Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):142-148
To understand the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinical pregnancy rates and analyze factors that may have influenced their outcome.
This was a retrospective observational study conducted at a tertiary-care Brazilian fertility center. All fresh IVF and embryo warming cycles performed from March 11 to December 31, 2018–2021 were analyzed, and their data were used to calculate fertilization, embryo cleavage, cycle cancellation, embryo transfer (ET), and clinical pregnancy rates. Statistical tests were used to evaluate the alterations found. Logistic regression models were used to explore the association of the categorical variables with the observed clinical pregnancy rates. Data from 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and 2020 and 2021 (pandemic) were grouped.
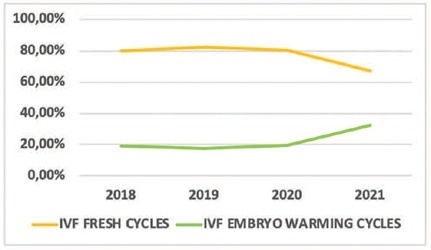
A total of 756 cycles were analyzed (n = 360 prepandemic and n = 396 pandemic). The age group of the patients, fertilization rates, and cleavage rates did not have significant differences (p > 0.05). There was a reduction in the percentage of fresh IVF and an increase in embryo warming cycles (p = 0.005) during the pandemic. There was also an increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001) and a reduction in ET rates (p < 0.001). The pandemic had a negative impact on clinical pregnancy rates (p < 0.001) especially due to the increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001).
Embryo warming cycles with subsequent frozen-thawed ET were presented as a viable alternative to continue assisted reproductive treatments against pandemic restrictions on fresh cycles, ensuring clinical pregnancy, albeit at a lower rate than that of the prepandemic period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Surrogacy is the process in which a woman carries and delivers a baby to other person or couple, known as intended parents. When carriers are paid for surrogacy, this is known as commercial surrogacy. The objective of the present work is to review the legal, ethical, social, and cultural aspects of commercial surrogacy, as well as the current panorama worldwide.
