-
Review Article09-18-2024
Immunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Abstract
Review ArticleImmunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Views279Abstract
Objective
To compare outcomes in patients with repeated implantation failure undergoing Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection/In vitro fertilization (IVF/ICSI) plus immunosuppressants such as prednisolone, prednisone, or cyclosporine A versus the use of IVF/ICSI alone.
Data source
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase databases in September 2023.
Study Selection
Randomized clinical trials and observational studies with the outcomes of interest were included.
Data collect
We computed odds ratios (ORs) for binary endpoints, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics. Data were analyzed using Review Manager 5.4.The main outcomes were live birth, miscarriage, implantation rate, clinical pregnancy, and biochemical pregnancy.
Data synthesis
Seven studies with 2,829 patients were included. Immunosuppressive treatments were used in 1,312 (46.37%). Cyclosporine A improved implantation rate (OR 1.48; 95% CI 1.01-2.18) and clinical pregnancy (1.89, 95% CI 1.14-3.14). Compared to non-immunosuppressive treatment, prednisolone and prednisone did not improve live birth (OR 1.13, 95% CI 0.88-1.46) and miscarriage (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.07-2.09). Prednisolone showed no significant effect in patients undergoing IVF/ICSI, clinical pregnancy (OR 1.34; 95% CI 0.76-2.36), or implantation rate (OR 1.36; 95% CI 0.76-2.42).
Conclusion
Cyclosporine A may promote implantation and clinical pregnancy rates. However, given the limited sample size, it is important to approach these findings with caution. Our results indicate that prednisolone and prednisone do not have any beneficial effects on clinical outcomes of IVF/ICSI patients with repeated implantation failure.
PROSPERO
CRD42023449655
Key-words Cyclosporine APrednisolone Immunosupressive agentsPrednisoneRepeated implantation failureReproductionReproductive techniques, assistedSee more -
Original Article04-09-2024
Fertility preservation in female cancer patients in Brazil: perceptions and attitudes of infertility specialists
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo25
Abstract
Original ArticleFertility preservation in female cancer patients in Brazil: perceptions and attitudes of infertility specialists
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo25
Views560Objective:
Fertility preservation is a priority in oncology for female cancer patients. However, there is a lack of communication between infertility specialists and oncologists. This study aimed to evaluate infertility specialists’ perceptions and experiences regarding fertility preservation.
Methods:
Conduct an online survey to profile infertility specialists. Participants were infertility affiliated with the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO). The specialists received an online survey, which response rate were 30.9%, most of whom were in southern and southeastern. The survey consisted on 14 questions about the infertility specialists’ location, techniques in clinical practice, treatment successful rate, patients idea, etc.
Results:
The average experience in human reproduction were 15.5 ± 10.2 years (mean ± standard deviation, range 1-40). Among reproductive-aged female cancer patients recommended for fertility preservation, 60.3 ± 28.8% (range 10-100%) underwent preservation procedures. Main barriers were cost (41%), oncologists’ knowledge or acceptance (35%) and accessibility (9%). Most infertility specialists (58%) considered 40 years the limit for fertility preservation. Leukemia, lymphoma, breast and ovarian cancers were prioritized for fertility preservation, while lung, thyroid, gastric, and brain cancers were less relevant.
Conclusion:
This is the first Brazilian study about infertility specialists’ perceptions on oncology patients access to fertility preservation. These patients primarily receive treatment in the public health system, while infertility specialists mainly work in the private healthcare. This healthcare mode is currently fragmented, but integrating these experts is enhancing patient access to fertility preservation. Studies on this topic are still warranted.
Key-words attitudesFertilityFertility preservationgynecologistshealth knowledgeNeoplasmsOncologistsOocyte retrievalpracticeReproductionsurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Review Article06-03-2022
Relation between Selenium and Female Fertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):701-709
Abstract
Review ArticleRelation between Selenium and Female Fertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):701-709
Views298See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the influence of selenium in female fertility.
