Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):594-602
Adhesive capsulitis is a condition characterized by shoulder pain and stiffness. Breast cancer treatment has been linked to the development of this condition, but its mechanisms are still little known. This study's objective was to identify predictors factors associated with the development of adhesive capsulitis in breast cancer patients.
A case control study was performed with women undergoing treatment for breast cancer in a single center. The sampling was nonprobabilistic and consecutive. Adhesive capsulitis was defined as constant pain associated with decreased active and passive shoulder movement in anterior elevation, external rotation at 0°/90° abduction, and internal rotation at 90° abduction. The study group consisted of patients with shoulder pain and range of motion limitations, while the control group consisted of women without any shoulder abnormalities. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were collected. A univariate logistic regression was used to assess the influence of variables on the studied outcome. For p< 0.20, a multivariate logistic regression was used. The probability of null hypothesis rejection was 5%.
A total of 145 women were assessed, with 39 (26.9%) on the study group and 106 (73.1%) on the control group. The majority was under 60 years old. In the multivariate analysis, variables correlated to the outcome under study were shoulder immobilization (OR = 3.09; 95% CI: 1.33–7.18; p = 0.009), lymphedema (OR = 5.09; 95% CI: 1.81–14.35; p = 0.002), and obesity (OR = 3.91; 95% CI: 1.27–12.01; p = 0.017).
Lymphedema, postsurgery immobilization, and obesity are predictive factors for the development of adhesive capsulitis in breast cancer patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):88-96
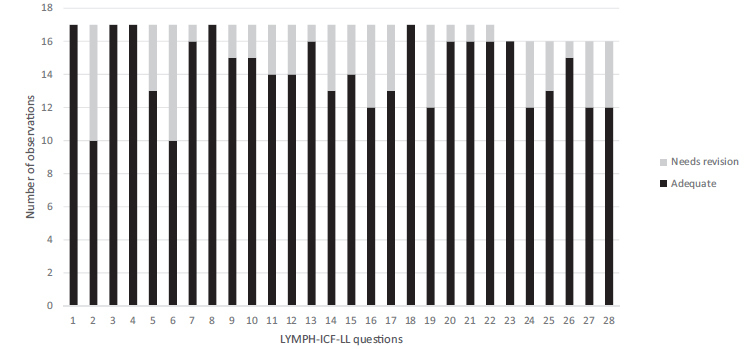
The objective of the study is to describe the process of translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Lymphoedema Functioning, Disability, and Health Questionnaire for Lower Limb Lymphoedema (Lymph-ICF-LL) into (Brazilian) Portuguese.
The process was comprised of five steps - translation, back translation, revision by an expert panel, pretest, and final translation. The first translation was performed by two professionals of the healthcare area, and the back translation was performed by two translators. An expert panel assessed the questions for semantics and idiomatic, cultural, and conceptual equivalence. The pretest was conducted on 10 patients with lymphedema.
Small differences were identified between the translated and back-translated versions, which were revised by the expert panel. The patients included in the pretest found 10 questions difficult to understand; these questions were reassessed by the same expert panel.
The results of the translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Lymph- ICF-LL resulted in a Brazilian Portuguese version, which still requires validation with various samples of the local population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):244-250
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005004
This study investigated short-term changes in body composition, handgrip strength, and presence of lymphedema in women who underwent breast cancer surgery.
Ninety-five women participated in a cross-sectional study, divided into two groups: Control (n=46), with healthy women, and Experimental (n=49), with women six months after breast cancer surgery . The Experimental Group was subdivided into right total mastectomy (RTM, n=15), left total mastectomy (LTM, n=11), right quadrant (RQ, n=13), and left quadrant (LQ, n=10). It was also redistributed among women with presence (n=10) or absence (n=39) of lymphedema. Presence of lymphedema, handgrip strength, and body composition were assessed.
Trunk lean mass and handgrip strength were decreased in the Experimental Group. Total lean mass was increased in the LTM compared to RTM or LQ. Left handgrip strength in LTM was decreased compared to RTM and RQ and in LQ compared to RTM and RQ. Finally, total lean mass, trunk fat mass, trunk lean mass, right and left arm lean mass were increased in women with lymphedema.
Breast cancer survivors have changes in their body composition and in handgrip strength six months after surgery; however, the interaction between the type of surgery and its impact is unclear. Furthermore, women who developed lymphedema in this period showed more significant changes in the body composition, but they were not enough to cause impairment in handgrip strength.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):171-177
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000400007
PURPOSE: To evaluate changes in the venous axillary-subclavian and lymphatic systems of women with lymphedema after axillary lymphadenectomy for breast cancer treatment. METHODS: This was a case series involving 11 women with unilateral upper limb lymphedema after axillary lymphedenectomy for the treatment of breast cancer. The study was carried out in the Mastology Program of the Clinical Hospital of the Federal University of Goiás, Goiânia, GO, during the period between March 2010 and March 2011. Doppler velocimetry ultrasonography was used to detect the presence of venous changes in the subclavian and axillary veins. Lymphatic changes were evaluated by lymphoscintigraphy in both upper limbs. Fisher's exact test was used for the comparison between limbs. RESULTS: Subclavian vein flow volume in the upper limb with lymphedema was significantly different from that in the contralateral limb (p<0.001), 54.6% of the women had increased flow. In the axillary vein, 45.4% had increased flow and 45.4% had decreased flow, with a statistically significant difference (p<0.01) between limbs. Compared to the contralateral limb, significant lymphatic changes (p<0.05) were also found in the vessel route (not visualized), number of lymphatic vessels (none), axillary lymph nodes (absent) and dermal reflux (present). In the contralateral upper limb without lymphedema, no venous or lymphatic alterations were encountered. CONCLUSION: The women subjected to axillary lymphadenectomy for the treatment of breast cancer presented both venous and lymphatic changes in the upper limb with lymphedema.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):75-80
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200004
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of lymphedema and its associated factors in breast cancer patients. METHODS: Two hundred and fifty women that had undergone more than six months of breast cancer treatment and were being treated at an oncology reference hospital in Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil. They were interviewed and submitted to physical evaluation. Data from the patients' medical records regarding the treatment of breast cancer, the extent of axillary intervention and the tumor were analyzed. Lymphedema was diagnosed when the difference between both upper limbs was 2 cm or more by perimetry. The groups of women with and without lymphedema were compared regarding the possible risk factors, and central tendency, dispersion, and prevalence were measured, with a significance level of 95%. RESULTS: One hundred and twelve women (44.8%) presented lymphedema. A significant difference was found between the groups of women with and without lymphedema regarding the median numbers of removed lymph nodes (p=0.02); presentation of superficial lymphatic thrombosis in the arm ipsilateral to the surgery (p<0.01); local application of radiotherapy, use of chemotherapy (p<0.01 for both); removal of the cuticles of the ipsilateral hand with pliers, and weightlifting after the treatment (p<0.01 and p=0.05, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: the association between lymphedema and the mentioned factors requires an interdisciplinary approach to this condition. It is of paramount importance that health teams and patients become aware of the prevention and treatment of lymphedema, a condition often undervalued.