Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(7):333-338
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005373
To describe the prevalence of malformations found in fetuses with trisomy of chromosomes 13, 18 and 21 by identifying the most frequent within each condition.
A retrospective cross-sectional study with the analysis of trisomy cases of chromosomes 13, 18 and 21 diagnosed through fetal karyotype obtained by amniocentesis/cordocentesis, between October 1994 and May 2014, at a Teaching Hospital in Brazil Southern Region. Malformations identified through morphological ultrasonography were described and, subsequently, confirmed in newborn examinations and/or fetal autopsy. The results were analyzed using Fisher's test and analysis of variance (ANOVA), with a 5% level of significance (p=0.05).
Sixty-nine cases of trisomy were diagnosed among 840 exams; nine were excluded due to outcome outside Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre or incomplete records, remaining 60 cases (nine cases of chromosome 13 trisomy, 26 of chromosome 18, and 25 of chromosome 21). In all three groups, heart disease occurred in most cases; the ventricular septal defect was more prevalent and occurred in 66.7% of the trisomy 13 group. Gastrointestinal abnormalities were more prevalent in the trisomy 18 group, especially omphalocele (38.5%; p<0.01). Genitourinary anomalies were more significantly frequent in the trisomy 13 group (pyelectasis, 55.6% - p<0.01; ambiguous genitalia, 33.3% - p=0.01). Central nervous system defects were identified in all cases of trisomy 13. Facial cracks were significantly more prevalent among fetuses with trisomy 13 (66.7%; p<0.01). Hand and feet malformations significantly differed among the trisomy groups. Hand defects occurred in 50% of trisomy 18 cases, and in 44.4% of all trisomy 13 cases (p<0.01); congenital clubfoot was more common in the trisomy 18 group, being detected in 46.2% of fetuses (p<0.01). The abnormalities were found in 50.9, 27.3 and 21.7% of trisomy 18, 13 and 21 cases respectively.
Many fetal malformations identified at ultrasound are suggestive of trisomy and represent an important tool for etiologic diagnosis and prenatal and pre-conception genetic counseling.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300004
To investigate the prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities in couples with two or more recurrent first trimester miscarriages of unknown cause.
The study was conducted on 151 women and 94 partners who had an obstetrical history of two or more consecutive first trimester abortions (1-12 weeks of gestation). The controls were 100 healthy women without a history of pregnancy loss. Chromosomal analysis was performed on peripheral blood lymphocytes cultured for 72 hours, using Trypsin-Giemsa (GTG) banding. In all cases, at least 30 metaphases were analyzed and 2 karyotypes were prepared, using light microscopy. The statistical analysis was performed using the Student t-test for normally distributed data and the Mann-Whitney test for non-parametric data. The Kruskal-Wallis test or Analysis of Variance was used to compare the mean values between three or more groups. The software used was Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 17.0.
The frequency of chromosomal abnormalities in women with recurrent miscarriages was 7.3%, including 4.7% with X-chromosome mosaicism, 2% with reciprocal translocations and 0.6% with Robertsonian translocations. A total of 2.1% of the partners of women with recurrent miscarriages had chromosomal abnormalities, including 1% with X-chromosome mosaicism and 1% with inversions. Among the controls, 1% had mosaicism.
An association between chromosomal abnormalities and recurrent miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy (OR=7.7; 95%CI 1.2--170.5) was observed in the present study. Etiologic identification of genetic factors represents important clinical information for genetic counseling and orientation of the couple about the risk for future pregnancies and decreases the number of investigations needed to elucidate the possible causes of miscarriages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(3):133-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000300008
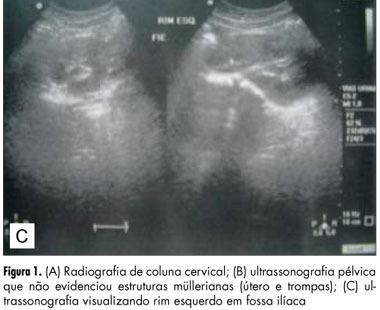
The atypical and more severe form of Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH) or MRKH type II is also known as MURCS association, an acronym meaning aplasia/hypoplasia of Müllerian ducts (MU), congenital renal dysplasia (R) and cervico-thoracic dysplasia (CS). It affects female patients with normal karyotype and ovarian function, evolving to primary amenorrhea. It has an incidence of 1:50,000, but it is underestimated due to late diagnosis and undefined etiology. We describe the cases of a child and an adolescent in order to predict the diagnosis even in childhood, before the onset of amenorrhea. Patients had in common renal malformation, agenesis or hypoplasia of Müllerian derivatives and vertebral anomalies, establishing the diagnosis of MURCS. The relevance of this paper is to show the importance of further investigation when some of pathologic signs are present, researching correlated abnormalities in order to establish an early diagnosis and consequently to provide guidance to the patients and their families about the best way to conduct the case, including genetic counseling.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):288-294
