-
Original Article
Cervical Cancer Registered in Two Developed Regions from Brazil: Upper Limit of Reachable Results from Opportunistic Screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
06-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleCervical Cancer Registered in Two Developed Regions from Brazil: Upper Limit of Reachable Results from Opportunistic Screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
06-01-2018Views102Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to assess the time trends and pattern of cervical cancer diagnosed in the period from 2001 to 2012 by means of an opportunistic screening program from two developed regions in Brazil.
Methods
An observational study analyzing 3,364 cancer records (n = 1,646 from Campinas and n = 1,718 from Curitiba region) available in hospital-based cancer registries was done. An additional 1,836 records of CIN3/AIS from the region of Campinas was analyzed. The statistical analysis assessed the pooled data and the data by region considering the year of diagnosis, age-group, cancer stage, and histologic type. The Cochran-Armitage trend test was applied and p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
The total annual cervical cancer registered from2001 to 2012 showed a slight drop (273-244), with an age average of 49.5 y, 13 years over the average for CIN3/AIS (36.8 y). A total of 20.6% of the diagnoses (1.6% under 25 y) were done out of the official screening age-range. The biennial rate of diagnoses by age group for the region of Campinas showed an increase trend for the age groups under 25 y (p = 0.007) and 25 to 44 y (p = 0.003). Stage III was the most recorded for both regions, with an annual average of 43%, without any trend modification. There was an increasing trend for stage I diagnoses in the region of Campinas (p = 0.033). The proportion of glandular histologic types registered had an increased trend over time (p = 0.002), higher for the region of Campinas (21.1% versus 12.5% for the region of Curitiba).
Conclusion
The number, pattern and trends of cervical cancer cases registered had mild and slow modifications and reflect the limited effectivity of the opportunistic screening program, even in developed places.
Key-words Cervical cancerCervical intraepithelial neoplasiaEpidemiologypreventive medicinePublic healthSee more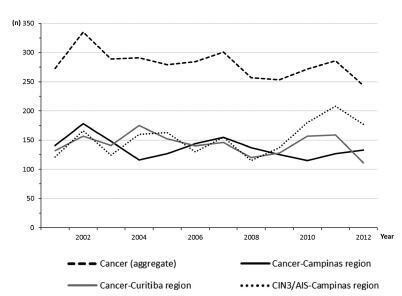
-
Original Article
Evaluation of the p16 and Ki-67 Biomarkers as Predictors of the Recurrence of Premalignant Cervical Cancer Lesions after LEEP Conization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):288-293
06-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleEvaluation of the p16 and Ki-67 Biomarkers as Predictors of the Recurrence of Premalignant Cervical Cancer Lesions after LEEP Conization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):288-293
06-01-2017Views134See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the expressions of biomarkers p16 and Ki-67 in low-grade (LG) or high-grade (HG) lesions, and to relate them to risk factors and the recurrence of these lesions.
Methods
A retrospective case-control study of 86 patients with LG and HG lesions who underwent a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) between 1999 and 2004. The control group was composed of 69 women with no recurrence, and the study group, of 17 patients with recurrence. All patients were followed-up over a two-year period after surgery, and screened every six months, including cytology and colposcopy. Biopsy samples collected from LEEP were submitted to immunohistochemical analysis for p16 and Ki-67. The statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software (SPSS, IBM-SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, US), with a significant p < 0.05.
Results
The biomarkers p16 and Ki-67, separately or combined, showed no relation to recurrence on the total analysis. However, evaluating specifically HG lesions, the positive expression (2+ and 3 + ) of p16/Ki-67 was associated with recurrence (0.010). In addition, p16 isolated was also more expressive in HG lesions (2+ and 3 + , p= 0.018), but it was unrelated to recurrence.
