Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):620-625
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200006
PURPOSE: to compare delivery and pregnancy follow-up among adolescent and non-adolescent pregnant women whose delivery occurred in a tertiary hospital from Região de Lisboa (Portugal). METHODS: retrospective study with 10,656 deliveries. Pregnancy follow-up, delivery type, need of episiotomy and severe lacerations, Apgar index at the fifth minute and the delivery weight have been evaluated. The pregnant women were divided into two groups, over and under 20 years old. The group with women under 20 was further subdivided in pregnant women under or over 16. The χ2 test has been used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: adolescents presented worse follow-up: first appointment after 12 weeks (46.4 versus 26.3%) and less than four appointments (8.1 versus 3.1%), less dystocia (21.5 versus 35.1%), less caesarian sections (10.6 versus 20.7%), and lower need for inducing labor (16.5 versus 26.5%). There was no significant difference concerning gestational age at delivery and ratio of low weight newborns. Among adolescents, the ones under 16 had more low weight newborns (12 versus 7.4%) and more deliveries between 34 and 37 weeks (10.8 versus 4.2%). CONCLUSIONS: in a hospital attending adolescents with social and psychological support, the fact of them having had a worse follow-up in the pre-natal phase, their performance has not been worse. Nevertheless, special attention might be given to pregnant women under 16.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):619-626
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000009
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of cytologic, colposcopic and histopathologic alterations observed in the uterine cervix of adolescents with suspected cervical neoplasia and to compare it with young adult women. METHODS: a cross-sectional, retrospective study that analyzed 366 medical records of females referred to clarify diagnosis of the suspected cervical neoplasia. The patients had been classified into two groups defined by age. The Adolescent group was composed of 129 females between 13 and 19 years and the Adult group was composed of 237 females between 20 and 24 years. Data were analyzed statistically by the prevalence ratio (PR), respective confidence intervals (CI) at 95% for each variable, chi2 test, or Fisher exact test used to compare proportion. RESULTS: the first sexual intercourse coitarche occurred on average at 15.0 years in the Adolescent group and 16.6 years in the Adult group. The possibility of diagnosis of cytological alterations in the first Papanicolaou smears (PR=2.61; CI 95%: 2.0-3,4), the condition of non-clarified cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) (PR=1.78; CI 95%: 1.26-2,52), and the colposcopic impressions of low grade (PR=1.42; CI 95%: 1.08-1.86) were statistically significant in the Adolescent group. The histopathologic analysis did not show differences at any grade of CIN. However, two cases of microinvasive carcinoma, one in each group, and three cases of clinical invasive carcinoma in the Adult group were identified. CONCLUSION: our study suggests that cervical cancer is rare among adolescents, but we verified that alterations associated with it occurred even in younger women. The evaluation of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with the careful application of the same tools used for adult women was appropriate also in adolescence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):509-514
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the luteal function in adolescents with regular menstrual cycles. METHODS: this prospective cohort study included 55 adolescents, aged 14-19 years, with menarche at 12.2 years. Ovulation was identified by ultrasound, starting on the second or fifth day of the cycle. The corpus luteum vascularization and the resistence index of the ovarian vessels were measured by Doppler on the tenth postovulatory day. Progesterone was measured by chemoluminescence on days 6, 9 and 12 of the luteal phase. The endometrial biopsy was performed 8 to 10 days after ovulation. The results were analyzed using the SPSS software and were considered significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: on average ovulation was on day 17. Progesterone levels were 11.4, 10.9 and 3.9 ng/mL on days 6, 9, and 12 after ovulation, respectively; the progesterone mean during the whole luteal phase was 10.3 ng/ml. Luteal vascularization was scarce in 34.6%, mild in 23.6% and exuberant in 41.8%. The resistance index was 0.441. On the tenth day post-ovulation the endometrium was normal in 85.5% and out-of-phase in 14.5%. There was no correlation between the ovulation day and endometrial dating (p=0.294), levels of progesterone and endometrial dating (p=0.454), progesterone and corpus luteum vascularization (p=0.994), or resistance index (p=0.237). There also was no association between endometrium development and degree of vascularization (p=0.611). CONCLUSION: abnormal luteal function in adolescents with regular menstrual cycles was found in 14.5%. Degree of vascularization, resistance index, and serum progesterone were not related to endometrium development.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(10):731-738
