Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo91
12-04-2024
The average age of patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) has been reported to have declined. Human papilloma virus (HPV)-related lesions have been shown to be associated with the expression of the immunohistochemical (IHC) marker p16. Non-HPV-related tumors have been characterized by p53 abnormal expression and PDL1 expression. We aimed to evaluate the correlation between these markers and vulvar SCC and to relate it to the clinical and pathological characteristics.
Histopathologic assessments and IHC analyses of p16, p53, and PDL1 were performed in 41 samples of vulvar SCC collected between 2016 and 2021. The data were correlated with clinical and pathological characteristics of the patients.
The mean age of the patients was 72.1 years. Positive p16 and PDL1 staining was detected in 24.4% and 17.1% of the samples, respectively. p53 expression was negative in 19.5% of the samples, whereas it was overexpressed in 24.4%. p16-positive tumors showed a smaller depth of invasion (DOI) (p = 0.014), while tumors with p53 abnormal expression showed greater DOI (p = 0.041). PDL1 expression was correlated with increased number of inflammatory cells (p = 0.055). In addition, lesions with lymphovascular space invasion were p16-negative.
In our sample, regarding to the SCC incidence the patients’ mean age did not change. The expression of p16 was inversely correlated with p53 results. Tumors with p53 abnormal expression and absence of p16 showed a greater DOI. Our data suggest an association between PDL1 expression and increased inflammatory infiltrates in vulvar SCC.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo61
07-26-2024
Endometrial cancer (EC) is a heterogeneous disease with recurrence rates ranging from 15 to 20%. The discrimination of cases with a worse prognosis aims, in part, to reduce the length of surgical staging in cases with a better prognosis. This study aimed to evaluate the association between Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3) expression and prognostic and morphological factors in EC.
This retrospective, cross-sectional, analytical study included 79 EC patients - 70 endometrioid carcinoma (EEC) and 9 serous carcinoma (SC) - and 74 benign endometrium controls. IMP3 expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry-based TMA (Tissue Microarray), and the results were associated with morphological and prognostic factors, including claudins 3 and 4, estrogen and progesterone receptors, TP53, and KI67.
IMP3 expression was significantly higher in SC compared to EEC in both extent (p<0.001) and intensity (p=0.044). It was also significantly associated with worse prognostic factors, including degree of differentiation (p=0.024, p<0.001), staging (p<0.001; p<0.001) and metastasis (p=0.002; p<0.001). IMP3 expression was also significant in extent (p=0.002) in endometrial tumors compared with controls. In addition, protein TP53 and KI67 showed significant associations in extent and intensity, respectively.
IMP3 expression was associated with worse prognostic factors studied. These findings suggest that IMP3 may be a potential biomarker for EC poorer prognosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo31
04-09-2024
To compare Transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1) expression in patients with and without adenomyosis.
A prospective design was performed including 49 patients submitted to hysterectomy. Immunohistochemistry was performed on anatomopathological samples staged in paraffin blocks from patients with and without adenomyosis. The sample contained 28 adenomyosis cases and 21 controls. Student's t-test and multivariate logistic regression tests were used for statistical analysis. Associations were considered significant at p < 0.05.
We found no significant association between adenomyosis and: smoking (p = 0.75), miscarriage (p = 0.29), number of previous pregnancies (p = 0.85), curettage (p = 0.81), pelvic pain (p = 0.72) and myoma (p = 0.15). However, we did find a relationship between adenomyosis and abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) (p = 0.02) and previous cesarean section (p = 0.02). The mean TGF-β1 intensity (mean ± SD) in the ectopic endometrium of women with adenomyosis showed no significant association (184.17 ± 9.4 vs.184.66 ± 16.08, p = 0.86) from the topic endometrium of women without adenomyosis.
TGF-β1 expression was not increased in the ectopic endometrium of women with adenomyosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):609-619
12-11-2023
To investigate the clinicopathological significance and prognosis of the expression of the anterior gradient 3 (AGR3) protein in women with breast cancer.
