- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Case Report04-12-1998
Necrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão, [ … ],
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views131

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportNecrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):221-224
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400008
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão,
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views131See moreA case of postsurgical necrotizing fasciitis is presented. A 68-year-old female patient was submitted to a lumpectomy for a big breast lipoma. After surgen there was an aggressive local infection, with extensive necrosis of the breast tissue, including the superficial and deep fasciae and also the skin over the breast. The gravity of the disease and the difficulties in its diagnosis due to the late skin necrosis are emphasized. Under such circunstances an early and aggressive approach is necessary.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-12-1998
Leiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
Abstract
Case ReportLeiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400007
Views104See moreA case of urethral leiomyoma – a mass of approximately 5 cm in diameter – located on the anterior wall of the vaginal lower third is reported. The patient was submitted to a surgical tumor excision. Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies indicated leiomyoma, which is always a benign, unusual neoplasm, rarely relapsing after excision. Its pathogenesis and clinical features are also focused on.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa, [ … ],
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views171

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):209-213
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400006
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa,
- Heitor Ricardo Cosiski Marana,
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views171See moreFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple method and free from complications, among great value in mastology. Its accuracy can suffer the influence of several factors, among which we can highlight the experience of the physician who performs it. With the objective of verifying the effectiveness of FNAC performed by general gynecologists, 341 patients were studied concerning the relationship between the results of FNAC and the histology of the breast lesion. We obtained sensitivity of 70.87%, specificity of 70.58%, predictive positive value of 92.40%, predictive negative value of 89.36% and accuracy of 70.67%. We concluded that FNAC is of great value in handling breast lesions and can be appropriately performed by general gynecologists. The method, however, may lead to errors of diagnosis. We do not recommend, therefore, the use of the result of FNAC as a definitive diagnosis; instead this result must be interpreted in the context of the clinical diagnosis and mammography.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Post-tubal sterilization syndrome: evaluation of the psychological and clinical disturbances in tubal ligation syndrome
- Rogério Dias,
- Eliana Aguiar Petri Nahás,
- Olívia Maria Rogenski,
- Laurival A. De Luca,
- Francesco A. Viscomi, [ … ],
- Reginaldo G. C. Lopes
Views93

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePost-tubal sterilization syndrome: evaluation of the psychological and clinical disturbances in tubal ligation syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):199-205
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400005
- Rogério Dias,
- Eliana Aguiar Petri Nahás,
- Olívia Maria Rogenski,
- Laurival A. De Luca,
- Francesco A. Viscomi,
- Reginaldo G. C. Lopes
Views93The purpose of the present study was to investigate the menstrual disturbances and the psychological effects of post-tubal sterilization – the so-called post-tubal sterilization syndrome. Does it exist? The authors followed-up prospectively 300 women from the Gynecological Endoscopy and Family Planning Section, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Botucatu Medical School, Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP) during one, three and five years after tubal sterilization surgery. Different parameters such as menstrual cycle length, duration of menstrual flow, dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, regret rates etc, after tubal ligation, were analyzed. Each woman served as her own control. In conclusion, our findings suggest that most women reported no menstrual changes subsequent to sterilization. These findings do not deny or diminish the importance or benefits of tubal sterilization, but serve as a focus for further investigation.
Key-words Family planningMenstrual disturbancesPost-tubal sterilization syndromeTubal ligation syndromeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Diabetes and pregnancy: clinical and perinatal features
- Francisco Mauad Filho,
- Cleusa C. Dias,
- Roberto S. Meirelles,
- Sergio P. Cunha,
- Antonio Nogueira, [ … ],
- Geraldo Duarte
Views75

