-
Original Article04-09-1998
Condyloma Acuminatum in Children and Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):377-380
Abstract
Original ArticleCondyloma Acuminatum in Children and Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):377-380
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700002
Views132See moreParpose: to analyze the epidemiologic factors, clinical manifestations and forms of treatment of infection with papiloma virus. Method: all cases of condyloma acuminatum in children and adolescents assisted in the period from 1990 to 1995 in the Service of Children and Adolescent Gynecology were revised. We present the following data: age, diagnosis, clinical manifestations, sites of the lesions, transmission modes and treatment. Results: the average age of the 18 studied cases, was 6 years and 11 months (ranging from 2 to 15 years). The most common clinical manifestation was the presence of warts (61.1%). The lesions were located in the vulvoperineal area in 44.4% of the patients, and perianal and vulvar lesions were observed respectively in 27.8% and 22,2% of the cases. It was not possible to confirm the occurrence of sexual abuse or of condyloma lesions in the parents in 66.7% of the cases. Probable sexual abuse (not confirmed) was reported in 2 cases. The basic therapy was chemical cauterization. Conclusions: sexual abuse in children and adolescents with condyloma acuminatum should be investigated in spite of the existence of other transmission ways including auto- or heteroinoculation. The presentation forms at young age differ from those in adults, and thus an appropriate therapy for this is necessary for this population.
-
Original Article04-09-1998
Clinicopathologic Analysis of Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia: review of 46 Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):371-376
Abstract
Original ArticleClinicopathologic Analysis of Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia: review of 46 Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):371-376
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700001
Views151See moreThe purpose of the present study was to evaluate some epidemiological, clinical and pathological characteristics of the different grades of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), and its relation with the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV). The charts of 46 women with VIN, examined from 1986 through 1997, were reviewed. For statistical analysis the chi² with yates correction when appropriate, and Fisher’s exact tests were used. Regarding the grade of VIN, six women presented VIN 1, six others had VIN 2 and the remaining 34 presented VIN 3. All women presented similar characteristics such as age, menstrual status and age at first sexual intercourse. Women with more than one lifetime sexual partner had a tendency to show more VIN 3 (p = 0.090). Cigarette smoking was significantly associated with the severity of the vulvar lesion (p = 0.031). HPV was significantly more frequent in women younger than 35 years of age (p = 0.005) and in women with multiple lesions (p = 0.089). Although the number of lesions were not related to the severity of VIN (p = 0.703), lesions with extensions greater than 2 cm were significantly associated with VIN 3 (p = 0.009). The treatment of choice for VIN 3 was surgery, including local resection and simple vulvectomy. Eight women relapsed, and only one had VIN 2. We concluded that among women with VIN, cigarette smoking and more than one lifetime sexual partner were associated with high-grade lesions. HPV was more frequent among patients younger than 35 years of age presenting multiple lesions. Women with VIN 3 presented lesions bigger than 2 cm and a high relapse rate, despite the type of treatment applied.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 37515
- Abstract Views: 768
- Captures
- Readers: 2
-
Original Article04-05-1998
Estimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
Abstract
Original ArticleEstimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000002
Views110See morePurpose: to assess the validity of fetal weight estimation by a method based on uterine height — Johnson’s rule. Methods: one hundred and one pregnant women and their newborn children were studied. The fetal weight was estimated using an adaptation of Johnson’s rule, which consists of the clinical application of a mathematical model to calculate the fetal weight based on the uterine height and the height of fetal presentation. The estimated weight was obtained on the day of delivery and was compared to the weight observed after birth. This, in turn, was the control of the analysis of validity of the method used. On the same date, a detailed obstetrical ultrasonography (US) was conducted which included the fetal weight, calculated by the use of Sheppard’s tables. This weight, estimated by US, was compared to the birth weight. Results: the results have proven that the clinical estimate used in this study has a similar value to that of the US calculation of birth weight. The accuracy of the clinical method, with variations of 5%, 10% and 15% between estimated and observed weights, was 55.3%, 73% and 86.7%, respectively. Those of the US were 60.7%, 75.4% and 91.1%, respectively. When comparing both sets of figures, values were not different from a statistical standpoint. Conclusion: the clinical evaluation has shown to be accurate, similarly to the US, when calculating the birth weight.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 33278
- Abstract Views: 3965
- Captures
- Readers: 1
-
04-05-1998
Indice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
Abstract
Indice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800011
Views65Indice de Líquido Amniótico em Gestantes Diabéticas e a Qualidade do Controle Glicêmico na Gestação.[…]See more -
04-05-1998
Avaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
Abstract
Avaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800010
Views73Avaliação do Grau Nuclear da Célula Maligna da Mama como Parâmetro de Atividade Proliferativa Tumoral: Comparação com a Expressão do Antígeno Nuclear de Proliferação Celular (PCNA/ciclina).[…]See more -
Case Report04-05-1998
Prenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
Abstract
Case ReportPrenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800009
Views91See moreArthrogryposis multiplex congenita is characterized by multiple joint contractures present at birth. Prenatal diagnosis is difficult. There are few reports in the literature. Fetal akinesia, abnormal limb position, intrauterine growth retardation, and polyhydramnios are the main findings of the ultrasonographic diagnosis. The authors describe a case of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita ultrasonographically diagnosed in the third gestational trimester. The main findings were absence of fetal movements, polyhydramnios, symmetrical and non-symmetrical fetal growth retardation with marked decrease of abdominal and thoracic circumference, low-set ears, micrognathia, continuous flexure contracture of limbs, internal rotation of the femur, and clubfoot on the right.
