-
Artigos Originais
Obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors during pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):449-455
10-03-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisObesity and cardiometabolic risk factors during pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):449-455
10-03-2014DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004946
Views132See morePURPOSE:
To assess cardiometabolic risk factors during normal pregnancy and the influence of maternal obesity on them.
METHODS:
This study included 25 healthy pregnant women with a single pregnancy and a gestational age of less than twenty weeks. Longitudinal analysis of blood pressure, body weight, body mass index (BMI), serum concentrations of leptin, adiponectin, cortisol, total cholesterol and fractions, triglycerides, uric acid, fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, HOMA-IR and insulin/glucose ratio was performed each trimester during pregnancy. In order to evaluate the impact of obesity, pregnant women were divided into two groups based on BMI for the first quarter of pregnancy: Gpn for pregnant women with BMI<25 kg/m2 and Gso for BMI≥25 kg/m2. One-Way ANOVA for repeated measurements or Friedman test and Student-t or Mann-Whitney tests for statistical comparisons and Pearson correlations test were used for statistical analysis.
RESULTS:
The mean values for the first quarter of pregnancy for the following parameters were: age: 22 years; weight: 66.3 kg and BMI 26.4 kg/m2, with 20.2 and 30.7 kg/m2 for the Gpn and Gso groups, respectively. Mean weight gain during pregnancy was ±12.7 kg with 10.3 kg for the Gso group and 15.2 kg for the Gpn group. Regarding plasma determinations, cortisol, uric acid and lipid profile increased during all trimesters of pregnancy, except for HDL-cholesterol, which did not change. Blood pressure, insulin and HOMA-IR only increased in the third quarter of pregnancy. The Gso group tended to gain more weight and to show higher concentrations of leptin, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, VLDL-cholesterol, TG, glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, besides lower HDL-cholesterol and greater diastolic blood pressure in the 3rdquarter of pregnancy. Three pregnant women developed gestational hypertension, presented prepregnancy obesity, excessive weight gain, hyperleptinemia and an insulin/glucose ratio greater than two. Weight and BMI were positively correlated with total cholesterol and its LDL fraction, TG, uric acid, fasting blood glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR; and were negatively correlated with adiponectin and HDL-cholesterol. Leptin level was positively correlated with blood pressure.
CONCLUSIONS:
The metabolic changes in pregnancy are more significant in obese women, suggesting, as expected, an increased risk of cardiometabolic complications. During their first visit for prenatal care, obese women should be informed about these risks, have their BMI and insulin/glucose ratio calculated along with their lipid profile to identify pregnant women at higher risk for cardiovascular diseases.
-
Artigos Originais
Factors associated with the onset of hypertension in women of 50 years of age or more in a city in Southeastern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):467-472
10-03-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFactors associated with the onset of hypertension in women of 50 years of age or more in a city in Southeastern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):467-472
10-03-2014DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005094