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDiabetes and pregnancy: clinical and perinatal features
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):193-198
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400004
- Francisco Mauad Filho,
- Cleusa C. Dias,
- Roberto S. Meirelles,
- Sergio P. Cunha,
- Antonio Nogueira,
- Geraldo Duarte
Views75See moreThe patients who do not adjust to the metabolic changes of pregnancy and those with previous alterations in carbohydrate metabolism show a significant increase in perinatal morbidity and mortality. In order to contribute to a better prenatal management of diabetic patients, the authors reviewed 60 cases of diabetes during pregnancy, assisted at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. The sample was divided into two groups: one with prenatal care according to the Department protocol, and referred to this center for pregnancy resolution, and the other without appropriate prenatal care. In the group with prenatal care according to the Department protocol the complications observed were related to prematurity. The group without appropriate care showed 3 cases of congenital malformations, 3 cases of prematurity, 1 case of severe neonatal hypoglycemia, 1 case of macrossomia, 1 case of intrauterine growth retardation and 1 neonatal death. Comparing the groups, it became clear that the appropriate prenatal care is essential for the diabetic pregnant patient, but also that a reference center, such as this Obstetrical and Gynecological Department, must be fully integrated with the regional health centers, in order to offer assistance before and during gestation to the diabetic patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Acute appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle: a study of 13 cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):187-192
Views93

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAcute appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle: a study of 13 cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):187-192
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400003
Views93See moreThe present study describes 13 cases of appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle, at the Maternidade Escola Januário Cicco, from Jan/89 to Dec/96. The cases were assisted by a team of obstetricians and surgeons. Eleven patients were pregnant (4 in the 1st trimester, 6 in the 2nd and 1 in the 3rd) and 2 were in the puerperal period. The incidence was 1/3.422; the age ranged from 18 to 30 years and the majority was nulliparous. The most frequent symptom was abdominal pain (intense or moderate). The appendix was perforated in 6 cases, 2 of them with abdominal wall abscess and 1 patient had an abortion. Pregnancy presented no complications in 9 cases, and delivery occurred at term. The authors observed that appendix perforations occurred more frequently in cases whose symptoms had begun earlier. The authors found that the earlier the diagnosis, the better the prognosis.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Social, demographic and medical care factors associated with maternal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):181-185
Views62

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSocial, demographic and medical care factors associated with maternal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):181-185
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400002
Views62See moreWith the purpose of identifying the social, demographic, pregnancy-related and medical care factors associated with maternal death, this study evaluated all deaths of women aged 10 to 49 years occurring in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, during 1992 and 1993. The data were obtained reviewing 1,013 death certificates, with 42 cases of identified maternal deaths. The data of these deaths were complemented with information from medical records, autopsies and also interviews with physicians from the hospitals where the death took place, and with the dead women’s relatives. Almost two thirds (62%) of maternal deaths occurred among women aged 20 to 29 years and more than half of them were single. There was a higher number of deaths among caesarean deliveries than among vaginal ones. The majority of deaths occurred within the first three days of hospitalization and approximately 90% of hospital charges were sponsored by the National Health System (SUS).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-12-1998
As Comissões Nacionais Especializadas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):179-179
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article01-01-2014
Doplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri, [ … ],
- Nina Masoom
Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDoplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):35-39
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100008
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri,
- Nina Masoom
Views392OBJETIVO:
O objetivo do presente estudo longitudinal foi avaliar o valor da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação para a predição de desfecho adverso da gravidez em mulheres de baixo risco.
MÉTODOS:
De julho de 2011 até agosto de 2012, 205 gestantes de feto único atendidas em nossa clínica de pré-natal foram incluídas no presente estudo prospectivo e avaliadas em termos de dados demográficos e obstétricos. As pacientes foram submetidas à avaliação de ultrassom durante o segundo e terceiro trimestres, incluindo avaliação Doppler das artérias uterinas bilaterais, visando determinar os valores do índice de pulsatilidade (IP) e do índice de resistência (IR), bem como a presença de incisura diastólica precoce. O desfecho do presente estudo foi a avaliação da sensibilidade, especificidade, valor preditivo positivo (VPP) e valor negativo preditivo (VNP) da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas para a predição de desfechos adversos da gravidez, incluindo pré-eclâmpsia, natimortalidade, descolamento prematuro da placenta e trabalho de parto prematuro.
RESULTADOS:
A média de idade das gestantes foi de 26,4±5,11 anos. Os valores de IP e IR das artérias uterinas para o primeiro (IP: 1,1±0,42 versus 1,53±0,59, p=0,002; IR: 0,55±0,09 versus 0.72±0.13, p=0,000, respectivamente) e para o terceiro trimestre (IP: 0,77±0,31 versus 1,09±0,46, p=0,000; IR: 0,46±0,10 versus 0,60±0,14, p=0,010, respectivamente) foram significativamente maiores em pacientes com desfecho adverso da gravidez em relação às mulheres com desfecho normal. A combinação de IP e IR > percentil 95 e a presença de incisura bilateral apresentou sensibilidade e especificidade de 36,1 e 97%, respectivamente, no segundo trimestre e de 57,5 e 98,2% no terceiro trimestre.
CONCLUSÕES:
Com base no presente estudo, o Doppler das artérias uterinas parece ser ferramenta valiosa para a predição de uma variedade de desfechos adversos no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryPregnancy outcomePregnancy trimester, secondPregnancy trimester, thirdUltrasonography, dopplerUterine artery/ultrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-21-2020
Use of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUse of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291See moreAbstract
Objective
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Data sources
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
Study selection
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
Data synthesis
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: – 3.81; 95%;CI : – 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: – 65.90; 95%;CI: – 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
Conclusion
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Thayane Delazari Corrêa
-
Review Article04-11-2022
Doppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views251

