Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):531-537
To analyze the internal consistency and the construct validity of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) State-Anxiety (S-Anxiety) scale for pregnant women during labor.
A study of measurement property including 150 pregnant women aged between 15 and 45 years old, during the first period of labor and with term pregnancies. The questionnaire used was the STAI S-Anxiety scale. In order to assess the internal consistency, Cronbach’s α was calculated through an exploratory factor analysis. The correlation between the factors was calculated using the Pearson coefficient. The state of significance used for this analysis was 0.05.
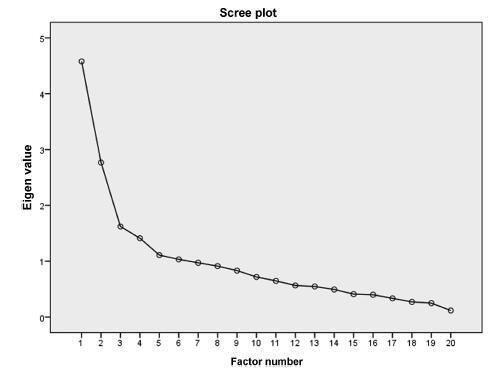
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in the context of labor showed two factors represented as the absence (factor 1) and the presence of anxiety (factor 2); item 4 (“I regret it”) did not show a representative value. Both factors showed high indications of Cronbach’s α, varying from 0.830 for factor 1, and 0.723 for factor 2. In the results of the Pearson coefficient between the two factors, a significant but weak correlation was observed (r = -0.188; p = 0.021).
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in pregnant women during labor presented appropriate values of internal consistency; however, item 3 did not show a significant factorial value. Therefore, this questionnaire must be applied cautiously and carefully without the use of the item 4 in the clinical practice and in researches about labor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):84-89
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200008
PURPOSES: To determine the prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in women with chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and its associated features; to determine whether IBS and CPP constitute the same syndrome. METHODS: Cross-sectional population survey with systematic sequential sampling according to census districts in which 1470 women were interviewed with respect to the sample calculation. The participants resided in their own homes, were at least 14 years of age, experienced menarche and presented CPP according to the American College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. The dependent variable was IBS based on Rome III criteria in women with CPP, and the following independent variables were possibly associated with IBS: age, schooling, duration of pain, sedentary lifestyle, migraine, depression, insomnia, back pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, depression, history of violence, and intestinal symptoms. The sample was subdivided into groups with and without IBS. After the descriptive analysis of the variables was performed, the respective frequencies were evaluated using GraphPad Prism 5 software. To evaluate the association between the dependent variable and the independent variables, the χ² test was used with a significance level of 5%. RESULTS: The prevalence of IBS in women with CPP was 19,5%. Pain duration (p=0.03), back pain (p=0.002), history of physical or sexual abuse (p=0.002), and intestinal complaints were more prevalent in the group with IBS and CPP. There was no difference between the groups regarding other criteria. CONCLUSION: The data confirmed the literature, identified several aspects that were shared between the pathologies and supported the hypothesis that both pathologies can constitute the same syndrome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(1):11-15
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000100003
PURPOSE: The present study examined the relationship between some clinical variables and quality of life in a group of patients with endometriosis. METHODS: A total of 130 women seen at a multidisciplinary center specializing in gynecology endometriosis in 2008 participated in the study. This was a cross-sectional study conducted with a convenience sample. The diagnosis of endometriosis was performed by biopsy according to the criteria of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. The clinical and demographic data were collected from the patients' records. Pain intensity was assessed by a visual numerical scale (0-10), and data on the quality of life were collected using the SF-36. Data analysis consisted of descriptive and inferential statistical tests, Spearman correlation coefficient and Kruskal-Wallis test to compare scores between groups. Nonparametric tests were used for analysis because data were not normally distributed. RESULTS: The patients were 21 to 54 years of age [ or = 34, standard diversion (SD)=6.56], 87% had a university degree, and 75% were married. Seventeen percent reported cases of endometriosis in the family. The average time of onset of symptoms was 4.5 years (SD=6.6), 63% of patients were in stage 3 or 4 of endometriosis 36% of patients had severe or disabling dysmenorrhea and the average intensity of pain according to a visual numerical scale was of 5.6 (SD=3.5). Results suggest that the staging of the disease did not determine the intensity of pain. The time of onset of symptoms also showed no relationship to pain intensity and SF-36 scores. On the other hand, the intensity of pain was associated with lower scores on some scales of the SF-36. CONCLUSION: Patients with endometriosis had lower scores of quality of life than the general population and lower than those of some other diseases.