Conclusion
Proteins p16 and Ki-67, both isolated and combined, are not reliable primary markers for the recurrence of cervical lesions in the majority of LG lesions. However, analyzing only the group with prior diagnosis of HG lesions, the expressions of p16 and of p16/Ki-67 were associated with recurrence, and they may be useful in monitoring these cases.
-
Original Article
Underdiagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 2 orWorse Lesion inWomenwith a Previous Colposcopy-Guided Biopsy Showing CIN 1
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):123-127
03-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleUnderdiagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 2 orWorse Lesion inWomenwith a Previous Colposcopy-Guided Biopsy Showing CIN 1
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):123-127
03-01-2017Views141Abstract
Objective
Expectant follow-up for biopsy-proven cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 1 is the current recommendation for the management of this lesion. Nevertheless, the performance of the biopsy guided by colposcopy might not be optimal. Therefore, this study aimed to calculate the rate of underdiagnoses of more severe lesions in women with CIN 1 diagnosis and to evaluate whether age, lesion extent and biopsy site are factors associated with diagnostic failure.
Methods
Eighty women with a diagnosis of CIN 1 obtained by colposcopy-guided biopsy were selected for this study. These women were herein submitted to large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ). The prevalence of lesions more severe than CIN 1 was calculated, and the histological diagnoses of the LLETZ specimens were grouped into two categories: "CIN 1 or less" and "CIN 2 or worse."
Results
The prevalence of lesions diagnosed as CIN 2 or worse in the LLETZ specimens was of 19% (15/80). Three women revealed CIN 3, and 1 woman revealed a sclerosing adenocarcinoma stage I-a, a rare type of malignant neoplasia of low proliferation, which was not detected by either colposcopy or previous biopsy. The underdiagnosis of CIN 2 was not associated with the women's age, lesion extension and biopsy site.
Conclusions
The standard methods used for the diagnosis of CIN 1 may underestimate the severity of the true lesion and, therefore, women undergoing expectant management must have an adequate follow-up.
Key-words BiopsyCervical intraepithelial neoplasiacolposcopic surgical proceduresColposcopyNeoplasmsuterine cervicalSee more -
Original Article
Early Age at First Sexual Intercourse is Associated with Higher Prevalence of High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):80-85
02-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleEarly Age at First Sexual Intercourse is Associated with Higher Prevalence of High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):80-85
02-01-2017Views131See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the association of age at first sexual intercourse with the results of the cervicovaginal cytology.
Study Design
Observational analytical study about the prevalence of altered cervicovaginal cytology results in women aged between 18 and 34 years from a densely populated area in Brazil, during 10 years. The patients were stratified into 2 categories according to their age at first sexual intercourse (13-16 years and 17-24 years).
Results
From the total of 2,505,154 exams, 898,921 tests were in accordance with the inclusion criteria. Considering women with 4 years or less from the first sexual intercourse as a reference, those with 5 to 9 years and 10 years or more showed a higher prevalence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs). Women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse (13-16 years) showed higher prevalence ratios for atypical squamous cells (ASC), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and HSIL. The prevalence ratio for HSIL adjusted by age at diagnosis and by age at first sexual intercourse was higher only for women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse.
Conclusions
The age of first sexual intercourse could be a variable that might qualify the selection among young women who are really at a higher risk for HSIL.
-
Original Article
Incidence of Cervical Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Women with Positive and Negative HIV Status
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):231-238
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleIncidence of Cervical Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Women with Positive and Negative HIV Status
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):231-238
05-01-2016Views167Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the incidence and factors associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical infection by human papillomavirus (HPV) among HIV-positive and HIV-negative women.
Methods
A cohort of 103 HIV positive and 113 HIV negative women were monitored between October 2008 and February 2012, for at least one year. Procedures included cervical cytology, DNA/HPV detection by polymerase chain reaction, colposcopy with biopsy if necessary, followed by an interview for exposure characteristics data. CIN was based on the histopathological results.