Views51See morePURPOSE:
To evaluate factors associated with hypertension in Brazilian women of 50 years of age or more.
METHODS:
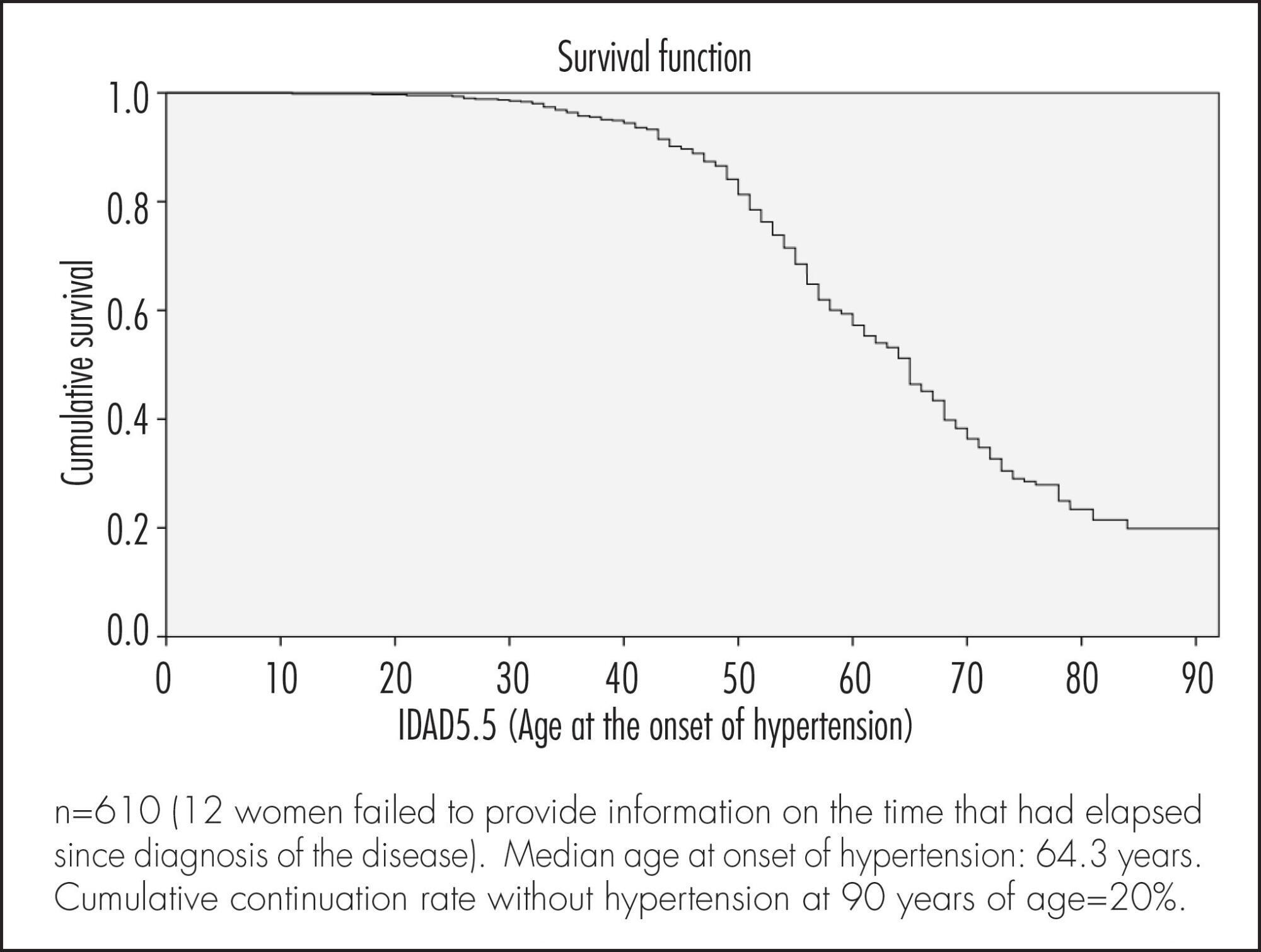
A cross-sectional population based study using self-reports. A total of 622 women were included. The association between sociodemographic, clinical and behavioral factors and the woman's age at the onset of hypertension was evaluated. Data were analyzed according to cumulative continuation rates without hypertension, using the life-table method and considering annual intervals. Next, a Cox multiple regression analysis model was adjusted to analyze the occurrence rates of hypertension according to various predictor variables. Significance level was pre-established at 5% (95% confidence level) and the sampling plan (primary sampling unit) was taken into consideration.
RESULTS:
Median age at onset of hypertension was 64.3 years. Cumulative continuation rate without hypertension at 90 years was 20%. Higher body mass index (BMI) at 20–30 years of age was associated with a higher cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient=0.078; p<0.001). Being white was associated with a lower cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient= -0.439; p=0.003), while smoking >15 cigarettes/day was associated with a higher rate over time (coefficient=0.485; p=0.004).
CONCLUSION:
The results of the present study highlight the importance of weight control in young adulthood and of avoiding smoking in preventing hypertension in women aged ≥50 years.
-
Artigos Originais
Factors associated with mode of delivery in women with pre-eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):259-263
06-01-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFactors associated with mode of delivery in women with pre-eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):259-263
06-01-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004812
Views60See morePURPOSE:
To analyze the factors related to route of delivery in patients with pre-eclampsia.
METHODS:
A retrospective analytical study was conducted from January 2009 to January 2011, during which 250 medical records of patients diagnosed with pre-eclampsia who gave birth to live fetuses with a gestational age of 28 weeks or more were selected. The variables evaluated were: maternal age (19 years, 20−34 years and over 35 full years), gestational age at delivery (28−37 weeks and more than 37 weeks), parity (primiparous or multiparous), previous cesarean section, history of pre-eclampsia or chronic hypertension, current diagnosis of mild or severe pre-eclampsia, and birth weight of the newborn. The information was transcribed to a questionnaire based on the variables being investigated. The chi-square test was applied to identify the relationship between the variables, with the level of significance set at p<0.05, and the Odds Ratio (OR) was calculated only for the variables showing a statistically significant difference in order to determine the odds for the patient to be submitted to a cesarean section.
RESULTS:
In this study, we observed a 78.4% rate of cesarean delivery, with 54.1% of the patients submitted to the procedure having a gestational age of 28 to 37 weeks (OR=3.1; p<0.01). Patients with a history of pre-eclampsia were 2.5 times more likely to have cesarean delivery (OR=2.5; p<0.02). All patients who had had a previous cesarean were submitted to cesarean delivery in the current pregnancy (p<0.01). Pregnant women with severe pre-eclampsia were 3.3 times more likely to progress to cesarean delivery than those with mild pre-eclampsia (OR=3.3; p<0.01).