or = 34, standard diversion (SD)=6.56], 87% had a university degree, and 75% were married. Seventeen percent reported cases of endometriosis in the family. The average time of onset of symptoms was 4.5 years (SD=6.6), 63% of patients were in stage 3 or 4 of endometriosis 36% of patients had severe or disabling dysmenorrhea and the average intensity of pain according to a visual numerical scale was of 5.6 (SD=3.5). Results suggest that the staging of the disease did not determine the intensity of pain. The time of onset of symptoms also showed no relationship to pain intensity and SF-36 scores. On the other hand, the intensity of pain was associated with lower scores on some scales of the SF-36. CONCLUSION: Patients with endometriosis had lower scores of quality of life than the general population and lower than those of some other diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(10):491-496
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001000004
PURPOSE: to evaluate painful sensitivity and factors involved in producing papillary fluid suitable for cytological analysis by means of automated collection. METHODS: we selected 50 asymptomatic women without a personal or family history of breast cancer, outside the pregnancy and childbirth cycle in order to collect papillary fluid by the automated system. We recorded and related to the production of papillary fluid patient age, smoking habit, previous breast surgery, parity, breastfeeding, menopausal status and age at menarche. All material collected was fixed in appropriate place, and sent separately for cytological analysis. The painful sensitivity of the collection procedure was assessed using the Borg Category-Ratio Scale (CR10 Scale). RESULTS: patient age ranged from 22 to 59 years, mean 41.6±8.6 years. Of the 50 patients, 20 (40%) showed no papillary fluid suitable for analysis in the breasts. In those patients from whom appropriate fluid was obtained for analysis of papillary cytology, parity was inversely related to the ability to obtain suitable cell samples with a level of statistical significance of p=0.035, OR=0.0032 (95%CI=0.0001-0.1388). Regarding soreness, the exam was well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS: the automated method of fluid collection for analysis of papillary cytology was well tolerated by the women; thus producing analyzable material in 60% of cases, a rate was inversely related to parity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):306-311
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000600007
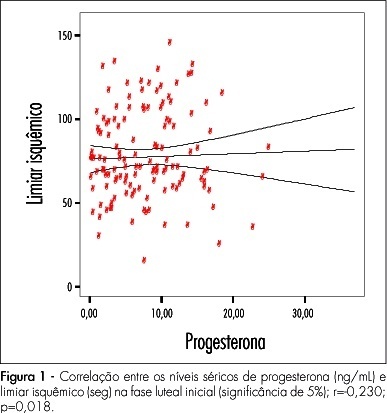
PURPOSE: to investigate the relationship between pain perception (experimental pain threshold and tolerance, in response to ischemia and pressure) in young and healthy young women and female sexual hormone seric levels (estradiol and progesterone). METHODS: 18 volunteers have participated of this study, during three consecutive menstrual cycles. A pressure algometer and a manual dynamometer have been used to measure painful responses to pressure and ischemia algesic stimuli. Blood has been collected for assessment of both hormonal and painful variables, during three menstrual cycles, whose characterization was based on daily oral temperature record, a diary of the menstrual cycles with the onset and end of each cycle, and on estradiol and progesterone plasmatic levels. The average for the algesic variables measured has been compared by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey-Kramer's post-test, among the menstrual cycle phases (follicular, periovulatory, early luteal, late luteal and menstrual). The Pearson's test has been used for correlation analysis between algesic and hormonal variables. Statistical significance has been defined as p<0.05. RESULTS: no significant change in pain parameters among the menstrual cycle phases has been observed. Nevertheless, there have been significant negative correlations between progesterone and ischemic threshold (r=-0.23; p<0.01), and pressure tolerance (r=-0.23; p<0.01) at the early luteal phase. CONCLUSIONS: these results indicate that the increase in progesterone levels correlates with a decrease of ischemic threshold and pressure tolerance, suggesting that progesterone plays a role in the pain modulation during the early luteal phase.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):25-30
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100005
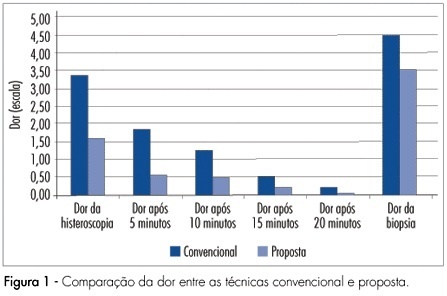