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDoppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views251See moreAbstract
Objective
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Methods
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
Results
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Conclusion
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article03-14-2024
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Wagner Iared

Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 ,
, - Wagner Iared

Views392See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Vanessa Merjane
-
Review Article10-07-2022
The Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 ,
, - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective
This systematic review aims at describing the prevalence of urinary and sexual symptoms among women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
A systematic search in six electronic databases was performed, in September 2019, by two researchers. The text search was limited to the investigation of prevalence or occurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual dysfunctions in women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer. For search strategies, specific combinations of terms were used.
Results
A total of 8 studies, published between 2010 and 2018, were included in the sample. The average age of the participants ranged from 40 to 56 years, and the dysfunctions predominantly investigated in the articles were urinary symptoms (n= 8). The rates of urinary incontinence due to radical abdominal hysterectomy ranged from 7 to 31%. The same dysfunction related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 35% and to laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 47%. Nocturia ranged from 13%, before treatment, to 30%, after radical hysterectomy. The prevalence rates of dyspareunia related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy ranged from 5 to 16% and 7 to 19% respectively. The difficulty in having orgasm was related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (10 to 14%) and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy (9 to 19%).
Conclusion
Urinary and sexual dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy to treat cervical cancer are frequent events. The main reported disorders were urinary incontinence and dyspareunia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Mariana Alves Firmeza
-
Review Article07-10-2023
Technologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views261

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleTechnologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 ,
, - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views261See moreAbstract
Objective:
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
Methods:
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
Results:
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
Conclusion:
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 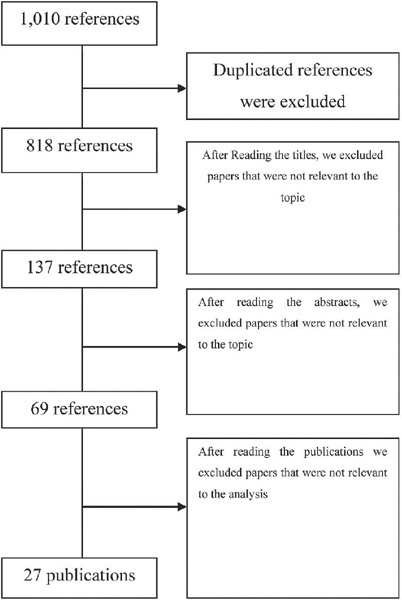
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Views392Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-11-2022
Exercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views270