CONCLUSION:
After individual analysis, only gestational age and a diagnosis of severe pre-eclampsia showed significant differences, representing risk factors for this type of delivery.
-
Artigos Originais
Cardiovascular risk in middle-aged breast cancer survivors: a comparison between two risk models
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):157-162
03-25-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCardiovascular risk in middle-aged breast cancer survivors: a comparison between two risk models
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):157-162
03-25-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0002
Views76PURPOSE:
It was to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in breast cancer survivors (BCS).
METHODS:
This cross-sectional study analyzed 67 BCS, aged 45 -65 years, who underwent complete oncological treatment, but had not received hormone therapy, tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors during the previous 6 months. Lipid profile and CVD risk were evaluated, the latter using the Framingham and Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) models. The agreement between cardiovascular risk models was analyzed by calculating a kappa coefficient and its 95% confidence interval (CI).
RESULTS:
Mean subject age was 53.2±6.0 years, with rates of obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia of 25, 34 and 90%, respectively. The most frequent lipid abnormalities were high total cholesterol (70%), high LDL-C (51%) and high non-HDL-C (48%) concentrations. Based on the Framingham score, 22% of the participants had a high risk for coronary artery disease. According to the SCORE model, 100 and 93% of the participants were at low risk for fatal CVD in populations at low and high risk, respectively, for CVD. The agreement between the Framingham and SCORE risk models was poor (kappa: 0.1; 95%CI 0.01 -0.2) for populations at high risk for CVD.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings indicate the need to include lipid profile and CVD risk assessment in the follow-up of BCS, focusing on adequate control of serum lipid concentrations.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsCardiovascular diseasesCoronary artery diseaseDyslipidemiasHypertensionModels, cardiovascularRadiotherapySee more -
Artigos Originais
Maternal and perinatal outcomes in women with decreased amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):342-348
10-10-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMaternal and perinatal outcomes in women with decreased amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):342-348
10-10-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000800002
Views100PURPOSE: To determine maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnant women with low amniotic fluid, according to the amniotic fluid index (AFI). METHODS: A cohort study conducted on 176 patients admitted to the high risk ward of Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira (IMIP), in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil. Amniotic fluid was measured by the amniotic fluid index, and classified as low when between 5.1 and 7.9 cm, moderate oligohydramnios between 3.1 and 5.0 cm, and severe oligohydramnios when less than or equal to 3.0 cm. To determine the difference between the three groups of categorical variables studied the chi-square and Fisher exact tests were used, when applicable, and for the numerical variables the Mann-Whitney test was applied, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Fetal malformation more frequently occurred when oligohydramnios was severe. Hypertensive disorders, however, were associated with moderate oligohydramnios. There was similarity between the three groups in relation to premature rupture of membranes and other causes. Low amniotic fluid was more frequently diagnosed when tested at the gestational age of 32 weeks or earlier. Regarding the perinatal outcomes, the incidence of Apgar score <7 in the 1st and 5th minutes, perinatal death, neonatal jaundice and pulmonary hypoplasia was higher when oligohydramnios was moderate to severe. CONCLUSIONS: Maternal and perinatal causes and outcomes in pregnant women with low amniotic fluid vary with respect to their AFI, severe oligohydramnios being associated with fetal malformation and other adverse perinatal outcomes.
Key-words Amniotic fluidFetal membranes, premature ruptureHypertensionOligohydramniosPrenatal ultrasonographySee more -
Artigos Originais
Changes of blood flow in the umbilical artery in hypertensive pregnancy and the implications in the neonatal outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):71-77
02-07-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisChanges of blood flow in the umbilical artery in hypertensive pregnancy and the implications in the neonatal outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):71-77
02-07-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200006
Views76PURPOSE: To evaluate the anthropometric characteristics of morbidity and mortality of premature newborns (NB) of hypertensive mothers according to the presence or absence of flow (DZ) or reverse (DR) diastolic flow in the dopplervelocimetry of the umbilical artery. METHODS: A prospective study was conducted on preterm newborns of pregnant women with hypertension between 25 and 33 weeks of gestational age, submitted to umbilical artery Doppler study during the five days before delivery. Delivery occurred at Hospital Regional da Asa Sul, Brasília - Federal District, between November 1st, 2009 and October 31st, 2010. The infants were stratified into two groups according to the results of Doppler velocimetry: Gdz/dr=absent end-diastolic velocity waveform or reversed end-diastolic velocity waveform, and Gn=normal Doppler velocimetry. Anthropometric measurements at birth, neonatal morbidity, and mortality were compared between the two groups. RESULTS: We studied 92 infants, as follows: Gdz/dr=52 infants and Gn=40 infants. In Gdz/dr, the incidence of infants small for gestational age was significantly greater, with a relative risk of 2.5 (95%CI 1.7 - 3.7). In Gdz/dr, infants remained on mechanical ventilation for a longer time: median 2 (0‒28) and Gn median 0.5 (0‒25) p=0.03. The need for oxygen at 28 days was higher in G dz/dr comparing to Gn (33 versus 10%; p=0.01). Neonatal mortality was higher in Gdz/dr compared to Gn (36 versus 10%; p=0.03; relative risk of 1.6; 95%CI 1.2‒2.2). Logistic regression showed that, with each 100 grams lower birth weight, the chance of death increased 6.7 times in G dz/dr (95%CI 2.0 - 11.3; p<0.01). CONCLUSION: In preterm infants of mothers with hypertensive changes in Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery, intrauterine growth restriction and neonatal prognosis are often worse, with a high risk of death related to birth weight.
