

Views448Abstract
Objective
To summarize the available evidence of TAP Block in efficacy in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy.
Data Sources
We searched databases and gray literature for randomized controlled trials in which transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block was compared with placebo or with no treatment in patients who underwent laparoscopic or robot-assisted hysterectomy.
Method of Study
Selection Two researchers independently evaluated the eligibility of the selected articles. Tabulation, Integration, and Results Seven studies were selected, involving 518 patients. Early postoperative pain showed a difference in the mean mean difference (MD): – 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI]: – 1.87-0.46) in pain scale scores (I2=68%), which was statistically significant in favor of using TAP block, but without clinical relevance; late postoperative pain: DM 0.001 (95%CI: – 0.43-0.44; I2=69%); opioid requirement: DM 0.36 (95%CI: – 0.94-1.68; I2=80%); and incidence of nausea and vomiting with a difference of 95%CI=- 0.11 (- 0.215-0.006) in favor of TAP.
Conclusion
With moderate strength of evidence, due to the high heterogeneity and imbalance in baseline characteristics among studies, the results indicate that TAP block should not be considered as a clinically relevant analgesic technique to improve postoperative pain in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy, despite statistical significance in early postoperative pain scale scores.
Key-words laparoscopic hysterectomyOpioidPainrobotic-assisted hysterectomytransversus abdominis plane blockSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Claudia López-Ruiz
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Abstract
Review ArticleCognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views425Abstract
Introduction
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Results
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Key-words Chronic pelvic paincognitive behavioral therapyEndometriosispsychological interventionQuality of lifesystematic reviewsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-26-2020
Tribulus Terrestris for Female Sexual Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
 ,
, - Rafael Leite Pacheco
 ,
, - Fábia Lima Vilarino
 ,
, - Carolina de Oliveira Cruz Latorraca
 ,
, - Maria Regina Torloni
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rachel Riera

Abstract
Review ArticleTribulus Terrestris for Female Sexual Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):427-435
- Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
 ,
, - Rafael Leite Pacheco
 ,
, - Fábia Lima Vilarino
 ,
, - Carolina de Oliveira Cruz Latorraca
 ,
, - Maria Regina Torloni
 ,
, - Rachel Riera

Views421See moreAbstract
Objective
We performed a systematic review to assess the effectiveness and safety of Tribulus terrestris to treat female sexual dysfunction (FSD).
Data sources
We performed unrestricted electronic searches in the MEDLINE, CENTRAL, EMBASE, LILACS, CINAHL, PsycINFO,WHO-ICTR, Clinicaltrials.gov and OpenGrey databases. Selection of studies We included any randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared T. terrestris versus inactive/active interventions. After the selection process, conducted by two reviewers, 5 RCTs (n = 279 participants) were included.
Data collection
Data extraction was performed by two reviewers with a preestablished data collection formulary.
Data synthesis
Due to lack of data and clinical heterogeneity, we could not perform meta-analyses. The risk of bias was assessed by the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool, and the certainty of evidence was assessed with Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE).
Results
After 1 to 3 months of treatment, premenopausal and postmenopausal women randomized to T. terrestris had a significant increase in sexual function scores. Three months of treatment with T. terrestris showed a significant increase in the serum testosterone levels of premenopausal women. There was no report of serious adverse events, and none of the studies assessed health-related quality of life. The certainty of the evidence was very low, whichmeans that we have very little confidence in the effect estimates, and future studies are likely to change these estimates.