This is a review of the literature published in the 21st century on commercial surrogacy.
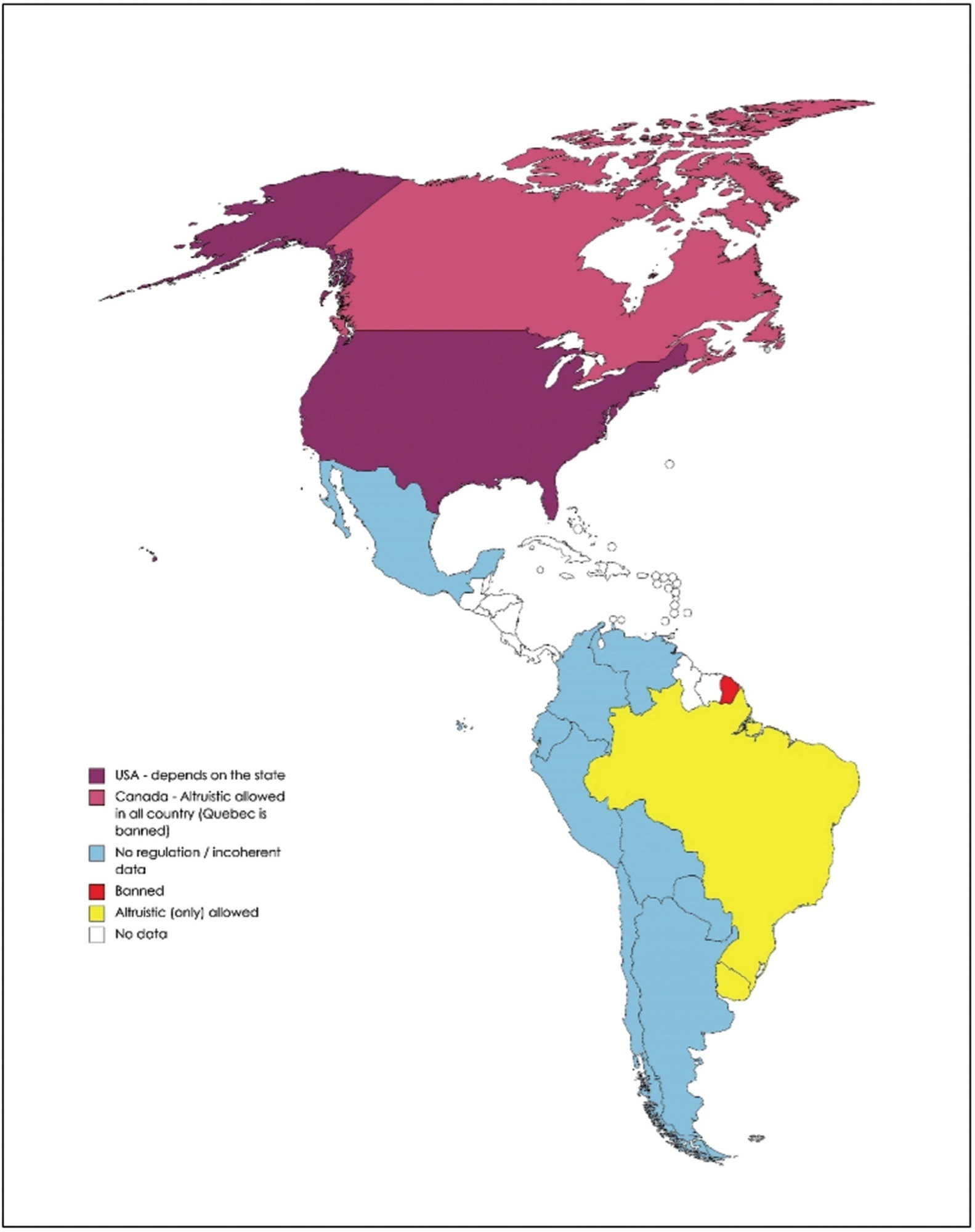
A total of 248 articles were included as the core of the present review. The demand for surrogate treatments by women without uterus or with important uterine disorders, single men and same-sex male couples is constantly increasing worldwide. This reproductive treatment has important ethical dilemmas. In addition, legislation defers widely worldwide and is in constant change. Therefore, patients look more and more for treatments abroad, which can lead to important legal problems between countries with different laws. Commercial surrogacy is practiced in several countries, in most of which there is no specific legislation. Some countries have taken restrictive measures against this technique because of reports of exploitation of carriers.
Commercial surrogacy is a common practice, despite important ethical and legal dilemmas. As a consequence of diverse national legislations, patients frequently resort to international commercial surrogacy programs. As of today, there is no standard international legal context, and this practice remains largely unregulated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):660-666
The present study aims to describe the main characteristics of female couples resorting to a fertility clinic, to understand whether these patients have clear previous plans concerning procreation and how they end up completing their family planning, and to briefly describe the main outcomes of the recepción de ovocitos de pareja (ROPA, in the Spanish acronym: in English, reception of partner's oocytes) method.
This is a descriptive retrospective study of the pathway and outcomes of female couples in a fertility clinic during a 2-year period.