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleExercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views270See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Results
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Larissa Antunes Miranda
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci, [ … ],
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci,
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial09-01-2018
Maternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra, [ … ],
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views222

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):501-506
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra,
- Carmen Simone Grilo Diniz,
- Brenno Belazi Nery de Souza Campos,
- Eliana Martorano Amaral,
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views222Maternal mortality is one of the health indicators that most reflect the social conditions of women. The inequities observed in this indicator between high- and low-income countries and among regions in the same country are explained by differences in the provision, in the access, and in the quality of obstetric care and of family planning. […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-27-2019
Quality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva, [ … ],
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):312-317
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva,
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the quality of life among university students with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Methods
The cross-sectional study was conducted at the Faculdade Pernambucana de Saúde, in Recife, Brazil, between August 2016 and July 2017. Sociodemographic, gynecological, and lifestyle variables, and PMS occurrence, were investigated among 642 students. The short form of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL Bref) questionnaire was used to evaluate four domains of the quality of life of the students: physical, mental, social relationships, and environmental. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ criteria were used to define PMS.
Results
Of the 642 students, 49.9% had PMS, 23.3% had mild PMS and 26.6% had premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Most of the students were between 18 and 24 years old, had regular menstrual cycles, and practiced physical activity. Regarding the physical and mental domains of the WHOQOL-Bref questionnaire, a statisticallysignificant difference was observed between the students who did not have and those who had mild or PMDD (p < 0.001). A difference was also found between the students who did not have PMS and those who had mild PMS in the social relationships (p = 0.001) and environmental domains (p = 0.009).
Conclusion
Mild PMS and PMDD are prevalent among university students on healthrelated courses, and the syndrome can affect the students’ self-assessment of all the domains of quality of life.
Key-words medical studentMenstruation disturbancespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuality of lifeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article06-01-2016
Selective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views197

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSelective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views197See moreAbstract
Introduction
Episiotomy is a controversial procedure, especially because the discussion that surrounds it has gone beyond the field of scientific debate, being adopted as an indicator of the “humanization of childbirth”. The scientific literature indicates that episiotomy should not be performed routinely, but selectively.
Objectives
To review the literature in order to assess whether the implementation of selective episiotomy protects against severe perineal lacerations, the indications for the procedure, and the best technique to perform it.
Methods
A literature search was performed in PubMed using the terms episiotomy or perineal lacerations, and the filter clinical trial. The articles concerning the risk of severe perineal lacerations with or without episiotomy, perineal protection, or episiotomy techniques were selected.
Results
A total of 141 articles were identified, and 24 of them were included in the review. Out of the 13 studies that evaluated the risk of severe lacerations with and without episiotomy, 5 demonstrated a protective role of selective episiotomy, and 4 showed no significant differences between the groups. Three small studies confirmed the finding that episiotomy should be performed selectively and not routinely, and one study showed that midline episiotomy increased the risk of severe lacerations. The most cited indications were primiparity, fetal weight greater than 4 kg, prolonged second stage, operative delivery, and shoulder dystocia. As for the surgical technique, episiotomies performed with wider angles (> 40°) and earlier in the second stage (before “crowning “) appeared to be more protective.
Conclusions
Selective episiotomy decreases the risk of severe lacerations when compared with the non-performance or the performance of routine episiotomy. The use of a proper surgical technique is fundamental to obtain better results, especially in relation to the angle of incision, the distance from the vaginal introitus, and the correct timing for performing the procedure. Not performing the episiotomy when indicated or not applying the correct technique may increase the risk of severe perineal lacerations.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 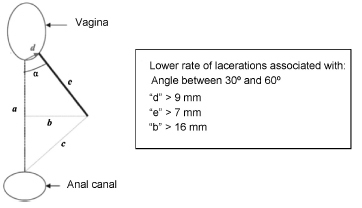
-
Review Article08-01-2017
Physical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views236

