- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Case Report04-12-1998
Necrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão, [ … ],
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views131

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportNecrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):221-224
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400008
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão,
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views131See moreA case of postsurgical necrotizing fasciitis is presented. A 68-year-old female patient was submitted to a lumpectomy for a big breast lipoma. After surgen there was an aggressive local infection, with extensive necrosis of the breast tissue, including the superficial and deep fasciae and also the skin over the breast. The gravity of the disease and the difficulties in its diagnosis due to the late skin necrosis are emphasized. Under such circunstances an early and aggressive approach is necessary.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-12-1998
Leiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
Abstract
Case ReportLeiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400007
Views104See moreA case of urethral leiomyoma – a mass of approximately 5 cm in diameter – located on the anterior wall of the vaginal lower third is reported. The patient was submitted to a surgical tumor excision. Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies indicated leiomyoma, which is always a benign, unusual neoplasm, rarely relapsing after excision. Its pathogenesis and clinical features are also focused on.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa, [ … ],
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views171

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):209-213
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400006
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa,
- Heitor Ricardo Cosiski Marana,
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views171See moreFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple method and free from complications, among great value in mastology. Its accuracy can suffer the influence of several factors, among which we can highlight the experience of the physician who performs it. With the objective of verifying the effectiveness of FNAC performed by general gynecologists, 341 patients were studied concerning the relationship between the results of FNAC and the histology of the breast lesion. We obtained sensitivity of 70.87%, specificity of 70.58%, predictive positive value of 92.40%, predictive negative value of 89.36% and accuracy of 70.67%. We concluded that FNAC is of great value in handling breast lesions and can be appropriately performed by general gynecologists. The method, however, may lead to errors of diagnosis. We do not recommend, therefore, the use of the result of FNAC as a definitive diagnosis; instead this result must be interpreted in the context of the clinical diagnosis and mammography.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Post-tubal sterilization syndrome: evaluation of the psychological and clinical disturbances in tubal ligation syndrome
- Rogério Dias,
- Eliana Aguiar Petri Nahás,
- Olívia Maria Rogenski,
- Laurival A. De Luca,
- Francesco A. Viscomi, [ … ],
- Reginaldo G. C. Lopes
Views93

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePost-tubal sterilization syndrome: evaluation of the psychological and clinical disturbances in tubal ligation syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):199-205
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400005
- Rogério Dias,
- Eliana Aguiar Petri Nahás,
- Olívia Maria Rogenski,
- Laurival A. De Luca,
- Francesco A. Viscomi,
- Reginaldo G. C. Lopes
Views93The purpose of the present study was to investigate the menstrual disturbances and the psychological effects of post-tubal sterilization – the so-called post-tubal sterilization syndrome. Does it exist? The authors followed-up prospectively 300 women from the Gynecological Endoscopy and Family Planning Section, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Botucatu Medical School, Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP) during one, three and five years after tubal sterilization surgery. Different parameters such as menstrual cycle length, duration of menstrual flow, dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, regret rates etc, after tubal ligation, were analyzed. Each woman served as her own control. In conclusion, our findings suggest that most women reported no menstrual changes subsequent to sterilization. These findings do not deny or diminish the importance or benefits of tubal sterilization, but serve as a focus for further investigation.
Key-words Family planningMenstrual disturbancesPost-tubal sterilization syndromeTubal ligation syndromeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Diabetes and pregnancy: clinical and perinatal features
- Francisco Mauad Filho,
- Cleusa C. Dias,
- Roberto S. Meirelles,
- Sergio P. Cunha,
- Antonio Nogueira, [ … ],
- Geraldo Duarte
Views75