Conclusion
MoreRCTs are needed to supportor refute the use of T. terrestris. The decision to use this intervention should be shared with the patients, and the uncertainties around its effects should be discussed in the clinical decision-making process. Number of Protocol registration in PROSPERO database: CRD42019121130


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
- Luiz Carlos Zeferino,
- Joana Bragança Bastos,
- Diama Bhadra Andrade Peixoto do Vale,
- Rita Maria Zanine,
- Yara Lucia Mendes Furtado de Melo, [ … ],
- Fábio Russomano
Abstract
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
- Luiz Carlos Zeferino,
- Joana Bragança Bastos,
- Diama Bhadra Andrade Peixoto do Vale,
- Rita Maria Zanine,
- Yara Lucia Mendes Furtado de Melo,
- Walquíria Quida Salles Pereira Primo,
- Flávia de Miranda Corrêa,
- Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val,
- Fábio Russomano
Views399See moreAbstract
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 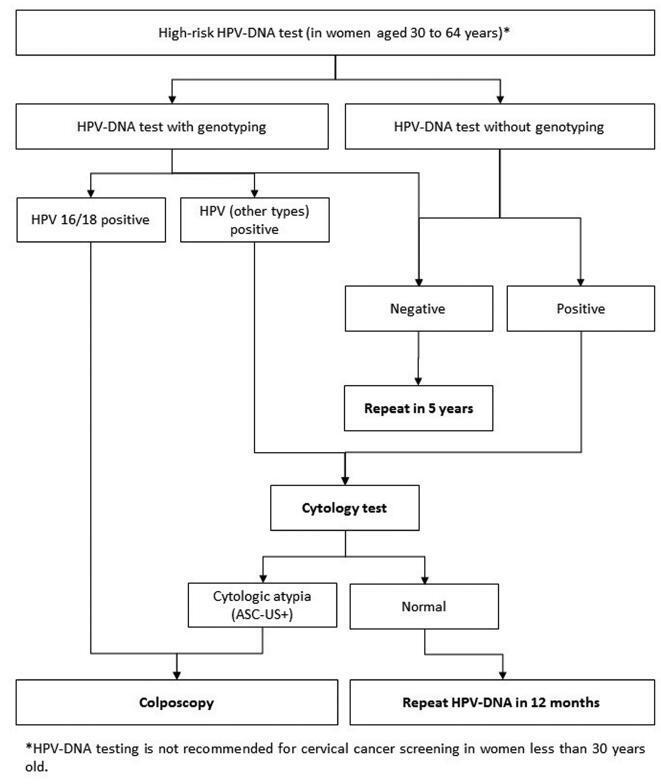
-
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
Original Article06-19-2019
Health-related Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer
- Larissa Nascimento dos Santos,
- Luciana Castaneda
 ,
, - Suzana Sales de Aguiar,
- Luiz Claudio Santos Thuler,
- Rosalina Jorge Koifman, [ … ],
- Anke Bergmann
Abstract
Original ArticleHealth-related Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):242-248
- Larissa Nascimento dos Santos,
- Luciana Castaneda
 ,
, - Suzana Sales de Aguiar,
- Luiz Claudio Santos Thuler,
- Rosalina Jorge Koifman,
- Anke Bergmann
Views264See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the factors associated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in women with cervical cancer (CC) in a single center in Rio de Janeiro, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Methods
A cross-sectional study in women with a diagnosis of CC followed-up in the gynecology outpatient clinic of the Hospital do Câncer II (HCII, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Instituto Nacional de Câncer (INCA, in the Portuguese acronym). The data were collected from March to August 2015. Women with palliative care, communication/cognition difficulty, undergoing simultaneous treatment for other types of cancer, or undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy were excluded. For the evaluation of the HRQoL, a specific questionnaire for women with CC was used (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Cervix Cancer [FACT-Cx]). The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 0 to 168, with higher scores indicating a better HRQoL.
Results
A total of 115 women were included in the present study, with a mean age of 52.64 years old (standard deviation [SD] = 12.13). The domains of emotional (16.61; SD = 4.55) and functional well-being (17.63; SD = 6.15) were those which presented the worst scores. The factors that had an association with better HRQoL in women with CC were having a current occupation, a longer time since the treatment and diagnosis, and women who had undergone hysterectomy.
Conclusion
Considering the domains of HRQoL of the women treated for cervical cancer, a better score was observed in the domains of physical and social/family wellbeing. For most domains, better scores were found between those with a current occupation, with a longer time after the diagnosis and treatment, and among those who had undergone a hysterectomy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article11-01-2018
Comparative Study of the Use of HPA Lanolin and Breast Milk for Treating Pain Associated with Nipple Trauma
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Rosemeire Sartori de Albuquerque,
- Sonia Cristina de Souza,
- Renata Oliveira Giesta,
- Andrea Penha Spinola Fernandes, [ … ],
- Bárbara Mondin
Abstract
Original ArticleComparative Study of the Use of HPA Lanolin and Breast Milk for Treating Pain Associated with Nipple Trauma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):664-672
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Rosemeire Sartori de Albuquerque,
- Sonia Cristina de Souza,
- Renata Oliveira Giesta,
- Andrea Penha Spinola Fernandes,
- Bárbara Mondin
Views290Abstract
Objective
To compare two different treatments—the use of highly purified anhydrous (HPA) lanolin and expressed breast milk—for women with pain and nipple trauma during the breastfeeding process.