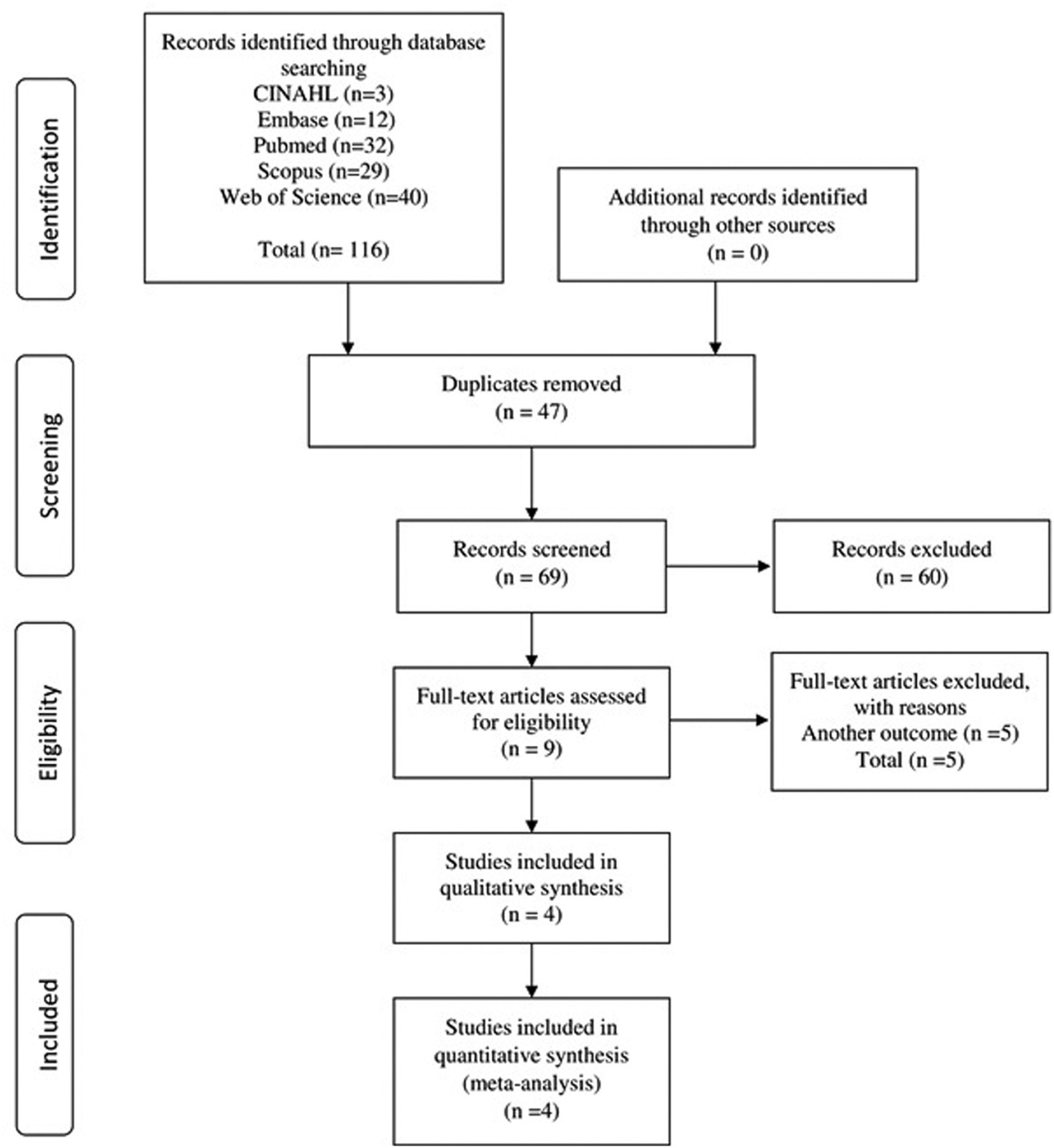
The PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were searched for studies published in English and without restrictions regarding the year of publication. The search terms were: breast cancer AND anterior gradient 3 OR AGR3 expression.
We included observational or interventional studies, studies on AGR3 protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and studies on invasive breast cancer. Case reports, studies with animals, and reviews were excluded. In total, 4 studies were included, containing 713 cases of breast cancer.
Data were extracted on clinicopathological characteristics and survival. A meta-analysis of the prevalence of AGR3 expression was performed according to the clinicopathological characteristics, hazard ratios (HRs), and overall survival and disease-free survival.
The expression of AGR3 was found in 62% of the cases, and it was associated with histological grade II, positivity of estrogen and progesterone receptors, low expression of ki67, recurrence or distant metastasis, and lumen subtypes. In patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 expression was associated with worse overall survival (HR: 2.39; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.628–4.159; p = 0.008) and worse disease-free survival (HR: 3.856; 95%CI: 1.026–6.686; p = 0.008).
The AGR3 protein may be a biomarker for the early detection of breast cancer and predict prognosis in luminal subtypes. In addition, in patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 protein expression may indicate an unfavorable prognosis in relation to survival.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):535-541
10-30-2023
Breast cancer (BC) biomarkers, such as hormone receptors expression, are crucial to guide therapy in BC patients. Antiandrogens have been studied in BC; however, limited data are available on androgen receptor (AR) expression test methodology. We aim to report the core needle biopsy (CNB) accuracy for AR expression in BC.
Patients diagnosed with stage I-III invasive BC from a single institution were included. Androgen receptor expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) using 1 and 10% cutoff and the AR expression in surgical specimens (SS) was the gold standard. Kappa coefficients were used to evaluate the intraprocedural agreement.