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDiabetes and pregnancy: clinical and perinatal features
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):193-198
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400004
- Francisco Mauad Filho,
- Cleusa C. Dias,
- Roberto S. Meirelles,
- Sergio P. Cunha,
- Antonio Nogueira,
- Geraldo Duarte
Views75See moreThe patients who do not adjust to the metabolic changes of pregnancy and those with previous alterations in carbohydrate metabolism show a significant increase in perinatal morbidity and mortality. In order to contribute to a better prenatal management of diabetic patients, the authors reviewed 60 cases of diabetes during pregnancy, assisted at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. The sample was divided into two groups: one with prenatal care according to the Department protocol, and referred to this center for pregnancy resolution, and the other without appropriate prenatal care. In the group with prenatal care according to the Department protocol the complications observed were related to prematurity. The group without appropriate care showed 3 cases of congenital malformations, 3 cases of prematurity, 1 case of severe neonatal hypoglycemia, 1 case of macrossomia, 1 case of intrauterine growth retardation and 1 neonatal death. Comparing the groups, it became clear that the appropriate prenatal care is essential for the diabetic pregnant patient, but also that a reference center, such as this Obstetrical and Gynecological Department, must be fully integrated with the regional health centers, in order to offer assistance before and during gestation to the diabetic patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Acute appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle: a study of 13 cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):187-192
Views93

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAcute appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle: a study of 13 cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):187-192
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400003
Views93See moreThe present study describes 13 cases of appendicitis in the gravidic-puerperal cycle, at the Maternidade Escola Januário Cicco, from Jan/89 to Dec/96. The cases were assisted by a team of obstetricians and surgeons. Eleven patients were pregnant (4 in the 1st trimester, 6 in the 2nd and 1 in the 3rd) and 2 were in the puerperal period. The incidence was 1/3.422; the age ranged from 18 to 30 years and the majority was nulliparous. The most frequent symptom was abdominal pain (intense or moderate). The appendix was perforated in 6 cases, 2 of them with abdominal wall abscess and 1 patient had an abortion. Pregnancy presented no complications in 9 cases, and delivery occurred at term. The authors observed that appendix perforations occurred more frequently in cases whose symptoms had begun earlier. The authors found that the earlier the diagnosis, the better the prognosis.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Social, demographic and medical care factors associated with maternal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):181-185
Views62

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSocial, demographic and medical care factors associated with maternal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):181-185
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400002
Views62See moreWith the purpose of identifying the social, demographic, pregnancy-related and medical care factors associated with maternal death, this study evaluated all deaths of women aged 10 to 49 years occurring in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, during 1992 and 1993. The data were obtained reviewing 1,013 death certificates, with 42 cases of identified maternal deaths. The data of these deaths were complemented with information from medical records, autopsies and also interviews with physicians from the hospitals where the death took place, and with the dead women’s relatives. Almost two thirds (62%) of maternal deaths occurred among women aged 20 to 29 years and more than half of them were single. There was a higher number of deaths among caesarean deliveries than among vaginal ones. The majority of deaths occurred within the first three days of hospitalization and approximately 90% of hospital charges were sponsored by the National Health System (SUS).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-12-1998
As Comissões Nacionais Especializadas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):179-179
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article01-01-2014
Doplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri, [ … ],
- Nina Masoom
Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDoplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):35-39
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100008
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri,
- Nina Masoom
Views392OBJETIVO:
O objetivo do presente estudo longitudinal foi avaliar o valor da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação para a predição de desfecho adverso da gravidez em mulheres de baixo risco.
MÉTODOS:
De julho de 2011 até agosto de 2012, 205 gestantes de feto único atendidas em nossa clínica de pré-natal foram incluídas no presente estudo prospectivo e avaliadas em termos de dados demográficos e obstétricos. As pacientes foram submetidas à avaliação de ultrassom durante o segundo e terceiro trimestres, incluindo avaliação Doppler das artérias uterinas bilaterais, visando determinar os valores do índice de pulsatilidade (IP) e do índice de resistência (IR), bem como a presença de incisura diastólica precoce. O desfecho do presente estudo foi a avaliação da sensibilidade, especificidade, valor preditivo positivo (VPP) e valor negativo preditivo (VNP) da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas para a predição de desfechos adversos da gravidez, incluindo pré-eclâmpsia, natimortalidade, descolamento prematuro da placenta e trabalho de parto prematuro.
RESULTADOS:
A média de idade das gestantes foi de 26,4±5,11 anos. Os valores de IP e IR das artérias uterinas para o primeiro (IP: 1,1±0,42 versus 1,53±0,59, p=0,002; IR: 0,55±0,09 versus 0.72±0.13, p=0,000, respectivamente) e para o terceiro trimestre (IP: 0,77±0,31 versus 1,09±0,46, p=0,000; IR: 0,46±0,10 versus 0,60±0,14, p=0,010, respectivamente) foram significativamente maiores em pacientes com desfecho adverso da gravidez em relação às mulheres com desfecho normal. A combinação de IP e IR > percentil 95 e a presença de incisura bilateral apresentou sensibilidade e especificidade de 36,1 e 97%, respectivamente, no segundo trimestre e de 57,5 e 98,2% no terceiro trimestre.
CONCLUSÕES:
Com base no presente estudo, o Doppler das artérias uterinas parece ser ferramenta valiosa para a predição de uma variedade de desfechos adversos no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryPregnancy outcomePregnancy trimester, secondPregnancy trimester, thirdUltrasonography, dopplerUterine artery/ultrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-21-2020
Use of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUse of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291See moreAbstract
Objective
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Data sources
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
Study selection
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
Data synthesis
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: – 3.81; 95%;CI : – 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: – 65.90; 95%;CI: – 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
Conclusion
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Thayane Delazari Corrêa
-
Review Article04-11-2022
Doppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views252

