Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):338-346
To discuss the implementation and contributions of the External Quality Monitoring in the city of Rio de Janeiro and to analyze the performance of the main providers of cervical cytopathology in this city from September 2013 to March 2017, here referred to as “Alpha laboratory” and “Beta laboratory.”
Observational, cross-sectional, retrospective study using information from the Cervical Cancer Control Information System (SISCOLO, in the Portuguese acronym), municipal coordinationmodule, External QualityMonitoring report. The proportions of false positives, false negatives, unsatisfactory samples and rejected samples were estimated. The agreement among the observers was analyzed through the Kappa index and the reduction of disagreements in the period for each laboratory studied, comparing the results of each cycle.
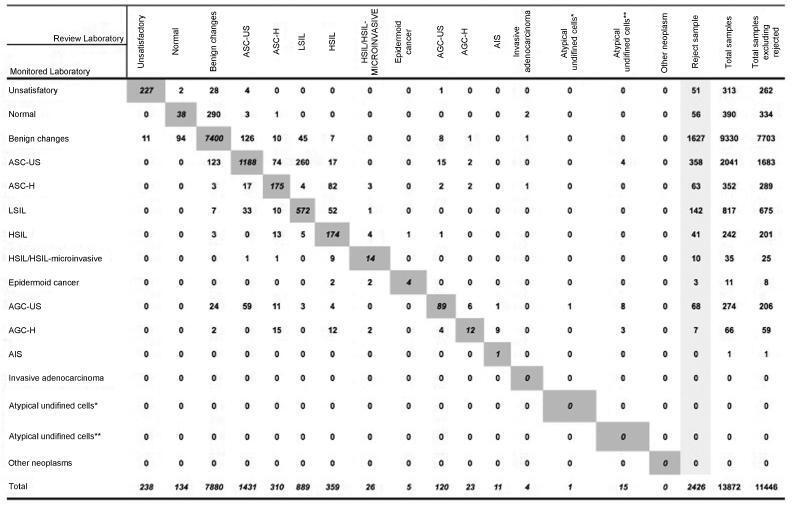
A total of 19,158 examinations were selected, of which 19,130 (99.85%) were monitored, 16.649 (87, 03%) were reviewed by the External Quality Monitoring Unit, 2,481 (12,97%) were rejected and 441 (2,65%) were considered unsatisfactory. The “Beta laboratory” presented excellent concordance in all cycles; the “Alpha laboratory” had good concordance in the first two cycles (K = 0.76 and 0.79), becoming excellent in the following four cycles. The average Kappa index was 0.85, with median of 0.86. The percentage of diagnostic disagreement was 6.63% of the reviewed exams, of which 5.38% required a change of conduct
External Quality Monitoring is an exercise in diagnostic improvement, and its implementation was fundamental to ensure the reliability of the cytopathological exams in the city of Rio de Janeiro.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):518-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100007
PURPOSE: To determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with failure of voluntary screening for cervical cancer during the gestational period in Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul State, Southern Brazil. METHODS: Previously trained interviewers applied a standardized questionnaire in the maternity to all mothers from this municipality who had delivered from January 1st to December 31st 2010 to obtain information about the demographic characteristics of the pregnant women, family socioeconomic status, and prenatal care received. The χ² test was used to compare proportions and Poisson regression with robust adjustment of variance was used in the multivariate analysis. RESULTS: Among the 2,288 respondents, 33% were not submitted to the Pap smear during pregnancy. Two thirds of these women stated that they were not aware of the need to perform it, 18% were not screened out of fear or shame, and the rest for other reasons. After adjustment, the highest prevalence ratios (PR) for noncompliance with the Pap smear occurred among young women (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.25 - 1.80), with lower educational level (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.12 - 2.12), who were living without a partner (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.24 - 1.62), smokers (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.07 - 1.39), who did not plan the current pregnancy (PR=1.3; 95%CI 1,21 - 1.61), who had attended less than six medical visits during the prenatal period (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.32 - 1.69) and among users of oral contraceptives (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.04 - 1.38). CONCLUSIONS: The higher the risk for uterine cervical cancer, the less likely a pregnant woman is to undergo a Pap smear. This definitely contributed to the increased morbidity and mortality from this disease in this setting.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):351-356
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800002
PURPOSE: To evaluate the diagnostic agreement between the cytopathology reports issued by accredited laboratories and those obtained by quality control. METHODS: We calculated the overall agreement and Cohen's kappa coefficients of a convenience sample of smears selected monthly by the Information System of Cervical Cancer (SISCOLO) for External Quality Control of the 15 laboratories that performed cytopathological PAP tests for the Brazilian Public Health System (SUS) between 2002 and 2011 in Mato Grosso do Sul, a State of the Midwest Region of the country. A comparison of the reliability values (coefficient of concordance and Kappa coefficient) between the initial and final years was computed by the absolute change (delta) and relative percent difference (RPD). RESULTS: There were 15.989 smears sent for rereading, 48.1% of which had a report of normal/benign changes, followed by atypical/low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (36.3%), high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion/carcinoma/adenocarcinoma (4.2%), and unsatisfactory (11.4%). The overall correlation coefficient ranged between 0.2 and 1.0, and the median value increased from 0.7 in 2002 to 1 in 2011 (RPD=+36.6%). During the same period, the median values of the Kappa coefficient increased from 0.5 to 0.9 (RPD=+80.8%). CONCLUSIONS: These results emphasize the feasibility of the External Quality Control of cytopathology at the state level and its implementation results in improvement in the diagnoses performed in the SUS network.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(10):491-496