Method
A total of 180 puerperal women were randomly assigned to 2 groups: one was treated with HPA lanolin and the other with their own expressed breast milk. All of the participants received the same breastfeeding technique instructions and therapeutic care standard. Three assessments were performed: at the time of inclusion in the study (after randomization); after 48 hours; and after 7 days. At each interval, data was collected in relation to pain and trauma. A numerical/verbal category scale was used for the pain variable, and the nipple trauma score for the trauma variable. The results were subjected to statistical analysis using the chi-squared test, the Fisher exact test, the student t-test, and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Generalized estimating equations were calculated using the STATA 12 statistical software package (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
There was pain improvement from the second to the third assessment in the group that used HPA lanolin, while the pain remained unchanged between these two periods (p< 0.001) in the breast milk group. In terms of trauma, improvement was identified in its extension and depth from the first to the third assessment, and it was higher in the HPA lanolin group than in the breast milk group (p= 0.025).
Conclusion
The treatment of pain and nipple trauma with HPA lanolin achieved better results than the one with breast milk, based on a 7-day treatment period.
Key-words breastfeeding/adverse effectsbreastfeeding/nipple painlanolin/therapeutic usenipples/injurieswound healing/drug effectsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 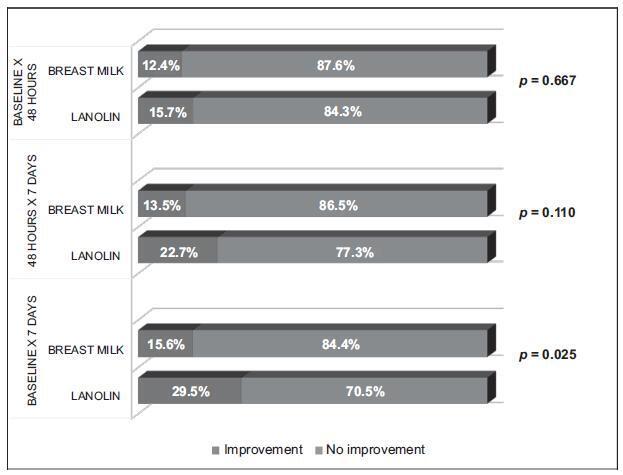
-
Original Article06-22-2020
Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Missed Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):235-239
Abstract
Original ArticlePlatelet to Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Missed Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):235-239
Views280See moreAbstract
Objective
Missed abortion occurs in ~ 15% of all clinical pregnancies. The pathogenesis is not clearly known. However, defective placentation resulting in maternal systemic inflammatory response is considered responsible for missed abortion. Platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are increasingly cited parameters of inflammation in the literature. However, no study evaluated the PLR and NLR rates in missed abortions so far. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether complete blood count (CBC) inflammatory parameters such as NLR and PLR are increased in patients with missed abortion.
Methods
Medical records of 40 pregnant women whose gestation ended in missed abortion at between 6 and14 weeks of gestation and of 40 healthy pregnant women were collected and compared retrospectively. The groups were compared regarding hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count (PLT), mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), PLR and NLR.
Results
Platelet distribution width, NLR and PLR values were higher in the missed abortion group compared with the healthy pregnant women group (rates are p = 0.043; p = 0.038; and p = 0.010, respectively). Hematocrit, MPV, and lymphocyte values were found to be lower in the missed abortion group compared with the healthy pregnant women group (p = 0.027, p = 0.044 and p = 0.025, respectively).