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePhysical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views236See moreAbstract
The literature that supports and recommends the practice of exercise during pregnancy is extensive.However, although a more complete research on ways to evaluate the physical activity performedby pregnant women has been perfomed, it is found that there is no gold standard and that the articles in the area are inconclusive. Thus, the objective of the present article is to review relevant aspects, such as, technique and applicability of the different methods for the assessment of physical activity during pregnancy to providemore reliable and safe information for health professionals to encourage their pregnant patients to engage in the practice of physical activity. This review concluded that all tools for the analysis of physical activity have limitations. Thus, it is necessary to establish the objectives of evaluation in an appropriate manner, as well as to determine their viability and costeffectiveness for the population under study.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article02-01-2017
Predictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePredictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232See moreAbstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate which risk factors may lead patients with gestational diabetes mellitus to cesarean delivery.
Methods
This was a retrospective, descriptive study. The subjects of the study were pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus attending a public maternity hospital in the south of Brazil. The primary outcomes assessed were based on maternal and fetal characteristics. The data were correlated using an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), calculated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 392 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were analyzed, and 57.4% of them had cesarean deliveries. Among the maternal characteristics, the mean age of the patients and the pregestational body mass index were greater when a cesarean delivery was performed (p = 0.029 and p < 0.01 respectively). Gestational age at birth, newborn weight, weight class according to gestational age, and Apgar score were not significant. The analysis of the OR showed that the chance of cesarean delivery was 2.25 times (95%CI = 1.49-2.39) greater if the pregnant woman was obese, 4.6 times (95%CI = 3.017-7.150) greater if she was a primigravida, and 5.2 times (95% CI = 2.702-10.003) greater if she had a previous cesarean delivery. The other parameters analyzed showed no differences.
Conclusion
The factors that led to an increase in the occurrence of cesarean deliveries included history of a prior cesarean section, first pregnancy, and obesity.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial12-01-2015
Maternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551
Views104

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article08-21-2015
Increased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu, [ … ],
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleIncreased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):411-416
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005397
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu,
- Fatma Meriç Yılmaz,
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91See morePURPOSE:
The aim of this study was to evaluate serum levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (INOS), myeloperoxidase (MPO), total antioxidant status (TAS), and total oxidative status (TOS) in women with primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) and to compare them with healthy fertile women. We also examined the possible risk factors associated with POI.
METHODS:
This cross-sectional case control study was conducted in Zekai Tahir Burak Women’s Health Education and Research Hospital. The study population consisted of 44 women with POI (study group) and 36 healthy fertile women (control group). In all patients, serum levels of INOS, MPO, TAS, and TOS were determined. INOS and MPO levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay whereas colorimetric method was used for evaluating TAS and TOS levels. Age, body mass index (BMI), obstetric history, smoking status, family history, comorbidities, sonographic findings, complete blood count values, C-reactive protein and baseline hormone levels were also analyzed. Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables between the groups; categorical data were evaluated by using Pearson χ2 or Fisher exact test, when appropriate. Binary logistic regression method was used to identify risk factors for POI.
RESULTS:
We found significantly elevated levels of INOS (234.1±749.5 versus133.8±143.0; p=0.005), MPO (3,438.7±1,228.6 versus 2,481.9±1,230.1; p=0.001), and TOS (4.3±1.4 versus 3.6±1.4; p=0.02) in the sera of the study group when compared to the BMI-age matched control group. However, difference in serum levels of TAS were not significant between the 2 groups (1.7±0.2 versus 1.6±0.2; p=0.15). Logistic regression method demonstrated that BMI <25 kg/m2, nulliparity, family history of POI, smoking, and elevated serum levels of INOS, MPO, and TOS were independent risk factors for POI.
CONCLUSION:
We found an increase in INOS, MPO, and TOS in women with POI. These serum markers may be promising in early diagnosis of POI. Further large-scale studies are required to determine whether oxidative stress markers have a role in diagnosing POI.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