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001000004
PURPOSE: to evaluate painful sensitivity and factors involved in producing papillary fluid suitable for cytological analysis by means of automated collection. METHODS: we selected 50 asymptomatic women without a personal or family history of breast cancer, outside the pregnancy and childbirth cycle in order to collect papillary fluid by the automated system. We recorded and related to the production of papillary fluid patient age, smoking habit, previous breast surgery, parity, breastfeeding, menopausal status and age at menarche. All material collected was fixed in appropriate place, and sent separately for cytological analysis. The painful sensitivity of the collection procedure was assessed using the Borg Category-Ratio Scale (CR10 Scale). RESULTS: patient age ranged from 22 to 59 years, mean 41.6±8.6 years. Of the 50 patients, 20 (40%) showed no papillary fluid suitable for analysis in the breasts. In those patients from whom appropriate fluid was obtained for analysis of papillary cytology, parity was inversely related to the ability to obtain suitable cell samples with a level of statistical significance of p=0.035, OR=0.0032 (95%CI=0.0001-0.1388). Regarding soreness, the exam was well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS: the automated method of fluid collection for analysis of papillary cytology was well tolerated by the women; thus producing analyzable material in 60% of cases, a rate was inversely related to parity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):556-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100005
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether the sample adequacy influences the detection of precursor cervical cancer lesions. METHODS: a transversal study from January 2004 to December 2005. A number of 10,951 results of cervical cytotopathological exams from users of the National Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde, SUS) in Goiânia, Goiás , Brazil, was studied. These women had spontaneously looked for the services from the Family Health Program or from the Basic Units of Health. Samples were collected by medical doctors and nurses, through the conventional technique to detect cervical cancer. The analyzed smears were classified by the Bethesda System, the sample adequacy being defined along the routine screening and categorized as: satisfactory, satisfactory but presenting factors that might partially jeopardize the analysis, and unsatisfactory. Results were stored in the Epi-Info 3.3.2 program. The χ2 test was used to compare altered results with the adequacy of the samples from cytopathological smears. Differences with probability of rejection of the null hypothesis lower than 5% (p<0.05) were considered as significant. RESULTS: From 10,951 smears, 51.1% were classified as having satisfactory adequacy for analysis, 46.6% as satisfactory, but presenting some limiting factors, and 2.3%, as unsatisfactory. The main factors which have partially jeopardized the analysis were: lack of endocervical cells (52.2%), dried smears (22.8%), purulence (14.9%), or smears with some thick areas (9.5%). There was a higher rate of altered smears when the sample had been classified as satisfactory for analysis and with representation of endocervical cells ASC-US (2.3%), ASC-H (0.6%), LSIL (3.2%), HSIL (1.7%) and 0.3% of AGC. Differences were significant when p=0.001. The rate of low and high grade lesions was higher when the smears were satisfactory for analysis. CONCLUSIONS: the rate of precursor uterine cervix cancer lesions varies according to the sample adequacy, and the main adequacy limitations of the sample are mainly related to the collection condition.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(9):437-444
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000900003