-
Original Article04-05-1998
Second-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):469-473
Abstract
Original ArticleSecond-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):469-473
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800007
Views138See morePurpose: to evaluate the association between second-degree family history of breast cancer and the risk to develop the disease. Methods: case-control study of incident cases. Sixty-six incident breast cancer cases and 198 controls were selected among women who were submitted to mammography in a private clinic between January 1994 and July 1997. Cases and controls were paired regarding age, age at menarche, at first live birth, at menopause, parity, oral contraceptives and use of hormonal replacement therapy. Results: there was no significant difference between cases and controls regarding all risk factors evaluated, besides second-degree family history. Patients with breast cancer were more likely to have second-degree relatives with breast cancer when compared to controls (OR=2.77; 95% CI, 1.03-7.38; p=0.039). Conclusions: malignant neoplasm of the breast is significantly associated with a second-degree family history of this disease.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 3
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 18588
- Abstract Views: 1099
- Captures
- Readers: 13
-
Original Article04-15-2019
Association between Dietary Glycemic Index and Excess Weight in Pregnant Women in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):04-10
Abstract
Original ArticleAssociation between Dietary Glycemic Index and Excess Weight in Pregnant Women in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):04-10
Views210See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the association between dietary glycemic index (GI) and excess weight in pregnant women in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Methods
A cross-sectional study in a sample of 217 pregnant women was conducted at the maternal-fetal outpatient clinic of the Hospital Geral de Fortaleza, Fortaleza, state of Ceará, Brazil, for routine ultrasound examinations in the period between 11 and 13 weeks + 6 days of gestation.Weight and height were measured and the gestational body mass index (BMI) was calculated. The women were questioned about their usual body weight prior to the gestation, considering the prepregnancy weight. The dietary GI and the glycemic load (GL) of their diets were calculated and split into tertiles. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Walls and chi-squared (χ2) statistical tests were employed. A crude logistic regression model and a model adjusted for confounding variables known to influence biological outcomes were constructed. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant for all tests employed.
Results
The sample group presented a high percentage of prepregnancy and gestational overweight (39.7% and 40.1%, respectively). InthetertilewiththehigherGIvalue, therewasa lower dietary intake of total fibers (p = 0.005) and of soluble fibers (p = 0.008). In the third tertile, the dietary GI was associated with overweight in pregnant women in the first trimester of gestation, both in the crude model and in the model adjusted for age, total energy intake, and saturated fatty acids. However, this association was not observed in relation to the GL.
Conclusion
A high dietary GI was associated with excess weight in women in the first trimester of pregnancy.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 6
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 794
- Abstract Views: 166
- Captures
- Readers: 33
-
Original Article10-23-2024
Validation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Views307ABSTRACT
Objective:
To traslate and validate of the Brazilian version of the SDI-2.
Methods:
This was a cross-sectional study. The cultural adaptation considered the stages of initial translation, synthesis of translations, evaluation by a committee of experts from different regions of Brazil, back-translation, and pre-test. The content validity and psychometric proprieties was assessed.