Conclusion
Selenium supplementation is promising in women with this micronutrient deficiency to promote improvement of the reproductive efficiency and prevent damage to the pregnancy. Further studies on this theme are still required.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Shared Oocyte Donation: Ideas and Expectations in a Bioethical Context Based on a Qualitative Survey of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):527-533
Abstract
Original ArticleShared Oocyte Donation: Ideas and Expectations in a Bioethical Context Based on a Qualitative Survey of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):527-533
Views153See moreAbstract
Objective
Assisted reproduction combines innovative technologies and new forms of procreation through gamete donation; however, it also leads to moral and ethical issues and to the wide application of referential bioethics. The objective of the present study was to understand the bioethical context of shared oocyte donation.
Methods
The present qualitative study used the Collective Subject Discourse methodology to interview donors and recipients in Brazil.
Results
Donors suffer from infertility, and in vitro fertilization opens the possibility of having a child; however, the cost is high, and helping the recipient is more important than the financial cost. The recipients regret delaying motherhood; adopting a child is their last option, and they desire to feel the physical stages of pregnancy. The recipients find the rules unfair regarding the lack of an oocyte bank and the fact that the treatment must be performed in shared cycles; however, oocyte donation makes it possible to realize the common dream of motherhood.
Conclusion
The obtained data showed that the patients are suffering and frustrated due to infertility, and they realize that in vitro fertilization may be the treatment they need. These women believe that children are essential in the constitution of the family, and scientific advances bring about innovative technologies and new forms of family constitution, with repercussions in the social, economic, political, and family contexts that lead to bioethical questions in Postmodernity.
-
Original Article06-01-2017
What do Infertile Women Think about Oocyte Reception, Oocyte Donation, and Child Adoption?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):282-287
Abstract
Original ArticleWhat do Infertile Women Think about Oocyte Reception, Oocyte Donation, and Child Adoption?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):282-287
Views115See moreAbstract
Purpose
The views of infertile couples regarding oocyte donation by third parties and adoption are unknown, as these may be interpreted as a final closure of the available options for conception. This study aimed to determine the acceptance of oocyte donation, oocyte reception, and child adoption of infertile women who submitted to assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment
Methods
Sixty-nine women who were under treatment for infertility and submitted to ART procedures were included in this cross-sectional study. They were evaluated using semi-structured questionnaires administered during ovulation induction in a treatment cycle. Marital status, religion, years of schooling, occupation, type of infertility, age, duration of infertility, number of previous ART cycles, mean oocyte number per cycle, and mean number of embryos per cycle had no influence on a woman’s acceptance of oocyte donation or oocyte reception.
Results
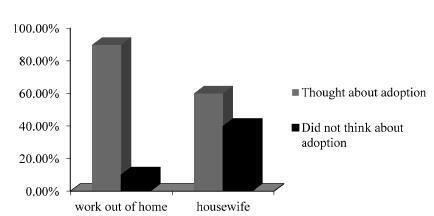
More than 90% of the patients thought that the subject of “adoption” should be brought up during their ART treatments, although they preferred to discuss this topic with psychologists, not doctors. Women with occupations were more willing to consider adoption.
Conclusion
The opinions of these patients on these issues seem to be based on personal concepts and ethical, religious, and moral values. Women preferred to discuss adoption with psychologists rather than doctors.
-
Original Article08-02-2013
Stress of men and women seeking treatment for infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):255-261
Abstract
Original ArticleStress of men and women seeking treatment for infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):255-261
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600004
Views106See morePURPOSE: To evaluate the level of stress in men and women seeking treatment for infertility and to identify the associated variables. METHODS: A cross-sectional study with 101 men and 101 women consulting for the first time at the Human Reproduction Unit. Participants completed the Brazilian version of the Fertility Problem Inventory (FPI) based on four domains: "social relationships", "life without children"; "marital relationship/sexual" and "maternity/paternity" and a structured questionnaire with socioeconomic and reproductive variables. Bivariate analysis was performed using the Chi-square and Fisher exact tests, considering p<0.05. Afterwards the multivariate correspondence analysis was done with variables with p<0.20. RESULTS: Overall, the participants presented a high level of stress in all domains, except in the "life without children" domain. Multivariate analysis of correspondence showed that variables associated with a high level of stress in the "social relationships" domains were: to be a woman, to have the infertility problem, and to consider the quality of the marital relationship to be regular. In the "life without children" domain the variables that approached the high stress were: to be woman, age between 18 and 24 years, and to have the infertility problem. To be a man, to consider adoption, parents/in-laws and other people knowing about the difficulty to become pregnant, and to consider the quality of the marital relationship to be excellent were the variables associated with high level of stress in "marital/sexual relationship" domain. For "maternity/paternity" domain the variables associated were to be women, consider marital relationship quality regular, age between 25 and 35 years, be evangelical or protestant were the variables associated with a high level of stress. CONCLUSION:Men and women seeking treatment for infertility present a high level of stress and it can be suggested that psychosocial support is important and should be different for men and women.