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDoppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views252See moreAbstract
Objective
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Methods
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
Results
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Conclusion
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article03-14-2024
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Wagner Iared

Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 ,
, - Wagner Iared

Views392See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Vanessa Merjane
-
Review Article10-07-2022
The Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 ,
, - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective
This systematic review aims at describing the prevalence of urinary and sexual symptoms among women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
A systematic search in six electronic databases was performed, in September 2019, by two researchers. The text search was limited to the investigation of prevalence or occurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual dysfunctions in women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer. For search strategies, specific combinations of terms were used.
Results
A total of 8 studies, published between 2010 and 2018, were included in the sample. The average age of the participants ranged from 40 to 56 years, and the dysfunctions predominantly investigated in the articles were urinary symptoms (n= 8). The rates of urinary incontinence due to radical abdominal hysterectomy ranged from 7 to 31%. The same dysfunction related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 35% and to laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 47%. Nocturia ranged from 13%, before treatment, to 30%, after radical hysterectomy. The prevalence rates of dyspareunia related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy ranged from 5 to 16% and 7 to 19% respectively. The difficulty in having orgasm was related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (10 to 14%) and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy (9 to 19%).
Conclusion
Urinary and sexual dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy to treat cervical cancer are frequent events. The main reported disorders were urinary incontinence and dyspareunia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Mariana Alves Firmeza
-
Review Article07-10-2023
Technologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleTechnologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 ,
, - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective:
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
Methods:
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
Results:
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
Conclusion:
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 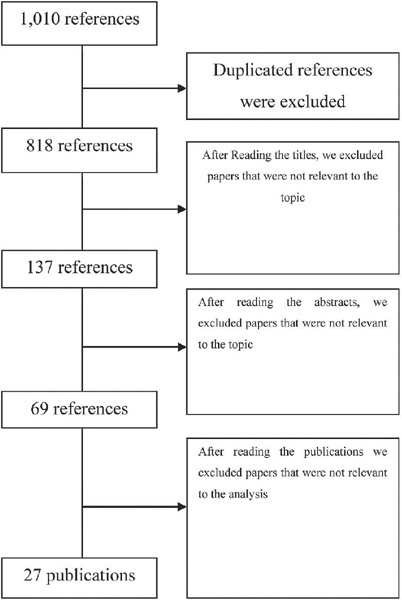
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Views392Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-11-2022
Exercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views271