Results:
Ten specialists participated in the cultural adaptation of the SDI-2. The content validity showed a Content Validity Ratio (CVR) ≥ 0.75 (p = 0.05). A total of 674 subjects participated in the field study. The Exploratory Factorial Analysis (EFA) presented factor loads ≥ 0.445, and commonalities ≥ 0.40; and two dimensions represented 77% of the total variance explained. The Confirmatory Factorial Analysis CFA presented X2/df = 4.265; the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation RMSEA = 0.110; the Non-Normed Fit Index NNFI = 0.946; the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.963; the Goodness of Fit Index GFI = 0.986; and the Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index AGFI = 0.979 for a two-factor model. The coefficient values for the total SDI-2 score were 0.91 for Cronbach’s alpha, 0.91 for McDonald’s Omega, and 0.97 for the Greatest Lower Bound GLB coefficients. The invariance between sexes was 0.01 for the ΔCFI and ΔRMSEA, showing model stability for these two populations.
Conclusion:
The Brazilian version of the SDI-2 is self-report, valid, reliable and invariant across sex.
Key-words cross cultural comparisonLibidoPsychometricsSexual behaviorSexual desiresurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article05-01-2016
Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Are Not Associated with the Clinical Under- or Overstaging of Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
Abstract
Original ArticleMolecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Are Not Associated with the Clinical Under- or Overstaging of Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
Views207See moreAbstract
Purpose
to evaluate the agreement between the clinical and pathological stagings of breast cancer based on clinical and molecular features.
Methods
this was a cross-sectional study, in which clinical, epidemiological and pathological data were collected from 226 patients who underwent surgery at the Prof. Dr. José Aristodemo Pinotti Women’s Hospital (CAISM/Unicamp) from January 2008 to September 2010. Patients were staged clinically and pathologically, and were classified as: understaged, when the clinical staging was lower than the pathological staging; correctly staged, when the clinical staging was the same as the pathological one; and overstaged, when the clinical staging was greater than the pathological staging.
Results
understaged patients were younger (52.2 years; p < 0.01) and more symptomatic at diagnosis (p = 0.04) when compared with correctly or overstaged patients. Clinicopathological surrogate subtype, menopausal status, parity, hormone replace therapy and histology were not associated with differences in staging. Women under 57 years of age were clinically understaged mainly due to underestimation of T ( tumor staging) (p < 0.001), as were the premenopausal women (p < 0.01). Patients whose diagnosis was made due to clinical complaints, and not by screening, were clinically understaged due to underestimation of N (lymph nodes staging) (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
the study shows that the clinicopathological surrogate subtype is not associated with differences in staging, while younger women diagnosed because of clinical complaints tend to have their breast tumors understaged during clinical evaluation.
-
Original Article06-19-2019
Correlation of Cervical Cancer Mortality with Fertility, Access to Health Care and Socioeconomic Indicators
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):249-255
Abstract
Original ArticleCorrelation of Cervical Cancer Mortality with Fertility, Access to Health Care and Socioeconomic Indicators
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):249-255
Views209See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study aimed to examine which development indicators are correlated with cervical cancer (CC) mortality rates in Brazil.
Methods
This was an ecological study that correlatedmortality rates and indicators, such as human development index (HDI), gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, illiteracy rate, fertility rate, screening coverage, proportion of private health insurance use, density of physicians, and density of radiotherapy centers. Themortality rateswere obtained fromthe Brazilian national registry, while the indicators were based on official reports from the Ministry of Health. Univariate and multivariate linear regression was used.
Results
Among the states of Brazil, the average age-specific CC mortality rate from 2008 to 2012 varied from 4.6 to 22.9 per 100,000 women/year. In the univariate analysis, HDI, proportion of private health insurance use, density of physicians, and density of radiotherapy centers were inversely correlated with the mortality rates. Fertility rate was positively correlated with the mortality rates. In the multivariate analysis, only fertility rate was significantly associated with the CC mortality rate (coefficient of correlation: 9.38; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.16-13.59).
Conclusion
A decrease in the fertility rate, as expected when the level of development of the regions increases, is related to a decrease in the mortality rate of CC. The results of the present study can help to better monitor the quality assessment of CC programs both among and within countries.
