-
Original Article01-23-2025
A comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Abstract
Original ArticleA comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Views277See moreAbstract
Objective
The study investigates the influence of positive-approach counseling through both online and face-to-face group therapy on the sexual intimacy of women after benign complete abdominal hysterectomy, addressing challenges such as the loss of femininity and other psychosexual complications that disrupt the couple’s relationship post-surgery.
Methods
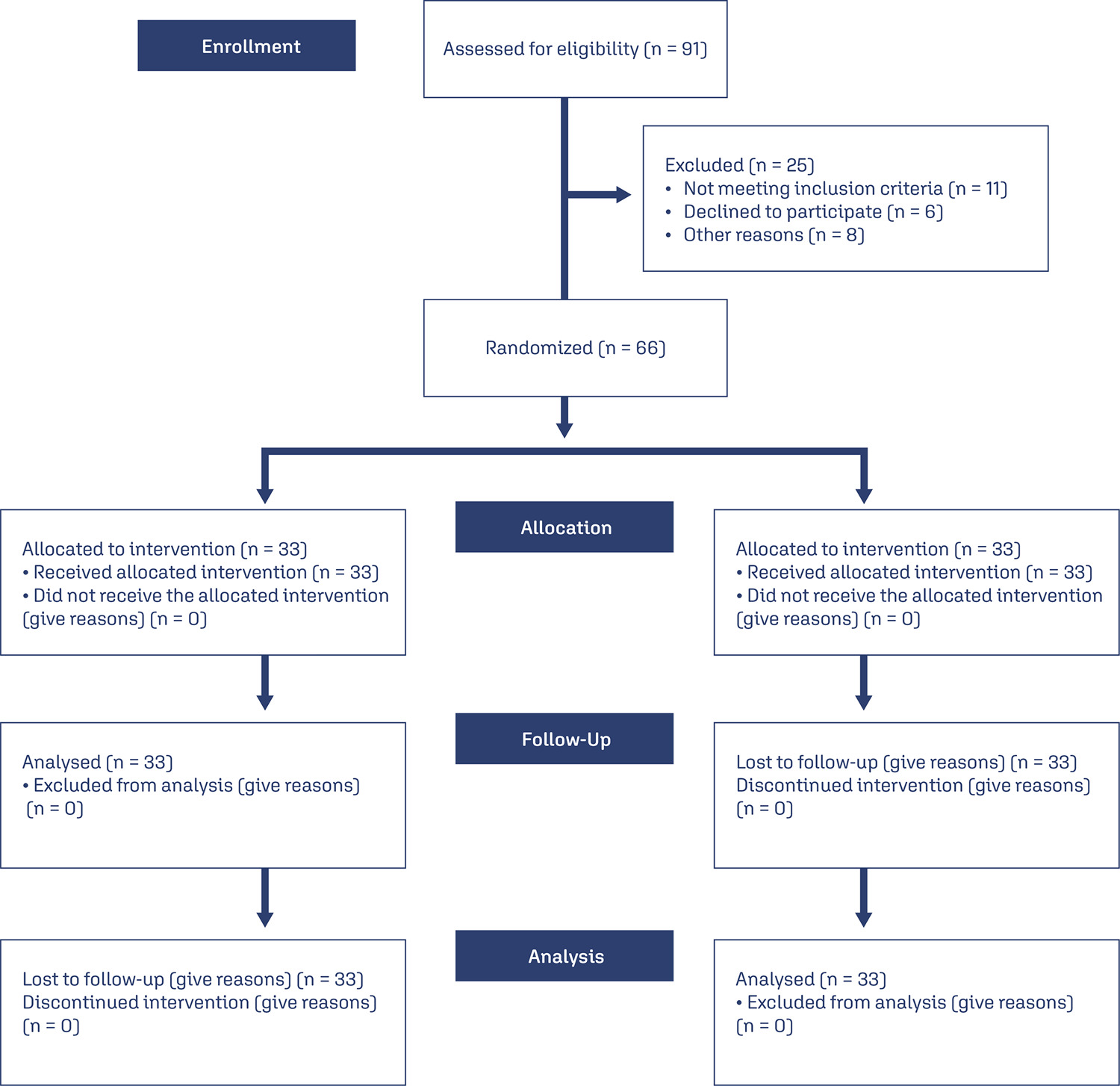
This is a parallel clinical trial, conducted in 2023 in Yazd, Iran; with sixty-six participants post- benign complete abdominal hysterectomy were randomly assigned to online and face-to-face counseling groups. Each group had eight 90-minute sessions, and data were collected using demographic and intimacy scale (IS) questionnaires at baseline, eighth week, and twelfth week follow-up. Statistical analysis used SPSS version 23 (P < 0.05).
Results
In the Online Group, the mean sexual intimacy score significantly increased from 72.42 ± 9.05 to 87.06 ± 7.98 at eight weeks and 90.30 ± 8.23 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). In the Face-to-Face Group, the mean score increased from 70.21 ± 6.75 to 81.24 ± 5.55 at eight weeks and 85.03 ± 5.40 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). Online counseling proved more effective than face-to-face counseling in enhancing sexual intimacy (P = 0.043).