Conclusion
The PDW, NLR and PLR values of the missed abortion group were reported high; and MPV values were reported low in the present study. These findings may help to speculate a defective placentation in the pathogenesis of missed abortion.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article11-07-2019
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome and Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):621-627
Abstract
Review ArticleAntiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome and Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):621-627
Views298See moreAbstract
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is a systemic, autoimmune, prothrombotic disease characterized by persistent antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs), thrombosis, recurrent abortion, complications during pregnancy, and occasionally thrombocytopenia. The objective of the present study was to review the pathophysiology of APS and its association with female infertility. A bibliographic review of articles of the past 20 yearswas performed at the PubMed, Scielo, and Bireme databases. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome may be associated with primary infertility, interfering with endometrial decidualization and with decreased ovarian reserve. Antiphospholipid antibodies also have direct negative effects on placentation, when they bind to the trophoblast, reducing their capacity for invasion, and proinflammatory effects, such as complement activation and neutrophil recruitment, contributing to placental insufficiency, restricted intrauterine growth, and fetal loss. In relation to thrombosis, APS results in a diffuse thrombotic diathesis, with global and diffuse dysregulation of the homeostatic balance. Knowing the pathophysiology of APS, which is closely linked to female infertility, is essential for new therapeutic approaches, specialized in immunomodulation andinflammatory signaling pathways, to provide important advances in its treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
Systematic Review11-01-2017
Preterm Preeclampsia and Timing of Delivery: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):622-631
Abstract
Systematic ReviewPreterm Preeclampsia and Timing of Delivery: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):622-631
Views189See moreAbstract
Introduction
Preeclampsia, a multifactorial disease with pathophysiology not yet fully understood, is a major cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, especially when preterm. The diagnosis is performed when there is an association between arterial hypertension and proteinuria or evidence of severity. There are unanswered questions in the literature considering the timing of delivery once preterm preeclampsia has been diagnosed, given the risk of developingmaternal complications versus the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes associated with prematurity. The objective of this systematic review is to determine the best timing of delivery for women diagnosed with preeclampsia before 37 weeks of gestation.
Methods
Systematic literature review, performed in the PubMed database, using the terms preeclampsia, parturition and timing of delivery to look for studies conducted between 2014 and 2017. Studies that compared the maternal and perinatal outcomes of women who underwent immediate delivery or delayed delivery, in the absence of evidence of severe preeclampsia, were selected.
Results
A total of 629 studies were initially retrieved. After reading the titles, 78 were selected, and their abstracts, evaluated; 16 were then evaluated in full and, in the end, 6 studies (2 randomized clinical trials and 4 observational studies) met the inclusion criteria. The results were presented according to gestational age range (< 34 weeks and between 34 and 37 weeks) and by maternal and perinatal outcomes, according to the timing of delivery, considering immediate delivery or expectant management. Before 34 weeks, thematernal outcomeswere similar, but the perinatal outcomes were significantly worse when immediate delivery occurred. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the progression to severe maternal disease was slightly higher among women undergoing expectant management, however, with better perinatal outcomes.
Conclusions
When there is no evidence of severe preeclampsia or impaired fetal wellbeing, especially before 34 weeks, the pregnancy should be carefully surveilled, and the delivery, postponed, aiming at improving the perinatal outcomes. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the decision on the timing of delivery should be shared with the pregnant woman and her family, after providing information regarding the risks of adverse outcomes associated with preeclampsia and prematurity.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-04-2022
Screening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Abstract
Original ArticleScreening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):452-457
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views523See moreAbstract
Objective
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Methods
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
Results
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
-
Systematic Review11-01-2017
Management of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Abstract
Systematic ReviewManagement of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):632-639
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Views262Abstract
Axillary web syndrome is characterized as a physical-functional complication that impacts the quality of life of women who have undergone treatment for breast cancer. The present study aims to verify the physiotherapy treatment available for axillary web syndrome after surgery for breast cancer in the context of evidence-based practice. The selection criteria included papers discussing treatment protocols used for axillary web syndrome after treatment for breast cancer. The search was performed in the MEDLINE, Scopus, PEDro and LILACS databases using the terms axillary web syndrome, lymphadenectomy and breast cancer, focusing on women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer who underwent surgery with lymphadenectomy as part of their treatment. From the 262 studies found, 4 articles that used physiotherapy treatment were selected. The physiotherapy treatment was based on lymphatic drainage, tissue mobilization, stretching and strengthening. The four selected articles had the same outcome: improvement in arm pain and shoulder function and/or dissipation of the axillary cord. Although axillary web syndrome seems to be as frequent and detrimental as other morbidities after cancer treatment, there are few studies on this subject. The publications are even scarcer when considering studies with an interventional approach. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to support the rehabilitation resources for axillary web syndrome.
Key-words axillary web syndromeconservative treatmentcordingLymphadenectomyPhysiotherapyRehabilitationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
