Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):249-255
06-19-2019
The present study aimed to examine which development indicators are correlated with cervical cancer (CC) mortality rates in Brazil.
This was an ecological study that correlatedmortality rates and indicators, such as human development index (HDI), gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, illiteracy rate, fertility rate, screening coverage, proportion of private health insurance use, density of physicians, and density of radiotherapy centers. Themortality rateswere obtained fromthe Brazilian national registry, while the indicators were based on official reports from the Ministry of Health. Univariate and multivariate linear regression was used.
Among the states of Brazil, the average age-specific CC mortality rate from 2008 to 2012 varied from 4.6 to 22.9 per 100,000 women/year. In the univariate analysis, HDI, proportion of private health insurance use, density of physicians, and density of radiotherapy centers were inversely correlated with the mortality rates. Fertility rate was positively correlated with the mortality rates. In the multivariate analysis, only fertility rate was significantly associated with the CC mortality rate (coefficient of correlation: 9.38; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.16-13.59).
A decrease in the fertility rate, as expected when the level of development of the regions increases, is related to a decrease in the mortality rate of CC. The results of the present study can help to better monitor the quality assessment of CC programs both among and within countries.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):800-802
12-01-2018
To describe a case of radiation-induced uterine carcinosarcoma 6 years after a cervical squamous cell carcinoma treatment, which imposed some diagnostic and management challenges.
A 57-year-old woman with a history of pelvic chemoradiotherapy ~ 6.5 years before the event described in this study, following an International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IIB cervical cancer, presented with a cervical mass, involving the uterine cavity, the cervical canal and the upper two thirds of the vagina. The biopsy showed a poorly differentiated carcinoma, and a positron emission tomography (PET) scan excluded distant metastasis, although it was unable to define the origin of the tumor as either a new primary malignancy of the endometrium/cervix or as a cervical recurrence. Surgical staging procedure was performed, and the diagnosis was endometrial carcinosarcoma, FIGO stage IIB. The patient was not able to complete the adjuvant therapy, and the progression of the disease was remarkable.
The present case highlights one of the less common but more serious consequences of radiotherapy for cervical cancer, which has an increasing incidence in younger women, raising concerns about the long-termconsequences of its management.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
06-01-2018
The aim of this study was to assess the time trends and pattern of cervical cancer diagnosed in the period from 2001 to 2012 by means of an opportunistic screening program from two developed regions in Brazil.
An observational study analyzing 3,364 cancer records (n = 1,646 from Campinas and n = 1,718 from Curitiba region) available in hospital-based cancer registries was done. An additional 1,836 records of CIN3/AIS from the region of Campinas was analyzed. The statistical analysis assessed the pooled data and the data by region considering the year of diagnosis, age-group, cancer stage, and histologic type. The Cochran-Armitage trend test was applied and p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
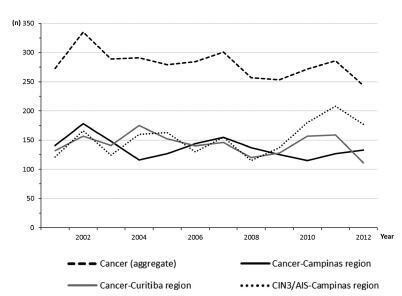
The total annual cervical cancer registered from2001 to 2012 showed a slight drop (273-244), with an age average of 49.5 y, 13 years over the average for CIN3/AIS (36.8 y). A total of 20.6% of the diagnoses (1.6% under 25 y) were done out of the official screening age-range. The biennial rate of diagnoses by age group for the region of Campinas showed an increase trend for the age groups under 25 y (p = 0.007) and 25 to 44 y (p = 0.003). Stage III was the most recorded for both regions, with an annual average of 43%, without any trend modification. There was an increasing trend for stage I diagnoses in the region of Campinas (p = 0.033). The proportion of glandular histologic types registered had an increased trend over time (p = 0.002), higher for the region of Campinas (21.1% versus 12.5% for the region of Curitiba).
The number, pattern and trends of cervical cancer cases registered had mild and slow modifications and reflect the limited effectivity of the opportunistic screening program, even in developed places.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):35-39
01-01-2017
Robotic surgeries for cervical cancer have several advantages compared with lapa-rotomic or laparoscopic surgeries. Robotic single-site surgery has many advantages compared with the multiport approach, but its safety and feasibility are not established in radical oncologic surgeries. We report a case of a Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IB1 cervical carcinoma whose radical hysterectomy, sentinel lymph node mapping, and lymph node dissection were entirely performed by robotic single-site approach. The patient recovered very well, and was discharged from the hospital within 24 hours.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):65-70
02-01-2016
The objective of this study is to assess the performance of cytopathology laboratories providing services to the Brazilian Unified Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde - SUS) in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil.
This descriptive study uses data obtained from the Cervical Cancer Information System from January to December 2012. Three quality indicators were analyzed to assess the quality of cervical cytopathology tests: positivity index, percentage of atypical squamous cells (ASCs) in abnormal tests, and percentage of tests compatiblewith high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs). Laboratories were classified according to their production scale in tests per year≤5,000; from 5,001 to 10,000; from 10,001 to 15,000; and 15,001. Based on the collection of variables and the classification of laboratories according to production scale, we created and analyzed a database using Microsoft Office Excel 97-2003.