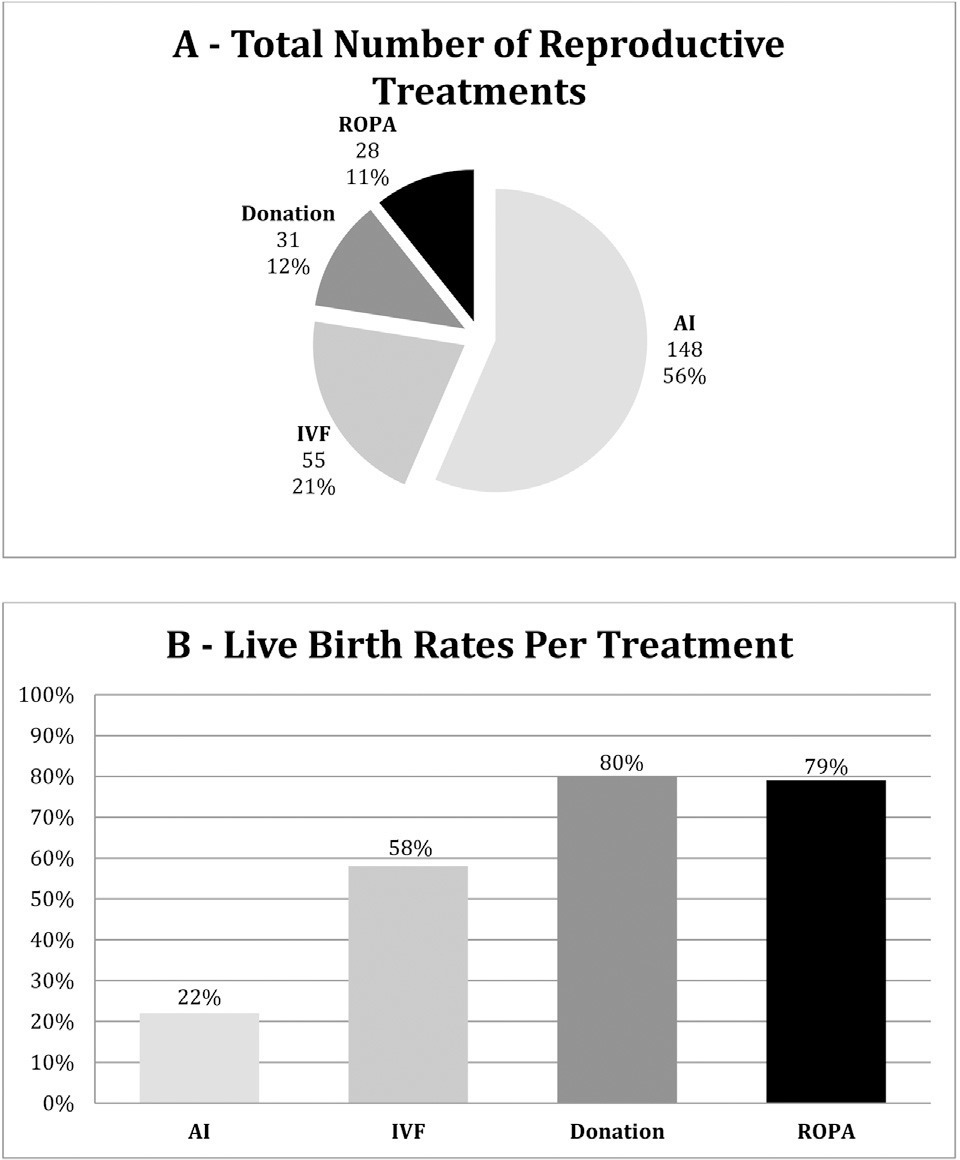
A total of 129 couples were treated. Only one third of the couples had no condition potentially affecting fertility or advanced age. Most couples were decided to undergo artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization and the majority kept their plans, as opposed to 38% of the couples who decided to the ROPA method (lesbian shared in vitro fertilization) who changed plans. Live birth rates per treatment (including frozen embryo transfers) for artificial insemination, 58% for in vitro fertilization, 80% for treatments with donated oocytes or embryos, and 79% for ROPA. Four in five couples achieved live births.
The present study highlights the importance of a thorough medical workup in same-sex couples resorting to assisted reproduction. Despite the higher-than-expected rates of fertility disorders, the outcomes were good. Most couples end up in a single parented method. Furthermore, the results of the ROPA method are reassuring.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):216-219
To evaluate the seroprevalence of positive markers for syphilis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) I and II, human T cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) I and II, and hepatitis B and C among women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
We conducted a retrospective analysis among patients who underwent IVF, between January 2013 and February 2016, and who had complete screening records.