-
Review Article08-15-2019
New Approaches to Fetal Growth Restriction: The Time for Metabolomics Has Come
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):454-462
Abstract
Review ArticleNew Approaches to Fetal Growth Restriction: The Time for Metabolomics Has Come
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):454-462
Views213See moreAbstract
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) diagnosis is often made by fetal biometric ultrasound measurements orDoppler evaluation, but most babies are only diagnosed after birth, using the birth weight as a proxy for intrauterine development. The higher risks of neurodevelopmental delay, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular illness associated with FGR impose a shift on the focus during pregnancy. New methodological approaches, like metabolomics, can provide novel biomarkers for intrauterine fetal development. Recent evidence on metabolites involved with fetal growth and weight show a consistent role played by lipids (especially fatty acids), amino acids, vitamin D and folic acid. Fetal energy source andmetabolism, structural functions, and nervous system functioning need further evaluations in different populations. In the near future, the establishment of a core set of outcomes for FGR studies may improve the identification of the role of each metabolite in its development. Thus, we will concretely progress with the perspective of a translational capacity of metabolomics for this condition.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-08-2021
Good practices for ultrasound examinations in gynecology and obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):74-79
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTGood practices for ultrasound examinations in gynecology and obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):74-79
-
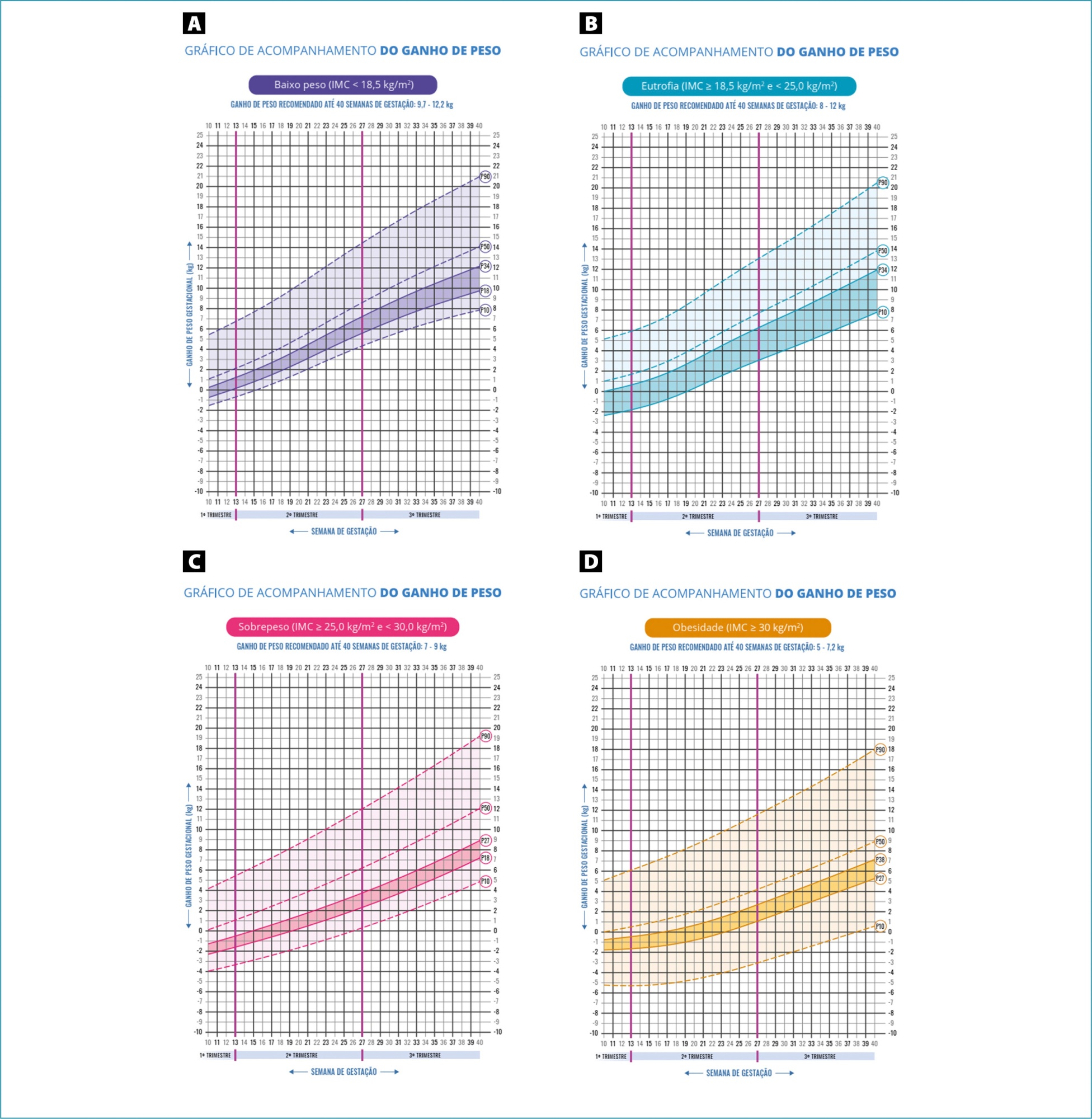
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT07-10-2023
Guidelines on how to monitor gestational weight gain during antenatal care: Number 2 – February 2023
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):104-108
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTGuidelines on how to monitor gestational weight gain during antenatal care: Number 2 – February 2023
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):104-108
-
Review Article09-06-2024
Biochemical markers for prediction of the first half pregnancy losses: a review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo72
Abstract
Review ArticleBiochemical markers for prediction of the first half pregnancy losses: a review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo72
Views306Abstract
Objective
26% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage, and up to 10% of clinically diagnosed pregnancies, and recurrent pregnancy loss is 5% among couples of childbearing ages. Although there are several known causes of pregnancy loss in the first half, including recurrent pregnancy loss, including parental chromosomal abnormalities, uterine malformations, endocrinological disorders, and immunological abnormalities, about half of the cases of pregnancy loss in its first half remain unexplained.