Results
The incidence of CIN was of 8.8 and 4.6 cases/100 women-years in HIVpositive and HIV-negative women, respectively. HIV-positive women presented a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.8 for CIN and developed lesions earlier (0.86 year) than HIVnegative women (2 years) (p = 0.01). The risk of developing CIN decreased with age (HR = 0.9) and marital status (HR = 0.4). HPV patients presented a higher incidence of CIN when compared HIV-positive and HIV-negative women (p = 0.01). The incidence of HPV cervical infection was 18.1 and 11.4 cases/100 women-years in HIV-positive and HIV-negative women, respectively. Those HIV-positive presented earlier HPV infection (p = 0.002). The risk of developing HPV infection decreased with age and was higher among HIV-positive women. HPV 16 was the most common type in HIV-positive women, and also the type most closely associated with CIN in HIV-negative women.
Conclusions
HIV-positive women had a greater incidence of HPV and CIN, and in a shorter time interval. More rigorous and timely clinical control is required for this group.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaHIV infectionsHPV DNA probesPapillomavirus infectionsPolymerase chain reactionSee more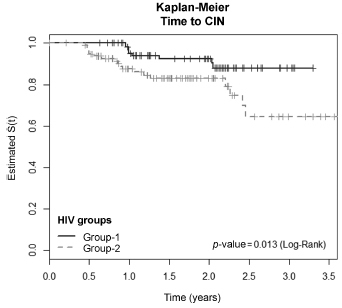
-
Original Articles
Expression of the Immunohistochemical Markers p16 and Ki-67 and Their Usefulness in the Diagnosis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasms
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):82-87
02-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesExpression of the Immunohistochemical Markers p16 and Ki-67 and Their Usefulness in the Diagnosis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasms
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):82-87
02-01-2016Views116See moreObjective
The aim of this study was to determine the expression of the immunohistochemical markers p16 and Ki-67 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasms and their influence on the level of agreement among different observers and for the same observer.
Methods
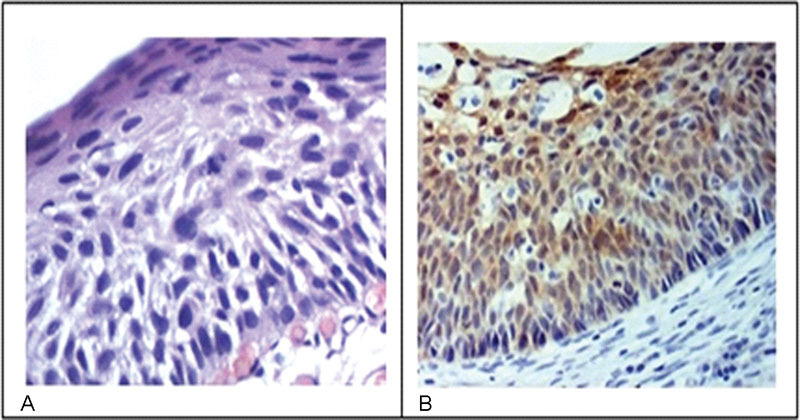
The study included 184 patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasms previously confirmed through biopsies performed between 2005 and 2006. Three pathologists reviewed the biopsies by using hematoxylin-eosin staining to reach a consensus on the diagnosis. Subsequently, an immunohistochemical study analyzed the expression of p16 and Ki-67 in such cases.
Results
The comparison among the reviewing pathologists revealed only moderate agreement (kappa = 0.44). The agreement improved when the differentiation of highgrade lesions (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm - CIN - 3) was analyzed (kappa = 0.59). p16 staining exhibited a high negative predictive value and sensitivity; however, the specificity was low. Overall, both qualitative and quantitative analyses of p16 and a quantitative analysis Ki-67 exhibited low accuracy. The agreement among diagnoses before immunohistochemistry was 0.47. The use of immunohistochemistry increased the agreement to 0.68.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the agreement among observers using traditional diagnostic criteria of cervical intraepithelial lesions can improve with the use of immunohistochemistry.