We analyzed 1,008 patients who underwent IVF, amounting to 2,445 cycles. Two patients (0.2%) tested positive for HIV I and II and none for HTLV I and II. Three patients (0.3%) had positive screening for syphilis, and two (0.2%) had positive hepatitis C antibody test (anti-HCV). A positive hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HbsAg) test was observed in 4 patients (0.4%), while 47 (4.7%) patients were positive for IgG antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgG), and only 1 (0.1%) was positive for IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HbC IgM). The anti-HbS test was negative in 659 patients (65.3%). Only 34.7% of the patients had immunity against the Hepatitis B virus. Patients with an anti-HbS negative result were older than those with a hepatitis B test (anti-HbS) positive result (36.3 versus 34.9; p<0.001).
The present study showed lower infection rates than the Brazilian ones for the diseases studied in patients undergoing IVF. Only a few patients were immunized against hepatitis B.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):473-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005046
To determine whether the antral follicle count can predict the number of retrieved oocytes in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) and to correlate it with maternal age and pregnancy rate.
This was a retrospective observational study based on a review of medical records from 193 patients who underwent assisted reproduction techniques between September 2010 and September 2012 in a Clinic for Human Reproduction. The study included women indicated for IVF who had follicle-stimulating hormone levels below 10 mIU/mL on third day of the menstrual cycle, with oocyte recipients being excluded. The patients were divided into three groups according to the number of antral follicle (up to 10 follicles, 11–22 follicles, and 23 or more follicles). To compare these three groups with the group of patients who became pregnant, patients who had not developed oocytes and had not undergone embryo transfer were also excluded. Spearman's correlation coefficient was used to measure the level of association between the numerical variables, and χ2 test was used to compare pregnancy rates with antral follicle count. To assess the likelihood of pregnancy, we used multivariate logistic regression, with the level of significance set at 5%.
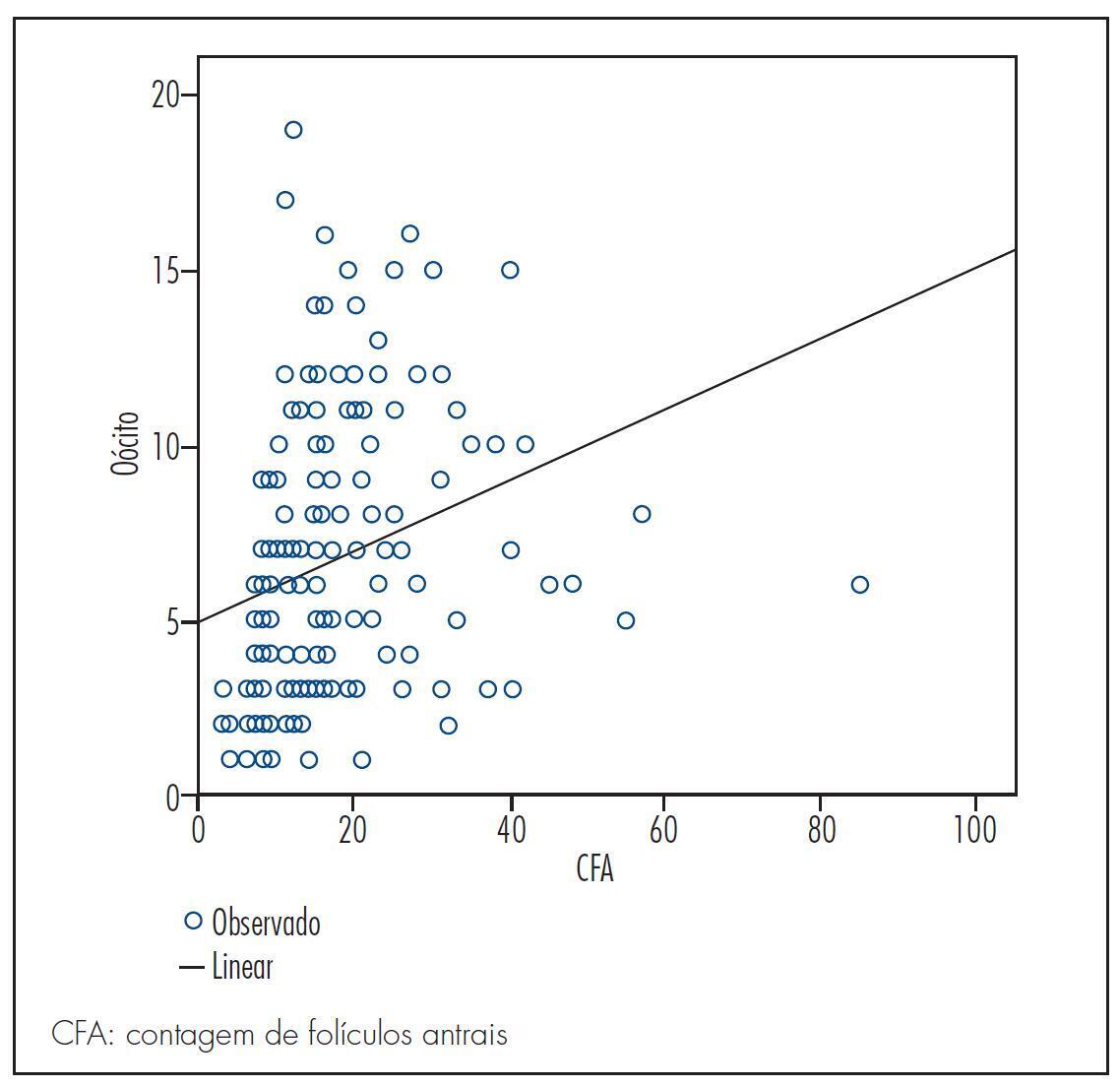
