Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):103-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200008
Male infertility affects 10% of couples in the reproductive age worldwide and is treatable in many cases. In addition to other well-described etiologies, genetic causes of male infertility are now more commonly diagnosed. In men with prior vasectomy or varicocele, microsurgical reconstruction of the reproductive tract or varicocelectomy is more cost-effective than sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection if no female fertility risk factors are present. If epididymal obstruction after vasectomy is detected or advanced female age is present, the decision to use either microsurgical reconstruction or sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection should be individualized. Sperm retrieval with in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection is preferred to surgical treatment when female factors requiring in vitro fertilization are present or when the chance for success with sperm retrieval and intracytoplasmic sperm injection exceeds the chance for success with surgical treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):643-651
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100003
PURPOSE: literature reports show that there are no conclusive data about the association between endometriosis and the concentrations of hormones involved in the control of reproduction. Thus, the present study was undertaken to determine FSH, LH, estradiol (E), progesterone (P), and histamine (Hi) concentrations in serum, peritoneal fluid and follicular fluid of women with and without endometriosis. METHODS: the extent of the disease was staged according to the revised American Fertility Society classification (1997). For the collection of serum and peritoneal fluid, 28 women with endometriosis undergoing diagnostic laparoscopy were selected (18 infertile women with endometriosis I-II and ten infertile women with endometriosis III-IV). For the control group, 21 fertile women undergoing laparoscopy for tubal sterilization were selected. Follicular fluid was obtained from 39 infertile women undergoing in vitro fertilization (21 women with endometriosis and 18 women without endometriosis). RESULTS: FSH and LH levels in serum, peritoneal fluid and follicular fluid did not differ significantly between groups. On the other hand, E and P concentrations in the peritoneal fluid were significantly lower in infertile women with endometriosis (E: 154.2±15.3 for stages I-II and 89.3 ng/mL±9.8 ng/mL for stages III-IV; P: 11.2±1.5 for stages I-II and 7.6 ng/mL±0.8 for stages III-IV) in comparison with control women (E: 289.1 ng/mL±30.1; P: 32.8±4.1 ng/mL) (Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests; p<0.05). In serum, estradiol and progesterone concentrations followed the same pattern. In the follicular fluid, E and Hi concentrations were significantly lower in women with endometriosis (E: 97.4±11.1 pg/mL; Hi: 6.6±0.9 ng/mL) in comparison to women without endometriosis (E: 237.5±28.5 pg/mL; Hi: 13.8±1.3 ng/mL) (Student t-test; p<0.05), while progesterone levels revealed no significant difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: our results indicate ovary dysfunction in women with endometriosis, with reduction on E, P and Hi concentrations, which may contribute to the subfertility often associated with the disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):220-226
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400003
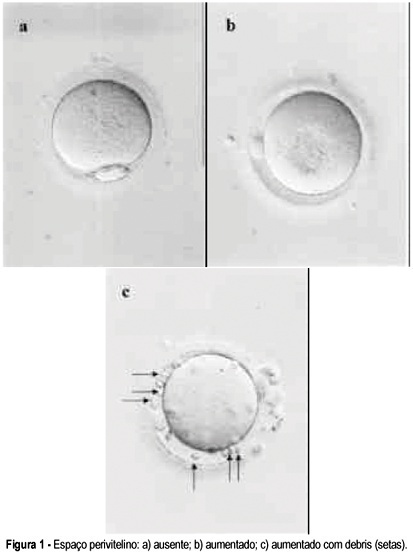
PURPOSE: to verify the possibility of identifying oocytes that would result in a higher fertilization rate. METHODS: retrospective analysis of the fertilization rate after ICSI of 957 oocytes in metaphase II according to three morphology parameters: cytoplasm inclusions, thickness of the perivitelline space, and fragmentation of the first polar body. Oocytes were obtained from 115 cycles performed among 107 women attended at the "Centro de Reprodução Humana de Campinas", from April to December of 2004. For the statistical analysis of differences in the fertilization rate between 'normal' oocytes and those presenting each alteration, the chi2 test was used with confidence levels of 5 and 10%. RESULTS: no significant difference in fertilization rate was observed regarding characteristics of the polar body or thickness of the perivitelline space. Fertilization rate among oocytes with perivitelline space with debris was 14 percentage points lower than among oocytes with absent space (p=0.055) and the rate among oocytes with granular cytoplasm was seven percentage points lower than among oocytes with normal cytoplasm (p<0.10>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the morphological parameters of oocytes currently being evaluated do not allow us to clearly distinguish those that would lead to a higher fertilization rate and could be used in clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(6):311-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000600002
Purpose: to verify the effects of the goserelin depot as GnRH agonist for hypophysis suppression, during the controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) for in vitro fertilization and intrauterine embryo transfer (IVF & ET). Method: this is a prospective study of 110 cycles of 101 women. Goserelin depot was administered subcutaneously as a single dose; for some women (87 cycles) it was administered in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, and in 23 cycles it was administered in the luteal phase. The administration of menopausal gonadotropins was daily, until the identification of at least two follicles with a diameter equal to or larger than 18 mm; at this time the chorionic gonadotropin was administered and the follicular aspiration was programmed. Results: the women's age average was 36.7 years (between 23 to 42 years). The main indications for IVF & ET were: tubo-peritoneal factor (75.2%), endometriosis (10.9%), ovulatory factor (7.9%), male factor (3.0%) and unexplained infertility (3.0%). Of the total of the cycles, 28 (25.5%) cycles were cancealed. In 7 cycles (8.04%), for which goserelin depot was administered in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, it was necessary to perform the ovarian cysts aspiration before beginning the ovulation induction. On the average, 3.3 embryos were transferred for each patient (1-5 embryos per woman). Of the total of 70 embryos transferred, 16 clinical pregnancies resulted (pregnancy rate: 22.85%). Conclusion: the goserelin depot administration is a useful alternative for pituitary suppression for IVF & ET, since its results are similar to those observed in the literature, and the patient does not need to come every day to receive medication, a fact of extreme importance in a public service.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):759-767