-
Original Article10-21-2009
Effects of androgenic anabolic steroids on the uterus and reproductive parameters of adult female rats
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(9):453-460
Abstract
Original ArticleEffects of androgenic anabolic steroids on the uterus and reproductive parameters of adult female rats
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(9):453-460
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000900006
Views120See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of the administration of two synthetic steroids in the uterus morphology and in the reproductive parameters of adult female rats. METHODS: divided into four experimental groups: control (C; physiological solution); treated with nandrolone decanoate (DN; 7.5 mg/kg of body weight); with a testosterone esters compound (T; 7.5 mg/kg); and simultaneously with DN and T (7.5 mg/kg of each steroid), in a single intraperitoneal weekly dose, for eight weeks. Five females of each group were sacrificed and the uterine horns were collected, weighted and prepared for histological and morphometrical evaluation. The remaining rats were mated with normal male rats for reproductive parameters evaluation, composing the groups treated during the pre-gestational period. Another group of 20 female rats were treated during the gestational period (7th-14th days). For data analysis, the Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric variance analysis was used, followed by the test of Dunn or of Student-Newman-Keus (5% significance level). RESULTS: there was a significant body weight increase in the androgenized females (ND: 305±50; T: 280±35; ND+T: 275±30 versus C: 255±22 g; p<0.05). Uterine weight was not affected by the steroidal treatment (ND: 0.6±0.2; T: 0.4±0.04; ND+T: 0.7±0.1 versus C: 0.4±0.09 g). All the androgenized females presented estral acyclicity and endometrium characterized by papilliferous luminal lining, oedematous stroma with hemorrhagic areas and secretory activity. There were changes in the morphometrical thickness parameters of the luminal epithelium, myometrium and perimetrium in the androgenized groups. None of the female rats got pregnant when treated with steroids in the pre-gestational period and the treatment during organogenesis affected negatively the reproductive parameters. CONCLUSIONS: steroidal agents alter the uterine structure and impair fertility and gestational outcome in female rats.
-
Original Article03-19-2006
Cryopreservation of human semen: comparison between methods of freezing and types of storage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):708-714
Abstract
Original ArticleCryopreservation of human semen: comparison between methods of freezing and types of storage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):708-714
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001200004
Views152See morePURPOSE: to compare two different methods of freezing and two types of human semen storage during cryopreservation process. METHODS: experimental research in which the cryopreservation of 18 semen samples from 18 volunteers was studied. Following the addition of the cryoprotectant medium, Test-yolk buffer, the semen samples were packaged into 0.25 mL straws or into 2 mL cryotubes and submitted to cryopreservation by slow or rapid methods, in four different treatments: RS (cryopreservation by rapid method and packaged in straws), RT (rapid-cryotubes), SS (slow-straws), and ST (slow-cryotubes). Samples were thawed after 24 hand then maintained at 37ºC. Data collected were analyzed by the Student t-test, with p<0.05, using the SPSS computer program for Windows®, version 11.0.0. RESULTS: the motility of spermatozoa decreased after the cryopreservation process. The initial motility rate was 58.1% and motilities after the different methods of cryopreservation were 19.2% (RS), 27% (RT), 21.1% (SS) and 30.3% (ST). There was a significant decrease of the normal morphology. The initial normal morphology was 14.2% and morphologies after the different methods of cryopreservation were 12.8% (RS), 12.6% (RT), 12.6% (SS) and 12.4% (ST). CONCLUSIONS: the slow method of cryopreservation with storage in cryotubes showed the best recovery of motile cells after freezing and thawing. There was no difference among the methods when appraised the morphology.