PURPOSE: to verify the accuracy of uterine cervix cytology for HPV diagnosis, as compared to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in samples of women with HIV. METHODS: 158 patients who had undergone a first collection of material from the uterine cervix with Ayre's spatula for PCR were included in the study. Then, another collection with Ayre's spatula and brush for oncotic cytology was performed. Only 109 slides were reviewed, as 49 of them had already been destructed for have being filed for over two years. RESULTS: the prevalence of HPV was 11% in the cytological exam and 69.7% in the PCR. Age varied from 20 to 61 years old, median 35 years. The HIV contagious route was heterosexual in 91.8% of the cases, and 79.1% of the patients had had from one to five sexual partners along their lives. The most frequent complaint was pelvic mass (5.1%), and 75.3% of the women had looked for the service for a routine medical appointment. The categorical variable comparison was done through contingency tables, using the χ2 test with Yates's correction to compare the ratios. The Fisher's test was used when one of the expected rates was lower than five. In the comparison of diagnostic tests, sensitivity, specificity and similarity ratios have been calculated. Among the 76 patients with HPV, detected by PCR, only 12 had the diagnosis confirmed by cytology (sensitivity=15.8%), which on the other hand did not present any false-positive results (specificity=100%). Concerning the HPV presence, the cytological prediction for positive results was 100% and 33.3% for negative, when both results were compared. Among the 12 patients with HPV positive cytology, four (33.3%) presented cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (OR=56; positive similarity ratio=positive infinity; negative similarity ratio=0.83). CONCLUSIONS: As the cytology specificity is quite high, it is possible to rely on the positive result, which means that a positive result will surely indicate the presence of HPV. The low sensitivity of cytology does not qualify it as a survey exam for HPV detection in this female group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):402-407
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800004
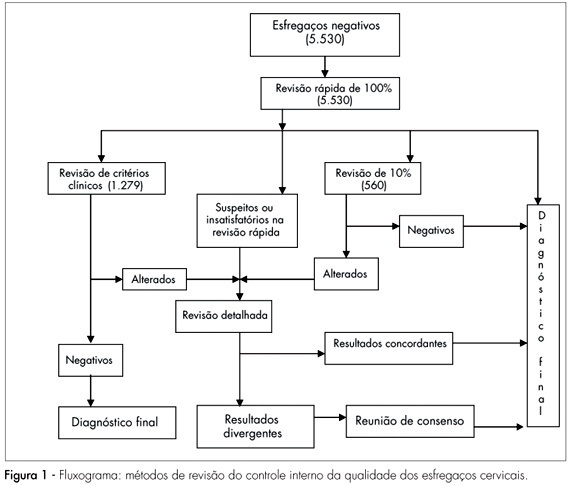
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficiency of the 100% rapid rescreening in the detection of false-negative results and to verify whether the results vary according to the adequacy of the sample and the woman’s age group. METHODS: to evaluate the efficiency of the rapid rescreening, the 5,530 smears classified as negative by the routine screening, after being submitted to the rapid rescreening of 100%, were compared with the rescreening of the smears on the basis of clinical criteria and 10% random rescreening. For statistical analysis, the variables were evaluated descriptively and the c² test and the Cochran-Armitage test were applied to compare results. RESULTS: of the 141 smears identified as suspicious according to the rapid rescreening method, 84 (59.6%) cases were confirmed in the final diagnosis, of which 36 (25.5%) were classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, five (3.5%) as atypical squamous cells that cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, 34 (24.1%) as low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, six (4.3%) as high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, and three (2.1%) as atypical glandular cells. Of the 84 suspect smears confirmed in the final diagnosis, 62 (73.8%) smears were classified as adequate and 22 (26.2%) as adequate but with some limitation, but no significant difference was observed with the woman’s age. CONCLUSIONS: the results of this study show that rapid rescreening is an efficient option for internal quality control for the detection of false-negative cervical smear results. In addition, it should be noted that rapid rescreening performed better when the sample was classified as adequate for analysis; however, it did not vary according to the woman’s age group.
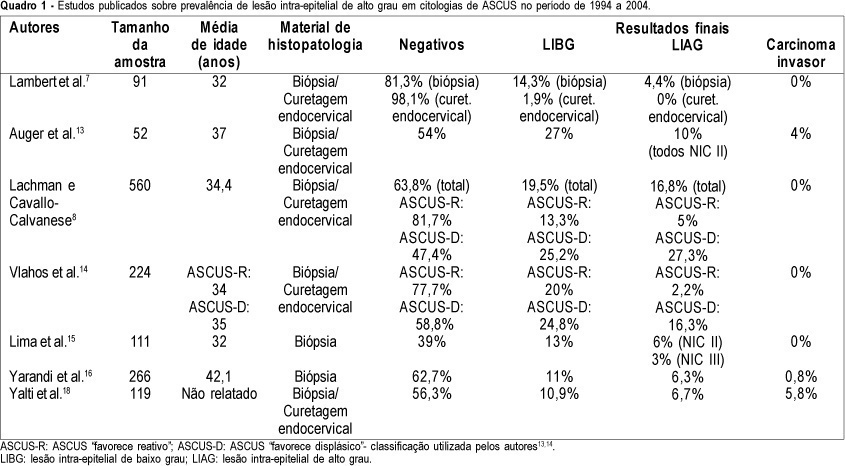
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):75-80
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200002
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) and cancer in women with cytological diagnosis of persistent ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) for 6 months in the last 7 years. We also assessed if age could be a predictive factor for presence of HSIL/cancer in this group. METHODS: we included 215 cases of non-pregnant and HIV-seronegative women with cytological diagnosis of persistent ASCUS (unespecific) with at least 6 months of interval between smears. This cytological diagnosis was compared to histological diagnosis obtained by biopsy (large loop excision of the transformation zone) or cone biopsies, and considered negative when colposcopy was satisfactory without lesions or, when unsatisfactory, no lesion was detected after at least one cytological and colposcopic follow-up. RESULTS: among the 215 cases, 49.3% had negative results (CI 95%: 42.6-55.9). The prevalence of histological confirmed low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion was 38.6% (CI 95%: 32.1- 45.1) and HSIL was 10.7% (CI 95%: 6.5-14.8). Cases of cancer were found in 1.4% of patients (CI 95%: 0-2.9). We could not find a significant difference between the prevalence of HSIL/cancer according to age group using the cutoff point of 35 years. CONCLUSION: HSIL/cancer prevalence observed in this study has shown the risk of finding this kind of lesions in about 12% of women assisted in our public health system with two cytological diagnosis of ASCUS. A higher probability of HSIL/cancer in the different age groups was not found but this result was limited by our small sample size.