-
Original Article
A New Brazilian Device for Cervical Cancer Screening: Acceptability and Accuracy of Self-sampling
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):235-241
08-07-2023
Summary
Original ArticleA New Brazilian Device for Cervical Cancer Screening: Acceptability and Accuracy of Self-sampling
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):235-241
08-07-2023Views155Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the accuracy and patient acceptability toward self-sampling using a new device - SelfCervix® - for detecting HPV-DNA.
Methods
A total of 73 women aged 25–65 who underwent regular cervical cancer screening from March to October 2016 were included. Women performed self-sampling followed by a physician-sampling, and the samples were analyzed for HPV-DNA. After that, patients were surveyed about their acceptability of self-sampling.
Results
HPV-DNA detection rate of self-sampling presented high accuracy and was similar to physician-collection. Sixty-four (87.7%) patients answered the acceptability survey. Most patients (89%) considered the self-sampling comfortable, and 82.5% preferred self-sampling to physician-sampling. The reasons cited were time-saving and convenience. Fifty-one (79.7%) reported that they would recommend self-sampling.
Conclusion
Self-sampling using the new Brazilian device SelfCervix® is not inferior in HPV-DNA detection rate compared with physician-collection, and patients are supportive of the method. Therefore, it might be an option to reach under-screened populations in Brazil.
Key-words Cytologydiagnostic screening programsearly detection of cancerHuman papillomavirusUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):871-877
06-06-2022
Summary
Original ArticleThe COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):871-877
06-06-2022Views191See moreAbstract
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic profile of breast cancer cases during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic compared with the previous year.
Methods
It is a retrospective study of cases diagnosed by a reference service in the public health system of Campinas, SP, Brazil. Two periods were analyzed: March to October 2019 (preCOVID period) and March to October 2020 (COVID-period). All women diagnosed during the periods were included. The Chi-Squared or Fisher exact and Mann-Whitney tests were used.
Results
In the preCOVID and COVID periods, breast cancers were diagnosed, respectively, in 115 vs 59 women, and the mean ages at diagnosis were 55 and 57 years (p = 0.339). In the COVID period, the family history of breast cancer was more observed (9.6% vs 29.8%, p < 0.001), cases were more frequently symptomatic (50.4% vs 79.7%, p < 0.001) and had more frequently palpable masses (56.5% vs 79.7%, p = 0.003). In symptomatic women, the mean number of days from symptom to mammography were 233.6 (458.3) in 2019 and 152.1 (151.5) in 2020 (p = 0.871). Among invasive tumors, the proportion of breast cancers in stages I and II was slightly higher in the COVID period, although not significantly (76.7% vs 82.4%, p = 0.428). Also in the COVID period, the frequency of luminal A-like tumors was lower (29.2% vs 11.8%, p = 0.018), of triple-negative tumors was twice as high (10.1% vs 21.6%, p = 0.062), and of estrogen receptor-positive tumors was lower (82.2% vs 66.0%, p = 0.030).
Conclusion
During the COVID-19 pandemic, breast cancer diagnoses were reduced. Cases detected were suggestive of a worse prognosis: symptomatic women with palpable masses and more aggressive subtypes. Indolent tumors were those more sensitive to the interruption in screening.
-
Original Article
Cervical Cancer Screening with HPV Testing: Updates on the Recommendation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):264-271
02-15-2022
Summary
Original ArticleCervical Cancer Screening with HPV Testing: Updates on the Recommendation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):264-271
02-15-2022Views226Abstract
The present update is a reassessment of the 2018 ‘Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil’ (Zeferino et al.)9, according to the changes observed in new international guidelines and knowledge updates. The most relevant and recent guidelines were assessed. Questions regarding the clinical practice were formulated, and the answers considered the perspective of the public and private sectors of the Brazilian health system. The review addressed risk-based strategies regarding age to start and stop screening, the use of cytology and colposcopy to support management decisions, treatment, follow-up strategies, and screening in specific groups, including vaccinated women. The update aims to improve the prevention of cervical cancer and to reduce overtreatment and the misuse of HPV testing.
Key-words accessibility of health servicesearly detection of cancerhuman papillomavirus DNA testsMass screeningUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
Regional and Socioeconomic Differences in the Coverage of the Papanicolau Test in Brazil: Data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):480-487
09-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleRegional and Socioeconomic Differences in the Coverage of the Papanicolau Test in Brazil: Data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):480-487
09-01-2017Views87Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the coverage of the Papanicolaou test in Brazil and the associated factors.
Methods
Cross-sectional study based on data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013 comprising the proportion of 25- to 64-year-old women who had undergone a Papanicolaou test within the previous 3 years, categorized by sociodemographic variables and access to healthcare services.
Results
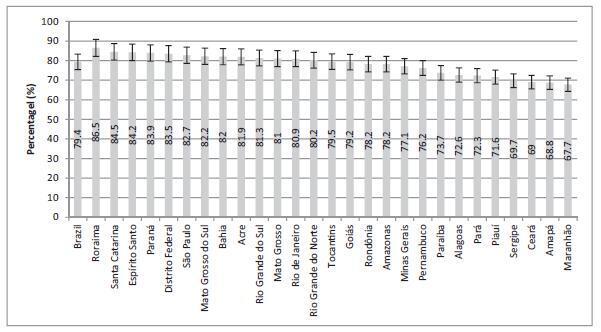
The screening coverage in Brazil was of 79.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 78.4-80.3), showing significant differences between the different states of the country, with the highest rate in the state of Roraima (86.5; 95%CI: 83.5-89.4), and the lowestone in the state ofMaranhão (67.7; 95%CI: 61.3-74.0).Undergoing the test was significantlymore frequent amongmarriedwomen (83.6%; 95%CI: 82.4-84.8), those with higher educational levels (88.7%; 95%CI: 87.0-90.5), of white ethnicity (82.6%; 95%CI: 81.3-83.9) and who reside in urban areas (80.1%; 95%CI: 79.1-81.2). Those who had undergone the test more than three years prior to the survey and the ones who had never undergone it were associated with a lower level of education, being of black or brown ethnicity, single or divorced, and rural dwellers.
Conclusions
The coverage of cervical cancer screening in Brazil is below the recommended rate and presents regional and sociodemographic disparities.
Key-words cervical neoplasmsearly detection of cancerEpidemiologyinequalities in healthPapanicolaou testWomen's healthSee more