Key-words Blood flow velocityDopplerFetal mortalityHypertensionInfant, newbornInfant, prematureLaser-doppler fluxometrypregnancy inducedPregnancy outcomeUltrasonographyUmbilical arteriesSee more -
Artigos Originais
Morbidity and associated factors in climacteric women: a population based study in women with 11 or more years of formal education
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):215-220
05-11-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMorbidity and associated factors in climacteric women: a population based study in women with 11 or more years of formal education
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):215-220
05-11-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000500005
Views57PURPOSE: To evaluate factors associated with morbidities among Brazilian women aged 40-65 years and with 11 or more years of schooling. METHODS: A secondary analysis of a cross-sectional population-based study was conducted, using an anonymous self-report questionnaire completed by 377 women. Were evaluated, with this instrument, some morbidities (hypertension, diabetes, insomnia and depression) and sociodemographic, behavioral, clinical and reproductive factors. The association between morbidities and independent variables was evaluated by the Χ2 test. Multiple logistic regression analysis with stepwise selection criteria was used to select the major factors associated with morbid conditions. RESULTS: In the multiple regression analysis, insomnia was associated with bad/fair self-perception of health (OR=2.3) and nervousness (OR=5.1). Depression was associated with bad/fair self-perception of health (OR=3.7) and bad/poor leisure (OR=2.8). Hypertension was associated with obesity (OR=3.1) and being in postmenopausal (OR=2.6). Diabetes was associated with age above 50 years (OR=3.9) and obesity (OR=12.5). CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of morbidities was high and a worse self-perception of health and obesity were the main factors associated with morbidity.
Key-words AgingDepressionDiabetes mellitusHypertensionMenopauseSleep initiation and maintenance disordersSee more -
Artigos Originais
Genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor in pre-eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(7):158-163
10-11-2011
Summary
Artigos OriginaisGenetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor in pre-eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(7):158-163
10-11-2011DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000700007
Views54See morePURPOSE: To identify genetic polymorphisms of endothelial growth factor (VEGF), positions +936C/T and -2578C/A, in women with pre-eclampsia. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study conducted on 80 women divided into two groups: pre-eclampsia and control. The sample was characterized using a pre-structured interview and data transcribed from the medical records. DNA extraction, amplification of sequences by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) with specific primers and polymorphism analysis of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) were performed to identify polymorphisms. The statistical analysis was performedin a descriptive manner and using the
 test. The multiple logistic regression model was used to determine the effect of polymorphisms on pre-eclampsia. RESULTS:Ahigher frequency of the T allele of theVEGF +936C/T polymorphism was observedin patients with pre-eclampsia, but with no significant difference. The presence of allele A of the VEGF -2578C/A was significantly higher in the control group. CONCLUSIONS:No significant association was observed between VEGF +936C/Tpolymorphism andpre-eclampsia. For the VEGF -2578C/A polymorphism a significant differencewas observed between thecontrol and pre-eclampsia group, with allele A being the most frequent in the control, suggesting the possibility that carriers of allele A have lower susceptibility to the development of pre-eclampsia.
test. The multiple logistic regression model was used to determine the effect of polymorphisms on pre-eclampsia. RESULTS:Ahigher frequency of the T allele of theVEGF +936C/T polymorphism was observedin patients with pre-eclampsia, but with no significant difference. The presence of allele A of the VEGF -2578C/A was significantly higher in the control group. CONCLUSIONS:No significant association was observed between VEGF +936C/Tpolymorphism andpre-eclampsia. For the VEGF -2578C/A polymorphism a significant differencewas observed between thecontrol and pre-eclampsia group, with allele A being the most frequent in the control, suggesting the possibility that carriers of allele A have lower susceptibility to the development of pre-eclampsia.


