Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):232-240
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500005
PURPOSE: to determine caffeine consumption in pregnant women and to evaluate its association with demographic, socioeconomic, reproductive, lifestyle and maternal nutritional status. METHODS: it is a cross-sectional study performed between 2005 and 2007. The present analysis refers to the period among the 8th and 13th gestational week and included 255 pregnant women from 18 to 40 years, clients of a municipal health center in Rio de Janeiro. The outcome variable was caffeine consumption, quantified by a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, which count with a list containing 81 items and eight options of consumption frequencies; besides it being previously validated in a sample of employees of the State University of Rio de Janeiro. The caffeine intake was quantified starting from the consumption of: powdered chocolate, chocolate bar or chocolate, soft drink, coffee and mate tea. The statistical analysis was performed by means of fitting a multivariate linear regression. RESULTS: the median and the mean caffeine consumption were, respectively, 97.5 and 121.1 mg (standard deviation, sd = 128.4). The high caffeine consumption (> 300 mg/day) was observed in 8.3% of pregnant women. It was observed in the multivariate model that women with earlier menarche (β = -0.15), with more household partners (b = 0.17) and who didn’t make use of medicines (β = -0.24) presented larger tendency to high caffeine consumption association that was statistically significant (p <0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the caffeine consumption for most of the pregnant women was inferior to the limit of 300 mg/day as commited in other studies. Tendency was observed toward higher consumption of caffeine in pregnant women with earlier menarche, with more household partners and who didn’t make use of medicines.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):12-18
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100003
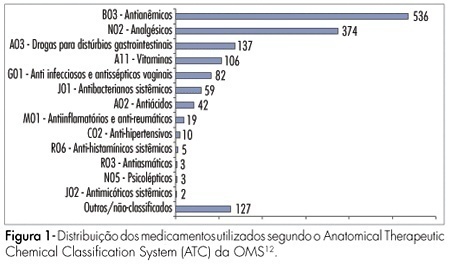
PURPOSE: to study the use of medicines by pregnant women during prenatal care in clinics of the national public health system in the city of Natal, Brazil. METHODS: a total of 610 pregnant women between the first and the third trimesters of pregnancy were interviewed in the public clinics of the four sanitary districts of Natal, from May to July 2006. The data were collected by a structured questionnaire, based in use-oriented and medicine-oriented questions. The drugs were classified according to the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC), in agreement with the gestation risk criteria from the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA). The statistical analysis was made by the chi2 test. RESULTS: a total of 1,505 drugs were used, with an average of 2.4 medications per woman. The use of at least one drug was found in 86.6% of the women. The most frequently used drugs were anti-anemics (35.6%), analgesics (24.9%), drugs for gastrointestinal disorders (9.1%) and vitamins (7%). According to the FDA classification, 42.7% belonged to category A risk, 27.1% to category B, 29.3% to category C, 0.3% to category D and none to category X. The use of medicines during the first trimester of pregnancy amounted to 43.6%. The rate of drug use increased with higher schooling level and family income. Self-medication was found in 12.2% of the drug intake and this rate was higher in the first trimester of gestation and with women with low education level and previous gestations. CONCLUSIONS: pregnant women from Natal are being exposed to a variety of medicines with uncertain safety in pregnancy. Therefore, more careful prescription is needed, to avoid possible fetal damage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(11):588-592
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001100007
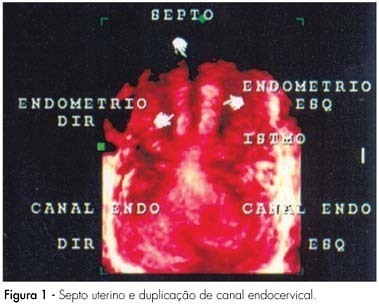
This report describes an unusual case of spontaneous pregnancy in a patient with Müllerian anomaly. The patient was a 34-years old, white, nulligravida, with regular menstrual cycles, and suspected uterine septum observed during a routine ultrasonographic examination. The gynecological examination revealed a complete longitudinal vaginal septum and two uterine cervices. Three-dimensional pelvic ultrasonography showed cervix duplication, uterine septum from isthmus to endometrial cavity and absence of uterine body division, compatible with complete uterine septum and true dual cervices. She returned after one month and reported unprotected sexual intercourse and delayed menstrual period. She was pregnant, had a good pregnancy evolution, and delivered a healthy term baby girl, by cesarean section, at 37 weeks of pregnancy. This report describes a case of normal-term pregnancy in a patient with a rare anomaly (vaginal septum and two cervices) who became spontaneously pregnant without treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(10):511-518
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000004
PURPOSE: to analyze the association between maternal pre-gestational nutritional status and maternal outcomes - hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, vitamin A deficiency, and anemia - and the newborn outcome - low birth weight. METHODS: cross-sectional study, with 433 adult puerperal women (> 20 years old) and their newborns, attending the Maternidade Escola of Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ). Data was collected through interviews and access to their medical records. Maternal pre-gestational nutritional status was established through pre-gestational body mass index according to the cut-offs for adult women defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 1995. The association between gestational outcomes and pre-gestational nutritional status was estimated through odds ratio (OR) and a 95% confidence interval (95%CI). RESULTS: frequency of pre-gestational weight deviation (low weight, overweight and obesity) was 31.6%. Considering the pre-gestational nutritional status, overweight and obese women presented a lower weight gain than eutrophic and low-weight women (p<0.05). Women with pre-gestational obesity presented a higher risk of developing hypertensive disordens of pregnancy (OR=6.3; 95%CI=1.9-20.5) and those with low pre-gestational weight were more likely to give birth to low birth weigh infants (OR=7.1; 95%CI=1.9-27.5). There was no evidence of the association between pre-gestational nutritional status and the development of anemia, vitamin A deficiency and gestational diabetes. The mean weight gain among overweight and obese pregnant women was significantly lower when compared to eutrophic and low-weight pregnant women (p=0.002, p=0.049, p=0.002, p=0.009). CONCLUSIONS: the high number of women with pre-gestational weight deviation reinforces the importance of a nutritional guidance that favors a good nutritional state and reduces the risks of maternal and newborn adverse outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):396-401