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleExercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views271See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Results
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Larissa Antunes Miranda
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT06-27-2019
Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
- José Carlos Peraçoli
 ,
, - Vera Therezinha Medeiros Borges,
- José Geraldo Lopes Ramos,
- Ricardo de Carvalho Cavalli,
- Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa, [ … ],
- Edson Viera da Cunha Filho
Views96

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTPre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):318-332
- José Carlos Peraçoli
 ,
, - Vera Therezinha Medeiros Borges,
- José Geraldo Lopes Ramos,
- Ricardo de Carvalho Cavalli,
- Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa,
- Leandro Gustavo de Oliveira,
- Francisco Lazaro Pereira de Souza,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Ione Rodrigues Brum,
- Maria Laura Costa,
- Mário Dias Corrêa Junior,
- Nelson Sass,
- Angélica Lemos Debs Diniz,
- Caio Antonio de Campos Prado,
- Edson Viera da Cunha Filho
Views96See moreAbstract
Pre-eclampsia is a multifactorial and multisystemic disease specific to gestation. It is classically diagnosed by the presence of hypertension associated with proteinuria manifested in a previously normotensive pregnant woman after the 20th week of gestation. Pre-eclampsia is also considered in the absence of proteinuria if there is target organ damage. The present review takes a general approach focused on aspects of practical interest in the clinical and obstetric care of these women. Thus, it explores the still unknown etiology, current aspects of pathophysiology and of the diagnosis, the approach to disease prediction, its adverse outcomes and prevention. Management is based on general principles, on nonpharmacological and on pharmacological clinical treatment of severe or nonsevere situations with emphasis on the hypertensive crisis and eclampsia. Obstetric management is based on preeclampsia without or with signs of clinical and/or laboratory deterioration, stratification of gestational age


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - José Carlos Peraçoli
-
Original Article02-01-2019
Syphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
- Rafael Garcia Torres,
- Ana Laura Neves Mendonça,
- Grazielle Cezarine Montes,
- Jacqueline Jácome Manzan,
- João Ulisses Ribeiro, [ … ],
- Marina Carvalho Paschoini

Views281

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSyphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
- Rafael Garcia Torres,
- Ana Laura Neves Mendonça,
- Grazielle Cezarine Montes,
- Jacqueline Jácome Manzan,
- João Ulisses Ribeiro,
- Marina Carvalho Paschoini

Views281See moreAbstract
Objective:
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Methods:
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
Results:
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births – this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Conclusion:
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Systematic Review05-01-2017
Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto, [ … ],
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Views372

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Systematic ReviewZika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Gutemberg Leão de Almeida Filho,
- Heron Werner Junior,
- Hilka Flavia Barra do Espírito Santo,
- João Alfredo Piffero Steibel,
- João Bortoletti Filho,
- Juvenal Barreto Borriello de Andrade,
- Marcelo Burlá,
- Marcos Felipe Silva de Sá,
- Newton Eduardo Busso,
- Paulo César Giraldo,
- Renato Augusto Moreira de Sá,
- Renato Passini Junior,
- Rosiane Mattar,
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Views372Abstract
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Key-words arbovirus infectionsblindness/ etiologydeafness/ etiologymicrocephaly/ ultrasonographyPregnancy complicationsReal-time polymerase chain reactionZika virusSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 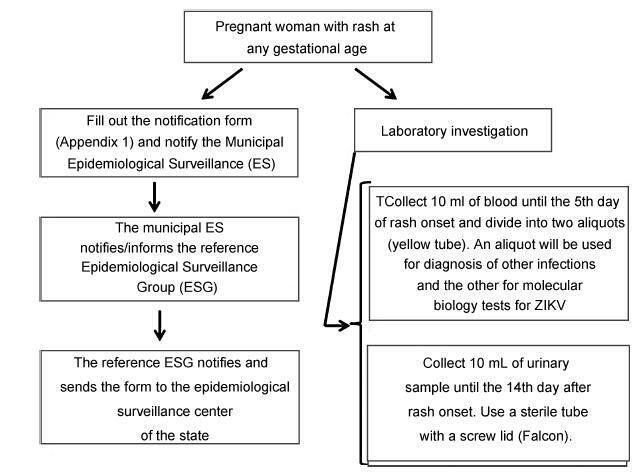
-
Editorial09-25-2020
COVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Rodolfo de Carvalho Pacagnella
 ,
, - Maira Libertad Soligo Takemoto
 ,
, - Fatima Cristina Cunha Penso
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Maria do Carmo Leal