Methods
The review includes observational controlled studies (case-control or cohort, longitudinal studies, reviews, meta-analyses), which include the study of biochemical factors for predicting pregnancy losses in the first half, in singlet pregnancy. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess the research quality.
Results
Finally, 27 studies were included in the review, which has 134904 examined patients. The results of the review include estimates of β-human chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone, pregnancy-associated protein – A, angiogenic vascular factors, estradiol, α-fetoprotein, homocysteine and CA-125 as a predictors or markers of the first half pregnancy losses.
Conclusion
It may be concluded that to date, research data indicate the unavailability of any reliable biochemical marker for predicting pregnancy losses in its first half and require either a combination of them or comparison with clinical evidence. A fairly new model shall be considered for the assessment of α-fetoprotein in vaginal blood, which may have great prospects in predicting spontaneous miscarriages.
Key-words Biochemical markerLaboratory markerMiscarriagemissed abortionpredictionPregnancySpontaneous abortionSee more
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT06-27-2019
Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):318-332
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTPre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):318-332
Views119See moreAbstract
Pre-eclampsia is a multifactorial and multisystemic disease specific to gestation. It is classically diagnosed by the presence of hypertension associated with proteinuria manifested in a previously normotensive pregnant woman after the 20th week of gestation. Pre-eclampsia is also considered in the absence of proteinuria if there is target organ damage. The present review takes a general approach focused on aspects of practical interest in the clinical and obstetric care of these women. Thus, it explores the still unknown etiology, current aspects of pathophysiology and of the diagnosis, the approach to disease prediction, its adverse outcomes and prevention. Management is based on general principles, on nonpharmacological and on pharmacological clinical treatment of severe or nonsevere situations with emphasis on the hypertensive crisis and eclampsia. Obstetric management is based on preeclampsia without or with signs of clinical and/or laboratory deterioration, stratification of gestational age
-
Systematic Review05-01-2017
Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
Abstract
Systematic ReviewZika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
Views410Abstract
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Key-words arbovirus infectionsblindness/ etiologydeafness/ etiologymicrocephaly/ ultrasonographyPregnancy complicationsReal-time polymerase chain reactionZika virusSee more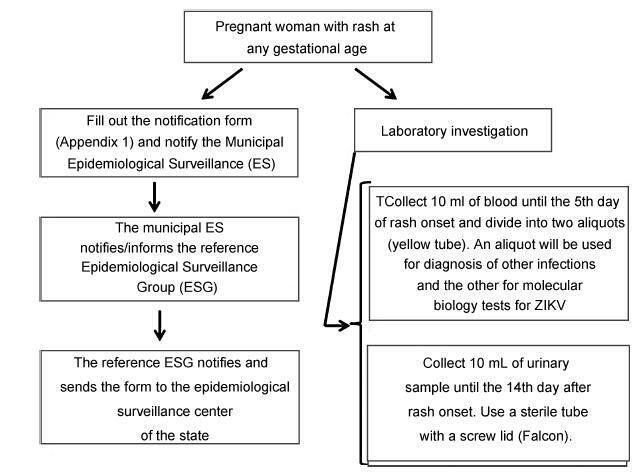
-
Original Article02-01-2019
Syphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
Abstract
Original ArticleSyphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
Views316See moreAbstract
Objective:
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Methods:
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
Results:
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births – this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Conclusion:
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.