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800003
PURPOSE: to translate and to validate the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) for Brazilian pregnant women. METHODS: ninety-two pregnant women attended at a low risk prenatal clinic, with diagnosis of the pregnancy confirmed by precocious ultrasonography, participated in the research. Initially, we translated the FSFI questionnaire for Portuguese language (of Brazil) in agreement with the international criteria. Cultural, conceptual and semantics adaptations of FSFI were accomplished, because of the differences of the language, so that the pregnant women understood the subjects. All the patients answered FSFI twice, in the same day, with two different interviewers, with an hour interval from one to other interview. After 7 to 14 days, the questionnaire was applied again in a second interview. Reliability (internal intra and interobserver consistence) and the validity of the constructo (to demonstrate that questionnaire measures the sexual function) were appraised. RESULTS: Cultural adaptations were necessary for us to obtain the final version. The internal intra-observer (alpha of Chronbach) consistence of the several domains oscillated from moderate to strong (0,791 to 0,911) and the interobserver consistence varied from 0,791 to 0,914. In the validation of the constructo, were obtained moderate correlations to fort among the final scores (general) of FSFI and of Female Sexual Quotient (QS-F) that has the capacity to evaluate the feminine sexual function. CONCLUSIONS: FSFI was adapted to the Portuguese language and to the Brazilian culture, presenting significant reliability and validity; it could be included and used in future studies of the Brazilian pregnant sexual function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):267-275
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500008
Sweeteners are frequently used by women of reproductive age. This is a narrative review about the sweeteners currently sold in the Brazilian commerce. There is a few information on the use of saccharin and cyclamates in pregnancy and their effects on the fetus. Due to the limited information available and their carcinogenic potential in animal species, saccharin and cyclamates should be avoided during pregnancy (risk C). Aspartame has been extensively studied in animals and it is considered safe for use during pregnancy (risk B), except by women homozygous for phenylketonuria (risk C). Sucralose and acessulfame-K are not toxic, carcinogenic or mutagenic in animals, but there are no controlled studies in humans. However, since these two sweeteners are not metabolized, it is unlikely that their use during pregnancy could be harmful (risk B). Stevia, a substance extracted from a native Brazilian plant, is innocuous in animal pregnancies, but there are no controlled studies in humans (risk B). Body agents found in the composition of artificial sweeteners (mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, erithrol, lactilol, isomalt, maltilol, lactose, fructose, maltodextrin, dextrin, and inverted sugar) are substances generally regarded as safe for human consumption. In conclusion, according to the currently available evidence, aspartame, sucralose, acessulfame-K and stevia can be safely used during pregnancy.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):253-259
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the insulin therapy protocol and its maternal and perinatal outcome in patients with clinical or gestational diabetes in a high risk reference service. METHODS: descriptive and prospective study including 103 pregnant women with gestational or clinical diabetes treated with insulin and attended by the reference service from October 2003 to December 2005. Gemellarity, miscarriages, unfinished prenatal care and deliveries not attended by the service were excluded. The gestational age at the beginning of the treatment, dosage, doses/day, increment of insulin (UI/kg), glycemic index (GI) and perinatal outcomes were compared. ANOVA, Fisher’s exact test and Goodman’s test considering p<0.05 were used. RESULTS: multiparity (92 versus 67.9%), pre-gestational body mass index (BMI) >25 kg/m² (88 versus 58.5%), weight gain (WG) <8 kg (36 versus 17%) and a high increment of insulin characterized the gestational diabetes. For the patients with clinical diabetes, despite the highest GI (120 mg/dL (39.2 versus 24%)) at the end of the gestational period, insulin therapy started earlier (47.2 versus 4%), lasted longer (56.6 versus 6%) and higher doses of insulin (92 versus 43 UI/day) were administered up to three times a day (54.7 versus 16%). Macrosomia was higher among newborns from the cohort of patients with gestational diabetes (16 versus 3.8%), being the only significant neonatal outcome. There were no neonatal deaths, except for one fetal death in the cohort of patients with clinical diabetes. There were no differences in the other neonatal complications in both cohorts, and most of the newborns were discharged from hospital up to seven days after delivery (46% versus 55.8%). CONCLUSIONS: the analysis of these two cohorts has shown differences in the insulin therapy protocol in quantity (UI/day), dosage (UI/kg weight) and number of doses/day, higher for the clinical diabetes cohort, and in the increment of insulin, higher for the gestational diabetes cohort. Indirectly, the quality of maternal glycemic control and the satisfactory perinatal outcome have proven that the treatment protocol was adequate and did not depend on the type of diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):99-104
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200007
Purpose: to study the actual conditions of medical assistance and types of delivery and factors contributing to their indication in Uberaba, MG. Method: the data of 4,294 puerperas who gave birth in the period from April 15, 1992 to April 14, 1993 in 7 maternities in Uberaba were studied. Results: it was seen that the Teaching Hospital had a greater participation in deliveries attending the younger population, probably the poorest and most unprepared regarding pregnancy. It was the only Hospital in which cesarean section rates were near those accepted by the who. Medical assistance in Uberaba was predominantly through Social Security (SUS), private health insurance and physicians representing a lower proportion. It was also verified that cesarean section frequency increased with age and type of medical assistance and the groups with private coverage presented a higher number of cesarean sections. Conclusion: it may be perhaps justified to consider the social factor as interfering with the indication of type of delivery.