Conclusion
Online and face-to-face counseling based on the positive approach improved sexual intimacy in women with a history of benign hysterectomy. Moreover, it seems that online counseling was more effective, so it is recommended that this method be employed in follow-up sessions after hysterectomy. Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials - IRCT20230209057373N1
-
Original Article10-23-2024
Validation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Views252ABSTRACT
Objective:
To traslate and validate of the Brazilian version of the SDI-2.
Methods:
This was a cross-sectional study. The cultural adaptation considered the stages of initial translation, synthesis of translations, evaluation by a committee of experts from different regions of Brazil, back-translation, and pre-test. The content validity and psychometric proprieties was assessed.
Results:
Ten specialists participated in the cultural adaptation of the SDI-2. The content validity showed a Content Validity Ratio (CVR) ≥ 0.75 (p = 0.05). A total of 674 subjects participated in the field study. The Exploratory Factorial Analysis (EFA) presented factor loads ≥ 0.445, and commonalities ≥ 0.40; and two dimensions represented 77% of the total variance explained. The Confirmatory Factorial Analysis CFA presented X2/df = 4.265; the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation RMSEA = 0.110; the Non-Normed Fit Index NNFI = 0.946; the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.963; the Goodness of Fit Index GFI = 0.986; and the Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index AGFI = 0.979 for a two-factor model. The coefficient values for the total SDI-2 score were 0.91 for Cronbach's alpha, 0.91 for McDonald's Omega, and 0.97 for the Greatest Lower Bound GLB coefficients. The invariance between sexes was 0.01 for the ΔCFI and ΔRMSEA, showing model stability for these two populations.
Conclusion:
The Brazilian version of the SDI-2 is self-report, valid, reliable and invariant across sex.
Key-words cross cultural comparisonLibidoPsychometricsSexual behaviorSexual desiresurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article04-08-2022
Habits of Genital Hygiene and Sexual Activity among Women with Bacterial Vaginosis and/or Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):169-177
Abstract
Original ArticleHabits of Genital Hygiene and Sexual Activity among Women with Bacterial Vaginosis and/or Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):169-177
Views322See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate genital hygiene among women with and without bacterial vaginosis (BV) and/or vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).
Methods
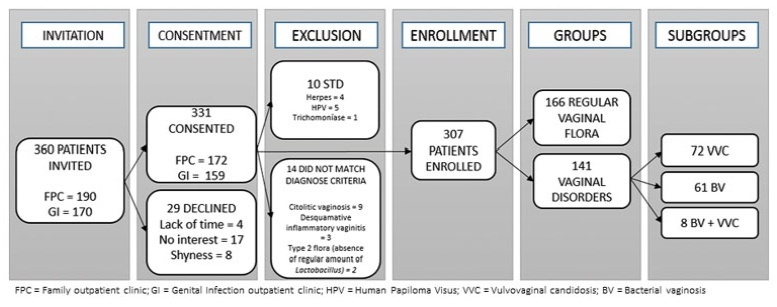
A cross-sectional study of reproductive-aged women who underwent gynecological and laboratory tests and fulfilled a genital hygiene questionnaire.
Results
This study evaluated 166 healthy controls and 141 women diagnosed with either BV (n=72), VVC (n=61), or both (n=8). The use of intimate soap and moist wipes after urination was more frequent among healthy women (p=0.042 and 0.032, respectively). Compared to controls, bactericidal soap was more used by women with BV (p=0.05).
Conclusion
Some hygiene habits were associated to BV and/or VVC. Clinical trials should address this important issue in women’s health.
-
Original Article09-01-2017
The Preference of Women and Men Regarding Female Genital Depilation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):488-495
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Preference of Women and Men Regarding Female Genital Depilation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):488-495
Views250See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate the preferences of women and men regarding female pubic hair depilation and identify possible reasons for these preferences.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study of men and women over 18 years old who were invited by the official blog of our institution to respond anonymously to an online and self-administered questionnairemade by the researchers. The analyses weremade using the Statistical Analysis System (SAS, SAS Inc., Cary, NC, US) software, version 9.3, and contingency tables were used to verify the distribution of variables. The univariate statistical analysis was performed using the Pearson chi-squared test, and the differences for values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
We obtained data from 69,920 subjects (52,787 women and 17,133 men). Themean age was 31.9 years formen, and 28.5 years for women. Most women (64.3%) and men (62.2%) preferred complete removal of female pubic hair, and this preference wasmore pronounced in younger women andmen. Most women reported performing depilation at home (55.8%), with 44.4% using hot wax and 40.1% using a razor blade. About half of the women (44.7%) and men (50.1%) reported sexual activity, having intercourse 2 to 3 times per week. The frequency of intercourse and sexual satisfaction in women correlated with total pubic hair removal.
Conclusion
Most Brazilian women and men prefer the complete removal of female pubic hair, especially those who are younger andmore sexually active.Women who are satisfied with the appearance of their own genitalia have a stronger preference for complete removal of pubic hair.