Views183

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialCOVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):445-447
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Rodolfo de Carvalho Pacagnella
 ,
, - Maira Libertad Soligo Takemoto
 ,
, - Fatima Cristina Cunha Penso
 ,
, - Jorge de Rezende-Filho
 ,
, - Maria do Carmo Leal

Views183The infection with the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), became a devastating threat to the health of the world population and was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020. Beginning in China at the end […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
-
Original Article04-01-2017
Influence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
- Ana Carolina Lagos Prates,
- Ruffo Freitas-Junior,
- Mariana Ferreira Oliveira Prates,
- Márcia de Faria Veloso,
- Norami de Moura Barros
Views263

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):175-183
- Ana Carolina Lagos Prates,
- Ruffo Freitas-Junior,
- Mariana Ferreira Oliveira Prates,
- Márcia de Faria Veloso,
- Norami de Moura Barros
Views263See moreAbstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to investigate the self-esteem of women with and without breast cancer regarding their body image.
Methods
A quantitative, case-control study in which 90 women with breast cancer were evaluated in the case group, and 77 women without breast cancer in the control group. For data collection, the body satisfaction scale (BSS), a scale adapted and validated in Brazil, and the Rosenberg self-esteem questionnaire were used. For the statistical analysis of the data, the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software (IBM-SPSS, Chicago, Il, US), version 16.0 was used.
Results
Compared with the women without breast cancer, those with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with body image related to appearance. Women undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy were more dissatisfied with their appearance compared with those with cancer who were not undergoing this treatment. Mastectomy also accounted for more dissatisfaction concerning appearance among women who underwent the procedure compared with the women who were submitted to breast-conserving therapy.
Conclusion
Women with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with their body image compared with those without breast cancer, particularly following mastectomy or during chemotherapy. The self-esteem was found to be negatively affected in patients who were dissatisfied with their body image.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-01-2018
Premenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
- Aline Henz,
- Charles Francisco Ferreira,
- Carolina Leão Oderich,
- Carin Weirich Gallon,
- Juliana Rintondale Sodré de Castro, [ … ],
- Maria Celeste Osório Wender
Views442