-
Editorial09-25-2020
COVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):445-447
Abstract
EditorialCOVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):445-447
Views246The infection with the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), became a devastating threat to the health of the world population and was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020. Beginning in China at the end […]See more -
Original Article01-01-2018
Premenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
Abstract
Original ArticlePremenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
Views513Abstract
Objective
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
Methods
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Results
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered “normal” (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
Conclusion
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Key-words Diagnosispremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuestionnaireSigns and symptomsSee more -
Original Article04-01-2017
Influence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):175-183
Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):175-183
Views303See moreAbstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to investigate the self-esteem of women with and without breast cancer regarding their body image.
Methods
A quantitative, case-control study in which 90 women with breast cancer were evaluated in the case group, and 77 women without breast cancer in the control group. For data collection, the body satisfaction scale (BSS), a scale adapted and validated in Brazil, and the Rosenberg self-esteem questionnaire were used. For the statistical analysis of the data, the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software (IBM-SPSS, Chicago, Il, US), version 16.0 was used.
Results
Compared with the women without breast cancer, those with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with body image related to appearance. Women undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy were more dissatisfied with their appearance compared with those with cancer who were not undergoing this treatment. Mastectomy also accounted for more dissatisfaction concerning appearance among women who underwent the procedure compared with the women who were submitted to breast-conserving therapy.
Conclusion
Women with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with their body image compared with those without breast cancer, particularly following mastectomy or during chemotherapy. The self-esteem was found to be negatively affected in patients who were dissatisfied with their body image.
-
Review Article07-01-2017
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):358-368
Abstract
Review ArticleAbnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):358-368
Views346Abstract
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a frequent condition in Gynecology. It may impact physical, emotional sexual and professional aspects of the lives of women, impairing their quality of life. In cases of acute and severe bleeding, women may need urgent treatment with volumetric replacement and prescription of hemostatic substances. In some specific cases with more intense and prolonged bleeding, surgical treatment may be necessary. The objective of this chapter is to describe the main evidence on the treatment of women with abnormaluterinebleeding, both acuteand chronic.Didactically,thetreatmentoptions were based on the current International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classification system (PALM-COEIN). The etiologies of PALM-COEIN are: uterine Polyp (P), Adenomyosis (A), Leiomyoma (L), precursor and Malignant lesions of the uterine body (M), Coagulopathies (C), Ovulatory dysfunction (O), Endometrial dysfunction (E), Iatrogenic (I), and Not yet classified (N). The articles were selected according to the recommendation grades of the PubMed, Cochrane and Embase databases, and those in which the main objective was the reduction of uterine menstrual bleeding were included. Only studies written in English were included. All editorial or complete papers that were not consistent with abnormal uterine bleeding, or studies in animal models, were excluded. The main objective of the treatment is the reduction of menstrual flow and morbidity and the improvement of quality of life. It is important to emphasize that the treatment in the acute phase aims to hemodynamically stabilize the patient and stop excessive bleeding, while the treatment in the chronic phase is based on correcting menstrual dysfunction according to its etiology and clinical manifestations. The treatment may be surgical or pharmacological, and thelatterisbasedmainlyonhormonaltherapy,anti-inflammatorydrugsandantifibrinolytics.
Key-words Abnormal uterine bleedingdysfunctional uterine bleedingheavy menstrual bleedingmenorrhagiaPALM-COEINSee more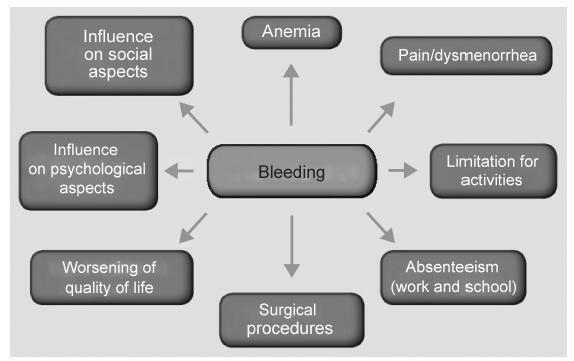
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
Abstract
Original ArticleObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
Views205See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)