The pregnancy rate of the sample was 35.6%. There was a positive significant correlation (sc) between antral follicle count and number of retrieved oocytes (sc=0.5; p<0.05) and a negative correlation between antral follicle count and age (sc= -0.5; p<0.05). There was no significant difference (p=0.16) when groups with different numbers of follicles were compared to the positive pregnancy test group; however, a cutoff of 27 antral follicles was observed in multivariate analysis, after which the probability of successful gestation tended to remain constant.
The antral follicle count decreases over the years, is a predictor of the number of retrieved oocytes and can predict the likelihood of the success of in vitro fertilization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):524-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100008
PURPOSE: To evaluate the concordance between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy techniques in the evaluation of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes matured in vivo. METHODS: Prospective study that evaluated oocytes with the first polar extruded body obtained from infertile women who had undergone ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmic sperm injection. The oocytes with the first polar extruded body were evaluated by polarization microscopy and were then immediately fixed and stained for microtubule and chromatin evaluation by high-performance confocal microscopy. We determined the correlation of polarization microscopy with confocal microscopy in the detection of meiotic oocyte anomalies, and we also evaluated the percentage of oocytes with a visible and non-visible cell spindle by polarization microscopy and with meiotic normality and abnormalities by confocal microscopy. Confidence intervals, Kappa's index and concordance between the methodologies were calculated, considering immunofluorescence microscopy analysis as the golden-standard for evaluating normal spindle and oocyte chromosome distribution. RESULTS: We observed that 72.7% of metaphase II oocytes with a nonvisible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy showed no meiotic abnormalities by confocal analysis and 55.6% of metaphase II oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be abnormal oocytes by the confocal analysis. Only 44.4% of oocytes with a visible meiotic spindle by polarization microscopy were found to be normal by confocal analysis. Concordance between the methods was 51.1% (Kappa: 0.11; 95%CI -0.0958 - 0.319). CONCLUSIONS: The low correlation between polarization microscopy and confocal microscopy in the assessment of oocyte meiotic spindle suggests that visualization of the meiotic spindle of human oocytes at metaphase II by polarization microscopy is not a good indicator of oocyte meiotic normality.