-
Original Article02-01-2017
Early Age at First Sexual Intercourse is Associated with Higher Prevalence of High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):80-85
Abstract
Original ArticleEarly Age at First Sexual Intercourse is Associated with Higher Prevalence of High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):80-85
Views156See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the association of age at first sexual intercourse with the results of the cervicovaginal cytology.
Study Design
Observational analytical study about the prevalence of altered cervicovaginal cytology results in women aged between 18 and 34 years from a densely populated area in Brazil, during 10 years. The patients were stratified into 2 categories according to their age at first sexual intercourse (13-16 years and 17-24 years).
Results
From the total of 2,505,154 exams, 898,921 tests were in accordance with the inclusion criteria. Considering women with 4 years or less from the first sexual intercourse as a reference, those with 5 to 9 years and 10 years or more showed a higher prevalence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs). Women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse (13-16 years) showed higher prevalence ratios for atypical squamous cells (ASC), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and HSIL. The prevalence ratio for HSIL adjusted by age at diagnosis and by age at first sexual intercourse was higher only for women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse.
Conclusions
The age of first sexual intercourse could be a variable that might qualify the selection among young women who are really at a higher risk for HSIL.
-
Original Article12-01-2015
Sexual dysfunction in obese women is more affected by psychological domains than that of non-obese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):552-558
Abstract
Original ArticleSexual dysfunction in obese women is more affected by psychological domains than that of non-obese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):552-558
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320155443
Views86See moreAbstract
PURPOSE:
To compare differences in the occurrence and changed domains of sexual dysfunction in obese and non-obese Brazilian women.
METHODS:
Female Sexual Function Index, based on six domains, to investigate 31 sexual dysfunction incidence for obese compared to 32 non-obese women, was used. Statistical analysis using ANOVA and MANOVA were performed to compare total scores of Female Sexual Function Index among groups and to identify the differences among domains, Student t -test was used. Statistical significant level was established for all tests for p<0.05.
RESULTS:
No difference in female sexual dysfunction frequency between obese (25.8%) and non-obese women (22.5%) was found. However, an important distinction in which aspects of sexual life were affected was found. While the obese group was impaired in three domains of sexual life (desire, orgasm, and arousal), in the control group five aspects were dysfunctional (desire, orgasm, arousal, pain and lubrication). Future research exploring psychological outcomes in obese females, such as body image and measures of positive and negative effect, might better characterize the female sexual dysfunction in this group.
CONCLUSIONS:
Obesity does not appear to be an independent factor for allow quality of female sexual life. However, disturbance associated to obesity indicates a low frequency of disorder in physical domains, suggesting that psychological factors seem to be mainly involved in the sexual dysfunction in obese women.
-
Original Article06-01-2015
Comparison of quality of life in women with sexual dysfunction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):266-271
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of quality of life in women with sexual dysfunction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):266-271
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005254
Views125See morePURPOSE:
To investigate the relationship between sexual function and quality of life in
pregnant women living in two cities of Northeastern Brazil.METHODS:
The sample consisted of 207 pregnant women. The data were collected through a
questionnaire containing questions about socio-demographic, gynecological and
obstetrical data, body and sexual knowledge. Quality of life was assessed by
applying the Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index (QLI Ferrans and Power).
Sexual function was assessed using the Female Sexual Function Index (IFSF). Data
were statistically analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon
tests.RESULTS:
The pregnant women studied had a median age of 30 years (quartile 26-33 years)
and were approximately at the 26th gestational week. A significant
decrease in the monthly frequency of sexual relations of the couple was observed,
with a median of 12 to 4 times per month (Z=-10.56; p<0.001). Sexual dysfunction was detected in 35.7% of the pregnant women studied, whose quality of life was lower when compared to women with unchanged sexual function (Z=-2.9; p=0.004).CONCLUSION:
The results of this study show that sexual dysfunction negatively affected the
quality of life of pregnant women, and this should be an important aspect for
review during prenatal consultations. -
Original Article03-01-2014
Translation and validation of the Pregnancy and Sexual Function Questionnaire (PSFQ)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):131-138
Abstract
Original ArticleTranslation and validation of the Pregnancy and Sexual Function Questionnaire (PSFQ)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300007
Views82See morePURPOSE:
To adapt the Pregnancy and Sexual Function Questionnaire (PSFQ) for use in Brazil and to evaluate its psychometric properties.
METHODS:
An adaptation and validation study was performed with women in the last trimester of pregnancy living in Rio Branco, Acre. The questionnaire was translated into Portuguese, reviewed and evaluated by specialists, and a pretest was carried out. Construct validity was evaluated by factor analysis; internal consistency was estimated by Cronbach's alpha coefficient and MacDonald's omega, and reproducibility was evaluated by the kappa statistics and test-retest in a sample of pregnant women.
RESULTS:
Factor analysis identified the following six domains: subjectivity, pain and discomfort; frequency and receptivity; desirability; satisfaction; orgasm; and stimulus. The internal consistency by Cronbach's alpha was 0.6, while MacDonald's omega was 0.7. The kappa value was higher than 0.7 in all questions.
CONCLUSION:
The Portuguese version of the PSFQ was considered to be adequate for evaluating sexual function during pregnancy.