PURPOSE: to compare diagnostic hysteroscopy through vaginoscopy, using warm saline solution, with traditional technique, regarding to pain, patient satisfaction and feasibility of the procedure. METHODS: randomized clinical trial, involving 184 women, referred for diagnostic hysteroscopy, between May and December of 2006. Participants were randomized to be submitted to hysteroscopy by the proposed technique, which consisted of access through vaginoscopy using normal saline at 36ºC as distension medium, no speculum or cervical grasping, or by the traditional technique with CO2. In both techniques, a 2.7 mm hysteroscope was used. Pain was assessed by the analogical visual scale, during the procedure and every five minutes after it. RESULTS: the mean pain score was 1.60 in the proposed technique and 3.39 in the traditional technique (p<0.01). Lower pain scores were also observed after 5, 10 and 15 minutes (p<0,01) as well as after 20 minutes (p=0.056). In the proposed technique, 82.4% of the procedures were feasible, while, in the traditional technique, 84.9% were so (p=0.64). Satisfaction with the procedure was referred by 88.7% of women submitted to the proposed technique and by 76.3% of women submitted to the traditional technique (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: diagnostic hysteroscopy by the proposed technique resulted in less pain, same feasibility and greater satisfaction of patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):446-451
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of patients with the diagnosis of phantom breast syndrome or with phantom phenomena lonely. METHODS: it was conducted an observational, descriptive and sectional study enrolling 98 patients treated for breast cancer at Hospital São Marcos, Teresina (PI), Brazil. A standardized questionnaire was applied. RESULTS: the phantom breast syndrome was observed in 11.2% of the patients and phantom sensation alone was observed in 30% of the patients. The mean age of the patients was 54 years. Fifty-nine patients were married (60%) and 79.5% were analphabetic or had not concluded the high school. Emotional alterations were present in 67.4%, even though in 66.7% the libido was not changed after surgical procedure. As a relief factor of phantom pain, resting was cited by 90.9% of the patients, while physical exercises were mentioned to exacerbate the symptoms in 63.6% of the cases. The mean grade attributed to the pain in a 0 to 10 scale was 3, ranging from 1 to 7. Only 3% of the patients knew about the existence of this syndrome before the interviews. CONCLUSIONS: phantom phenomena are frequent in mastectomized patients, being necessary more studies to know about its characteristics and effects in these women's quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(4):221-226
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000400002
Purpose: to evaluate the relationdhip between preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve and pain sensitivity of the arm, total time of the surgery, and number of dissected nodes in patients submitted to axillary lymphadenectomy due to breast cancer. Methods: an intervention, prospective, randomized and double-blind study was performed on 85 patients assisted at the State University of Campinas, Brazil, from January 1999 to July 2000. The patients were divided into two groups, according to the intention of preserving or not the intercostobrachial nerve. The surgeries were performed by the same researchers, utilizing the same technique. The postoperative evaluations were performed within 2 days, 40 days and after 3 months. The pain sensitivity of the arm was evaluated through a specific questionnaire (subjective evaluation) and through a neurological physical examination (objective evaluation). Results: the surgical technique was applied to all patients and the preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve was related to a significant decrease in the alterations of pain sensitivity of the arm, both by the subjective and objective evaluations. After three months, in the subjective evaluation, 61% of the patients were asymptomatic in the intercostobrachial nerve preservation group and 28.6% in the nerve section group (p<0.01). By the objective evaluation, 53.7% of the patients presented normal neurological examination in the intercostobrachial nerve preservation group and 16.7% in the nerve section group (p<0.01). No significant difference was observed regarding total time of surgery (p=0.76) and number of dissected nodes between the two evaluated groups (p=0.59). Conclusions: these data show that the preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve is feasible and leads to a significant decrease in the alterations of pain sensitivity of the arm, without interfering in the total time of surgery and the number of dissected nodes.