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the performance of the combined first trimester screening for chromosomal abnormalities in a group of the Brazilian population. METHODS: a retrospective study including pregnant women with single fetuses referred to a fetal medicine center to perform the first trimester screening that combines maternal age, nuchal translucency measurement and two maternal serum biochemical markers: free B-hCG and PAPP-A. To evaluate the performance of the test, the detection rate, specificity, negative and positive predicted values and false-positive rates were calculated, considering as high risk the cut-off value above 1 in 300. RESULTS: we studied 456 patients submitted to the test. Advanced maternal age above 35 years was observed in 36.2% of cases. The incidence of chromosomal abnormalities in the study population was 2.2%. Twenty-one patients (4.6%) presented a high risk (above 1:300) by the combined test. Using this cut-off level, the detection rate of the test was 70% for all chromosomal abnormalities and 83.3% for trisomy 21, for a false-positive rate of 3.1%. CONCLUSIONS: the combined first trimester screening was effective to detect chromosomal abnormalities, mainly for trisomy 21, with low false-positive rates. The combined test contributed to decreasing the indication of an invasive test if we compare to maternal age alone as a risk factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):49-57
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100008
This is a traditional (narrative) review with the objective of highlighting the contribution of obstetric ultrasonography (US) between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy, commonly called first trimester anomaly scan. In addition to being used for the screening of chromosomal anomalies, US can be employed during this period to confirm or determine gestational age, evaluate fetal anatomy, diagnose malformations, screen major structural abnormalities and genetic syndromes, define the prognosis of pregnancy, diagnose and characterize multiple pregnancies, and screen preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. The most important studies about this subject published between 1990 and 2010 in the Cochrane and PubMed libraries were included. The selected studies can be classified with scientific levels I to III.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):381-385
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800004
PURPOSE: to examine the association between cytogenetic characteristics and clinical and epidemiological changes in patients with Turner syndrome (TS). METHODS: Forty-two patients were included. Data were collected using a standardized questionnaire in interviews conducted with the responsible person and, when possible, with the patient. A detailed physical examination was performed. The association between karyotype, stigmata and clinical disorders were examined using the χ2 test. RESULTS: Sixty-four percent of TS patients were 45,X; 26,2% 45,X/46,X;7% 45,X/46Xi(Xq), and 2,3% 45,X/46,X,Del(Xq). Regardless of the karyotype, all patients had short stature. Low hair implantation was more frequent in patients with 45,X (p=0.03). Cardiovascular abnormalities (45%), otitis (43%), thyroid dysfunction (33%) and hypertension (26.6%) were the most frequent clinical disorders, but without correlation with the karyotype. Anthropometric measurements revealed a positive linear correlation of waist and hip circumference with age (r=0.9, p=0.01). Thirty-one patients (74%) were using or had previously used growth hormone (43%), sex steroids (30%), thyroxine (11.9%) or oxandrolone (9.5%). Comparison between gestational age at birth and learning difficulties showed a prevalence ratio of 1.71 (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Low hair implantation is the most prevalent stigma in patients with a 45,X karyotype and the most common clinical changes were cardiovascular problems, otitis, thyroid dysfunction and hypertension; however, they did not show any correlation with the karyotype.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):68-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200004
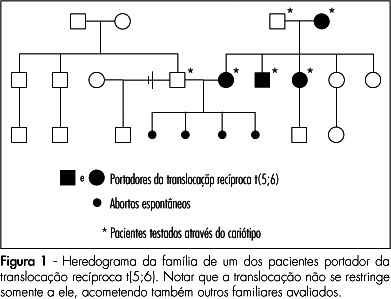
PURPOSE: to asses the prevalence and clinical characteristics of couples with history of recurrent spontaneous abortion and chromosome abnormality, attended at the present service. METHODS: all the couples referred to our service due to history of recurrent spontaneous abortion, from January 1975 to June 2008, were evaluated. Only the ones whose chromosome karyotype analysis by GTG bands has been successfully made were included in the study. Clinical data on their age, as well as on the number of abortions, stillbirth, multiple malformations, livebirth per couple, and the result of the karyotype exam were collected. Fisher's exact test (p<0.05) has been used to compare the incidence of chromosome alterations found in our study, with data in the literature. RESULTS: there were 108 couples in the sample. Their ages varied from 21 to 58 years old among the men (average of 31.4 years old), and from 19 to 43 among the women (average of 29.9 years old). In ten couples, one of the mates (9.3%) presented chromosome alterations, which corresponded respectively to three cases (30%) of reciprocal translocation [two of t(5;6) and one of t(2;13)], two (20%) of Robertsonian translocation [two of der(13;14) and one of der(13;15)], five(50%) of mosaicism (mos) [two cases of mos 45,X/46,XX, one of mos 46,XX/47,XXX, one of mos 46,XY/47,XXY and one of mos 46,XY/47,XYY] and one (10%) of chromosome inversion [inv(10)]. In one of the couples, the female presented two concomitant alterations: t(2;13) and der(13;14). Chromosome abnormalities were found in 5% of the couples with a history of two abortions, in 10.3% with three abortions, and in 14.3% with four or more abortions. CONCLUSIONS: the incidence of chromosome abnormalities seen in our study (9.3%) was similar to most of the studies carried out in the last 20 years, varying from 4.8 to 10.8%. Nevertheless the high percentage of patients with mosaicism in our sample, has called our attention. It is believed that this fact may be associated to the high number of metaphases ordinarily analyzed in the present service.