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200009
PURPOSE: to carry out a literature review to evaluate the impact of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) on maternal and perinatal morbidity. METHODS: specialized data bases such as SCI and MEDLINE were used to identify studies related to the terms: "in vitro fertilization", "assisted reproduction" and "reproductive techniques" in combination with "morbidity", "maternal mortality", "perinatal mortality", and "neonatal mortality". RESULTS: data from published studies allow us to conclude that maternal morbidity is related to an increase in the number of multiple pregnancies. In addition, some studies have reported an increased incidence of pregnancy-induced hypertension and gestational diabetes. Specialized multidisciplinary prenatal care has been recommended to obtain optimal results. An increase in the number of multiple pregnancies considerably increases maternal, fetal and neonatal complications. There is also evidence of an increase in congenital malformations. The particular characteristics of this group of women and the different techniques of assisted reproduction, particularly ICSI, in the etiology of congenital defects were discussed, but no clear differences have been established between the various procedures. Some recent metanalyses show that the number of fetal malformations in infants born as a result of ICSI is greater than in spontaneously conceived infants, but not more frequent than in those born as a result of other ART. There is no consensus regarding whether this fact is a result of the procedure itself, of manipulation of the gametes, ovulation induction, if it is due to the fact that these couples are infertile or a result of the time they take to become pregnant. Few studies have carried out a prolonged, consistent and systematic evaluation of the perinatal evolution of infants born following the use of frozen embryos. CONCLUSIONS: with respect to fetal malformations, there is definitely a higher incidence rate among infants born as a result of ART compared to those conceived naturally (RR: 1.4-2.0; 95% CI: 1.3-2.7). Insufficient time and data do not yet permit analysis of the outcome of pregnancies resulting from the use of frozen embryos. It is not clear whether these findings are due to the characteristics of the couples who are submitted to these procedures or to the peculiarities of each method. Many of the problems related to maternal and perinatal morbidity are due to the significant number of multiple pregnancies originating from ART. More studies are required in order to clarify these aspects of human reproduction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):665-671
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100006
PURPOSE: to define the characteristics of unviable embryos that may be donated for stem-cell research. METHODS: a retrospective evaluation of in vitro fertilzation cycles between January 1995 and January 2005 was structured. Cycles were chosen in which the embryos transferred to the uterine cavity had the same morphological characteristics. Subsequently, the rates of pregnancy, implantation, and involution of the gestational sacs of the fresh embryos as well as of those cryopreserved were analyzed and distributed into groups according to their morphology. Embryos that were symmetric and with 0% of fragmentation were designated type A; asymmetric with up to 25% of fragmentation were designated type B; between 25 and 50% of volume occupied were designated type C, and those with 50% or more of fragmentation were designated type D. RESULTS: one hundred and seventy-two type D embryos transferred in 87 cycles presented low rates of implantation (11%) with 50% of those implanted persisting in development. Embryos with the same morphology, after cryopreservation and thawing, did not show the capacity to evolve. In 36 cycles, 113 thawed type D embryos were transferred, resulting in only one implantation, presenting a minute 3% pregnancy rate. The implanted gestational sac did not evolve, showing a 100% rate of involution. CONCLUSION: embryos with low morphological scores cannot be considered unviable because they are capable, even though with a very low frequency, of supporting gestation. However, these same embryos, after cryopreservation, thawing and transfer showed an insignificant rate of pregnancy, that did not result in viable pregnancy. Therefore, when in excess to requirements, type D embryos should not be cryopreserved; instead, rather than discarded, they should be donated for embryo stem-cell research.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):599-606
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000006
PURPOSE: comparative analysis of the outcome of women with advanced pelvic endometriosis and women with tubal sterilization submitted to intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). METHODS: ninety-three infertile women, with normal menstrual cycle, without hormonal or surgical treatment during 12 months, body mass index of 20-25, ovaries with no tumors or cysts were included in the present study and divided into two groups: tubal sterilization (TUB), 39 women, and endometriosis (EDT), 54 women with III-EDT and IV-EDT, undergoing ovulatory induction using r-FSH and ICSI. Clinical and laboratorial data were compared. chi2, Fisher, Student's t, and Mann-Whitney tests were employed. RESULTS: lower estradiol levels (2,243.1 vs 1,666.3; p=0.001) and lower number of follicles per patient (16.9 vs 13.9, p=0.001) were noted in EDT group, in spite of more units of r-FSH (1,775.6 vs 1,998.6; p=0.007, for TUB and EDT, respectively). There were no differences in the rates of retrieved oocyte (69 vs 73.5%; p=0.071) as well as in normal fertilization rates (83.7 vs 81.7%; p=0.563, for TUB and EDT, respectively. However, lower number of top quality preembryos were obtained in patients from EDT group (36.5 vs 24.8%, TUB and EDT, respectively; p=0.005). Total pregnancy (41.0 vs 42.6%; p=0.950) and implantation rates (13.9 vs 14.5%; p=0.905) were not different when groups TUB and EDT were compared. CONCLUSIONS: ovaries of women from EDT group seem to be less responsive to ovulatory induction with r-FSH. EDT seems to impair the mean number of follicles and top quality preembryos with no impairment of retrieved oocyte and fertilization rates. However, once obtained, preembryos from EDT patients are able to exhibit similar implantation potential and pregnancy when compared with patients from TUB group.