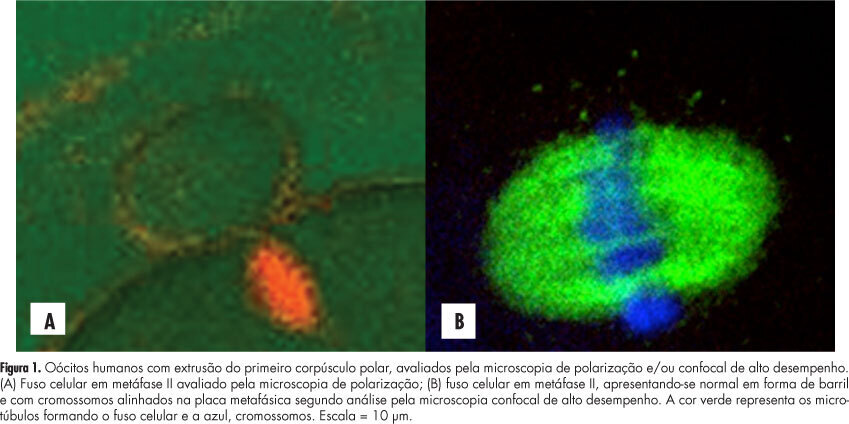
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):425-431
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900007
PURPOSE: To evaluate the prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) among women candidates to in vitro fertilization (IVF) in a reference public service in southeastern Brazil. METHODS: Women who were referred for IVF from April 1st, 2008 to December 31st, 2009 were enrolled sequentially in the study. A ginecological-obstetrical background questionnaire was applied and endocervical swab samples were obtained to search for CT and NG using hybrid capture and PCR. The variables studied were: age, color, education, duration of infertility, number of pregnancies and living children, history of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, number of sex partners, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), pelvic surgery, manipulation of the uterine cavity, smoking, and illicit drug use. The women were distributed according to the presence/absence of confirmed chlamydia infection and descriptive analysis was employed. RESULTS: Among 176 women tested the prevalence of CT infection was 1.1% and there was no NG infection. Two thirds of the women were >30 years old, with schooling >8 years and <5 years of infertility, and 56.2% had no children. The main background data were pelvic surgery (77.8%), manipulation of the uterine cavity (62.5%) and PID (27.8%). The tubal factor was the most prevalent, 73.3% of women (from 129), 37.5% had been sterilized, 35.8% had not been sterilized, and other factors had a prevalence <30%. CONCLUSIONS: CT and NG infections had a low prevalence in this sample. Studies at other centers in the country are needed to confirm the prevalence of infection in this particular group of infertile women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):536-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of body mass index (BMI) on in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) outcomes performed at the Human Reproduction Center of Faculdade de Medicina do ABC. METHODS: retrospective data from 488 IVF cycles of 385 patients. Patients were classified into two groups according to BMI: normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m²) and overweight/obesity (>25 kg/m²). We evaluated the dose of recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (FSHr), the cancellation rates for ovarian cycle response, and the results of the assisted reproduction laboratory such as number of oocytes, number of good quality embryos, number of embryos transferred, and pregnancy rates, chemical pregnancy rates, miscarriage rate and live birth rate. The t test was used for comparison of quantitative variables between groups, and the χ2 test for comparison between qualitative variables. P values <0.05 were considered significant. RESULTS: considering ovulation induction characteristics, there was no statistically significant difference between groups regarding the FSHr dose administered or the cancellation rates, p=0.47 and p=0.85, respectively. Regarding laboratory findings, the number of oocytes retrieved per cycle was similar for both groups (p=0.09), as also was the number of good quality embryos obtained and transferred (p=0.7 and p=0.6). The pregnancy rate per embryo transfer was 27.6% for the group of normal weight and 29.6% for the overweight/obese group (p=0.76). Miscarriage rates and birth rates were similar for both groups, p=0.54 and p=0.94. CONCLUSION: BMI did not influence IVF/ICSI outcomes evaluated.