-
Artigos Originais
Prevalence of HPV-induced lesions in the anal canal among women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 and 3: cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):480-485
10-01-2015
Summary
Artigos OriginaisPrevalence of HPV-induced lesions in the anal canal among women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 and 3: cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):480-485
10-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005279
Views110See morePURPOSE:
To determine the prevalence of HPV-induced lesions in the anal canal of women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade 2/3.
METHODS:
A cross-sectional study was carried out from December 2008 to June 2009, in Pernambuco, northeastern Brazil. Only women with grade 2/3 CIN were included, and those who could not undergo anoscopy during their first visit were excluded. A cyttobrush was used for sample collection in order to identify HPV DNA through PCR and anal cytology. An anal biopsy was obtained in cases of abnormal anal cytology or major alterations in high resolution anoscopy (HRA).
RESULTS:
Thirty-two percent (n=37/115) of HRA were normal and 63.5% (n=73/115) showed acetowhite epithelium. Twenty-two percent (n=26/115) of anal cytologies were abnormal. Among the latter, 12.2% (n=14/26) were low-grade anal intraepithelial lesions and 3.4% (n=4/26) were high-grade anal intraepithelial lesions. Twenty-two anal biopsies were performed, 13.7% of which (n=3/22) were grade 2 anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN2) and 9% (n=2/22) were grade 3 AIN. Th HPV DNA was identified in 72.1% of cases (n=83/115).
CONCLUSION:
Women with CIN grade 2/3 showed a high prevalence of anal HPV infection and HPV-induced lesions.
-
Artigos Originais
Prevalence of cervical infection by human papillomavirus and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in HIV-positive and negative women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):178-185
04-01-2015
Summary
Artigos OriginaisPrevalence of cervical infection by human papillomavirus and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in HIV-positive and negative women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):178-185
04-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005184
Views107See morePURPOSE:
To conduct a comparative study between two groups of women (HIV positive and negative) analyzing: the prevalence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical HPV infection; viral risk and relationship with development of CIN; and sociodemographic and behavioral parameters that influence cervical HPV infection and the development of CIN.
METHODS:
A cross-sectional study in which 202 HIV-positive women and 164 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of CIN and 171 HIV-positive women and 160 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of cervical HPV infection. The following procedures were performed on the occasion of each medical visit: collection of cervical samples for cytology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect HPV DNA; colposcopy; standardized questionnaire to collect demographic and behavioral data; and biopsy of all colposcopic changes. Histopathology was the gold standard for the diagnosis of CIN.
RESULTS:
The prevalence of CIN was 2.4 and 15.3% (p<0.001) and the prevalence of cervical HPV infection was 37.1 and 55.5% (p=0.002), respectively, among HIV-negative and -positive women. HIV-positive women had a higher risk of HPV infection (35.7 and 23.6%) (p=0.02). HPV 16 was the most prevalent virus type, occurring in 11.3 and 10.2% of HIV-positive and negative women and was also more prevalent among women presenting CIN in both groups. Factors associated fwith the development of CIN were: HIV infection (HT=4.64; 95%CI 2.23-9.65), age (HT=0.95; 95%CI 0.93-0.98 for each year of life) and marital status(HT=0.49; 95%CI 0.30-0.80). Associated factors for HPV infection were: HIV presence (HT=2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.17), greater number of sexual partners (HT=1.87; 95%CI 1.23-2.84), age (HT=0.97; 95%CI 0.95-0.99 for each year of life) and marital status (HT=0.65; 95%CI 0.42-1.0 for stable union/widows).
CONCLUSION:
The prevalence of CIN and cervical HPV infection was higher in HIV-positive women, who also presented a higher risk of HPV infections and multiple viral types. Type 16 was predominant in both groups and in women with CIN. Older women and women with stable union/widows were less likely to acquire cervical HPV infection and CIN.