In the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais, 146 laboratories provided services to the SUS in 2012 by performing a total of 1,277,018 cervical cytopathology tests. Half of these laboratories had production scales≤5,000 tests/year and accounted for 13.1% of all tests performed in the entire state; in turn, 13.7% of these laboratories presented production scales of > 15,001 tests/year and accounted for 49.2% of the total of tests performed in the entire state. The positivity indexes of most laboratories providing services to the SUS in 2012, regardless of production scale, were below or well below recommended limits. Of the 20 laboratories that performed more than 15,001 tests per year, only three presented percentages of tests compatible with HSILs above the lower limit recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health.
The majority of laboratories providing services to the SUS in Minas Gerais presented quality indicators outside the range recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):75-80
08-16-2006
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200002
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) and cancer in women with cytological diagnosis of persistent ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) for 6 months in the last 7 years. We also assessed if age could be a predictive factor for presence of HSIL/cancer in this group. METHODS: we included 215 cases of non-pregnant and HIV-seronegative women with cytological diagnosis of persistent ASCUS (unespecific) with at least 6 months of interval between smears. This cytological diagnosis was compared to histological diagnosis obtained by biopsy (large loop excision of the transformation zone) or cone biopsies, and considered negative when colposcopy was satisfactory without lesions or, when unsatisfactory, no lesion was detected after at least one cytological and colposcopic follow-up. RESULTS: among the 215 cases, 49.3% had negative results (CI 95%: 42.6-55.9). The prevalence of histological confirmed low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion was 38.6% (CI 95%: 32.1- 45.1) and HSIL was 10.7% (CI 95%: 6.5-14.8). Cases of cancer were found in 1.4% of patients (CI 95%: 0-2.9). We could not find a significant difference between the prevalence of HSIL/cancer according to age group using the cutoff point of 35 years. CONCLUSION: HSIL/cancer prevalence observed in this study has shown the risk of finding this kind of lesions in about 12% of women assisted in our public health system with two cytological diagnosis of ASCUS. A higher probability of HSIL/cancer in the different age groups was not found but this result was limited by our small sample size.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(2):81-86
07-04-2003
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000200002
PURPOSE: to describe the frequency of precursor lesions of cervical cancer in 15 to 29-year-old women, associating the degree of damage with the epidemiologic characteristics and associated risk factors. METHODS: a transverse study was performed, where the precursor lesions of cervical cancer were investigated through Papanicolaou test in 15 to 29 year-old women with active sexual life, living in Rio Branco (AC), in the period from January to September 2001. The investigated data included epidemiologic information, risk factors and physical-ginecological examination results, including Schiller test and smears for cytopathologic test. RESULTS: of the 2,397 women studied, 155 (6.4%) showed some kind of cellular epithelial alteration, 146 (94.2%) squamous lesions and 9 (5.8%) glandular lesions. In 15 to 19 year old women, the frequency (6.9%) of cellular epithelial alteration was similar to that observed in 20 to 29-year-old women (p>0.65). These alterations were associated with low educational level (p<0.003), with the number of sexual partners (p<0.04), with STD history (p<0.001) and smoking habits (p<0.01). CONCLUSION: the high frequency of precursor lesions in an age lower than expected, and following an epidemiologic pattern observed in other phases of women's life, shows the early exposure to risk factors, which anticipates the development of cervical cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):209-215
06-27-2001
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400003
Purpose: to evaluate a populational sample of the screening proposed by the National Program of Uterine Cervical Cancer Control (PNCC), regarding the following issues: frequency of unsatisfactory cytologic results, cytologic frequency of atypical squamous or glandular cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS, AGCUS), low- or high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL), comparing the cytologic results with anatomicopathological results of colposcopically directed biopsies. Methods: through the written, broadcasting television and oral midia, women between 35 and 49 years were requested to have a preventive cytopathological test, to be collected by the authorized public health or other institutions accredited by SUS. The slides were analyzed by the program-authorized laboratories and all those patients from the populational sample from the municipality of Naviraí in the State of Mato Grosso do Sul with cellular alterations were submitted to colposcopy and directed biopsy. Results: the frequency of cytologic alterations of the ASCUS, AGCUS and SIL types was 3.3%, an index that is close to that predicted by the PNCC (4%); the percentage of samples that were unsatisfactory for evaluation was high (12.5%); among the ASCUS, AGCUS or low grade-SIL patients, 27.3% presented intraepithelial lesions of a high grade in the anatomicopathological study; while patients with cytology compatible with high grade-SIL, the directed biopsy revealed that 12.5% presented low-grade intraepithelial lesions. Conclusions: the choice of oncological cytology as the only method for the screening in the program allowed high indexes of false-negatives (27.3%) and of false-positives (12.5%). In the screening of cervical neoplasms, colposcopy has shown to be an important and indispensable method to guide the therapeutical management to be adopted.