A total of 72 patients were included, with a mean age of 61 years old and 84% were Luminal A or B tumors. The prevalence of AR expression in all BC samples was 87.5% using a cutoff ≥ 10% in SS. With a cutoff value ≥ 1%, CNB had an accuracy of 95.8% (Kappa value = 0.645; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.272–1.000; p < 0.001) and 86.1% (Kappa value = 0.365; 95% CI: 0.052–0.679; p < 0.001) when ≥ 10% cutoff was used for AR positivity. Androgen receptor expression in CNB (cutoff ≥ 1%) had a sensitivity of 98.5%, specificity of 60%, positive predictive value of 97.0%, and a negative predictive value of 76.9% in the detection of AR expression in SS.
Core needle biopsy has good accuracy in evaluating AR expression in BC. The accuracy of CNB decreases with higher cutoff values for AR positivity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):761-770
04-25-2022
The study aimed to characterize the clinical, histological, and immunohistochemical profile of women with invasive breast cancer, according to the risk for Hereditary Predisposition Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome in a Brazilian population.
This is a retrospective study performed from a hospital-based cohort of 522 women, diagnosed with breast cancer treated at an oncology referral center in the Southeast region of Brazil, between 2014 and 2016.
Among the 430 women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer who composed the study population, 127 (29.5%) were classified as at increased risk for hereditary predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. There was a lower level of education in patients at increased risk (34.6%) when compared with those at usual risk (46.0%). Regarding tumor characteristics, women at increased risk had higher percentages of the disease diagnosed at an advanced stage (32.3%), and with tumors > 2cm (63.0%), with increased prevalence for both characteristics, when compared with those at usual risk. Furthermore, we found higher percentages of HG3 (43.3%) and Ki-67 ≥ 25% (64.6%) in women at increased risk, with prevalence being about twice as high in this group. The presence of triple-negative tumors was observed as 25.2% in women at increased risk and 6.0% in women at usual risk, with the prevalence of absence of biomarkers being 2.5 times higher among women in the increased risk group.
From the clinical criteria routinely used in the diagnosis of breast cancer, the care practice of genetic counseling for patients at increased risk of hereditary breast cancer in contexts such as Brazil is still scarce.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):820-828
01-11-2020
To evaluate the distribution of the main sociodemographic and clinicalpathological characteristics in women with breast cancer according to the molecular profile by immunohistochemistry.
A cross-sectional, retrospective, analytical and quantitative study was performed, with an analysis of 137 medical records from January 2015 to December 2018 of women attending the High Complexity in Oncology Unit of the city of Imperatriz, state of Maranhão, Brazil. The immunohistochemical profile of tumors based on the estrogen and progesterone receptor, Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor-type 2 (HER2) overexpression and Ki67 cell proliferation indexwas defined, fromwhich six molecular subtypes were determined: luminal A, luminal B-HER2 negative, luminal B-HER2 positive, triple negative, overexpression of HER2 and inconclusive.
A total of 52.6% of the patients were postmenopausal, mean age 52.1 years old, brown (56.2%), had a schooling level < 9 years (40%), staging > IIB (52.6%) and 23.4% hadmetastasis. Invasive ductal carcinoma accounted for 84.7%, tumor size was 2 to 5 cm (48.9%), with lymph node involvement (56.2%), axillary lymphadenectomy in 67.2%, andmastectomy in 73.7% of the patients. Themost frequentmolecular subtype was the luminal B-HER2 negative (36.5%), and the luminal A subtype showed characteristics of better prognosis when compared with the others.
It was concluded that in the association of molecular subtypes with sociodemographic and clinical-pathological characteristics, there were no statistically significant results obtained, except for complementary therapy, referring to hormone therapy, and there was a high index of metastasis at diagnosis, which was a worrying factor and indicative of failures in the screening and early diagnosis of this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):79-85
02-01-2018
The current study evaluated the expression of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX), its association with clinicopathological features and with p53, Ki-67 (cell proliferation) and CD31 (angiogenesis) expression in patients with invasive cervical squamous cell carcinoma (ICSCC). To the best of our knowledge, no other study has evaluated this association.
Women with IB stage-ICSCC (n = 20) and women with uterine leiomyoma (n = 20) were prospectively evaluated. Patients with ICSCC were submitted to type BC1 radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. Patients in the control group underwent vaginal hysterectomy. Tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation and protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry studies.
The WWOX expression was significantly lower in the tumor compared with the expression in thebenign cervix (p = 0.019). TheWWOXexpressionwas inversely associated with the CD31 expression in the tumor samples (p = 0.018). There was no association betweentheWWOXexpression with the p53 expression (p = 0.464)or the Ki-67expression (p = 0.360) in the samples of invasive carcinoma of the cervix. There was no association between the WWOX expression and tumor size (p = 0.156), grade of differentiation (p = 0.914), presence of lymphatic vascular invasion (p = 0.155), parametrium involvement (p = 0.421) or pelvic lymph node metastasis (p = 0.310) in ICSCC tissue samples.
The results suggested that WWOX may be involved in ICSCC carcinogenesis, and this marker was associated with tumor angiogenesis.