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePremenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
- Aline Henz,
- Charles Francisco Ferreira,
- Carolina Leão Oderich,
- Carin Weirich Gallon,
- Juliana Rintondale Sodré de Castro,
- Maiara Conzatti,
- Marcelo Pio de Almeida Fleck,
- Maria Celeste Osório Wender
Views442Abstract
Objective
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
Methods
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Results
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered “normal” (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
Conclusion
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Key-words Diagnosispremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuestionnaireSigns and symptomsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article07-01-2017
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa-e-Silva,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- José Maria Soares Júnior
Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleAbnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):358-368
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa-e-Silva,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- José Maria Soares Júnior
Views291Abstract
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a frequent condition in Gynecology. It may impact physical, emotional sexual and professional aspects of the lives of women, impairing their quality of life. In cases of acute and severe bleeding, women may need urgent treatment with volumetric replacement and prescription of hemostatic substances. In some specific cases with more intense and prolonged bleeding, surgical treatment may be necessary. The objective of this chapter is to describe the main evidence on the treatment of women with abnormaluterinebleeding, both acuteand chronic.Didactically,thetreatmentoptions were based on the current International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classification system (PALM-COEIN). The etiologies of PALM-COEIN are: uterine Polyp (P), Adenomyosis (A), Leiomyoma (L), precursor and Malignant lesions of the uterine body (M), Coagulopathies (C), Ovulatory dysfunction (O), Endometrial dysfunction (E), Iatrogenic (I), and Not yet classified (N). The articles were selected according to the recommendation grades of the PubMed, Cochrane and Embase databases, and those in which the main objective was the reduction of uterine menstrual bleeding were included. Only studies written in English were included. All editorial or complete papers that were not consistent with abnormal uterine bleeding, or studies in animal models, were excluded. The main objective of the treatment is the reduction of menstrual flow and morbidity and the improvement of quality of life. It is important to emphasize that the treatment in the acute phase aims to hemodynamically stabilize the patient and stop excessive bleeding, while the treatment in the chronic phase is based on correcting menstrual dysfunction according to its etiology and clinical manifestations. The treatment may be surgical or pharmacological, and thelatterisbasedmainlyonhormonaltherapy,anti-inflammatorydrugsandantifibrinolytics.
Key-words Abnormal uterine bleedingdysfunctional uterine bleedingheavy menstrual bleedingmenorrhagiaPALM-COEINSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 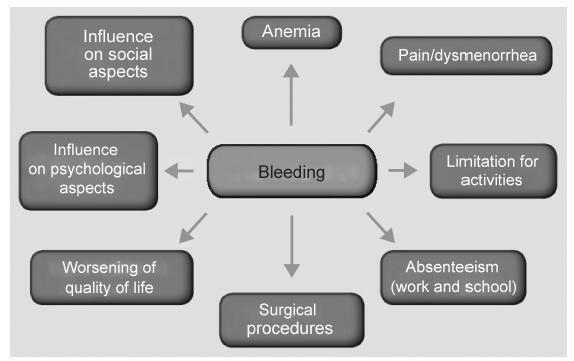
-
Original Article03-01-2018
Late-Stage Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Brazil: Analysis of Data from Hospital-Based Cancer Registries (2000-2012)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):127-136
Views152

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleLate-Stage Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Brazil: Analysis of Data from Hospital-Based Cancer Registries (2000-2012)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):127-136
Views152Abstract
Objective
To analyze the time trend and the factors regarding the diagnosis of latestage breast cancer in Brazil from 2000 to 2012.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from hospital-based cancer registries. Joinpoint regression was used to analyze the time trends of stage at diagnosis. The risk of late-stage presentation was estimated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 170,757 cases were analyzed. The median time from diagnosis to treatment was of 43 days (range: 0-182 days). The percentage of cases with late-stage diagnosis decreased from2000 to 2002, with an annual percent change (APC) of -6.6%(95%confidence interval [95%CI]: -7.6–5.5%); it increased from 2002 until 2009, with an APC of 1.1% (95% CI: 0.9-1.3%), and remained stable up to 2012.Women with college education (compared with illiterate women) had less chance of having a late-stage diagnosis (odds ratio [OR]: 0.32; 95%CI: 0.29-0.35). The odds were greater among brown women (OR: 1.30; 95%CI: 1.21-1.41) and black women (OR: 1.63; 95%CI: 1.47-1.82), compared with white women. The odds were also higher for women treated in facilities located and in the Northern region of Brazil (OR: 1.23; 95%CI: 1.04-1.45) and in the Midwest (OR: 1.61;95%CI: 1.34-1.94), compared with those treated in the southern region of the country. Age, histological type, and marital status were some of the other factors that were positively related to staging at the diagnosis.
Conclusion
Access to diagnosis of breast cancer is uneven in Brazil, and women with lower socioeconomic status present a greater probability of having an advanced stage at diagnosis.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsdisease registriesHealth services accessibilityoncologywomen’s health serviceSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