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003001000006
PURPOSE: to evaluate, in pregnant adolescents, the incidence of iron deficiency, using the following blood tests: hemoglobin, ferritin, serum iron, transferrin saturation rate and serum transferrin receptor, and their relationships. METHODS: a total of 56 adolescents were included at the first prenatal evaluation between the 12th and the 20th week of gestation. The normal values for each test were: above 11 mg/dL for hemoglobin, 12 µg/dL for ferritin, 50 mg/L for serum iron, 16% for transferrin saturation rate and below 28.1 nmol/L for serum transferrin receptor. Each result was evaluated using percentages and the McNemar test was used to compare the results. RESULTS: incidence of anemia using the hemoglobin concentration test was 21.4%. All pregnant women presented mild anemia. In the present study, 21.4% of the patients had iron deficiency with a ferritin concentration <12 mug/dL. Serum iron concentration was reduced in 3.6% of the adolescents and transferrin saturation rate in 26.8% of the sample. The value obtained by the transferrin receptor test was unclear, due to the lack of international standardization regarding measure unit. Comparing the hemoglobin concentration test to the other iron deficiency tests, it was found that the latter do not show a better evaluation than the hemoglobin concentration test in patients with hypoferremia. CONCLUSIONS: the hemoglobin concentration test in patients with mild anemia was effective to identify iron deficiency.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(2):81-86
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000200002
PURPOSE: to describe the frequency of precursor lesions of cervical cancer in 15 to 29-year-old women, associating the degree of damage with the epidemiologic characteristics and associated risk factors. METHODS: a transverse study was performed, where the precursor lesions of cervical cancer were investigated through Papanicolaou test in 15 to 29 year-old women with active sexual life, living in Rio Branco (AC), in the period from January to September 2001. The investigated data included epidemiologic information, risk factors and physical-ginecological examination results, including Schiller test and smears for cytopathologic test. RESULTS: of the 2,397 women studied, 155 (6.4%) showed some kind of cellular epithelial alteration, 146 (94.2%) squamous lesions and 9 (5.8%) glandular lesions. In 15 to 19 year old women, the frequency (6.9%) of cellular epithelial alteration was similar to that observed in 20 to 29-year-old women (p>0.65). These alterations were associated with low educational level (p<0.003), with the number of sexual partners (p<0.04), with STD history (p<0.001) and smoking habits (p<0.01). CONCLUSION: the high frequency of precursor lesions in an age lower than expected, and following an epidemiologic pattern observed in other phases of women's life, shows the early exposure to risk factors, which anticipates the development of cervical cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):513-519
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800003
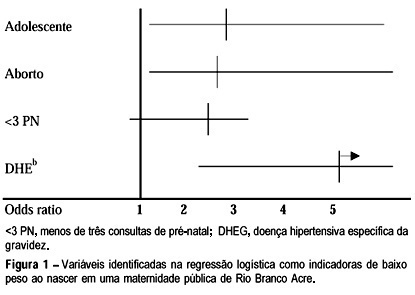
Purpose: to study pregnancy in adolescent women as a possible risk factor for low birth weight. Material and Methods: a cross-wide study was performed on 562 adolescent and non-adolescent mothers who were interviewed during the first 24 h after delivery in the period from January 10,2002, to March 25, 2002, in a public maternity hospital located in Rio Branco, Acre State, Brazil. Those who delivered dead fetuses, whose babies died after being born, or had twins were excluded from the study. Results: among the 562 mothers who were studied, 37.0% (n=208) were teenagers (16±1.6 years), and 63.0% (n=354) were 20 or more years old (22.9±6.3 years). The average weight of the newborns was statistically higher (p<0.010) among the adult mothers (3,158.64±626.50 g) than among the adolescent mothers (3,019.93±587.43 g). When the 32 (5.7%) premature newborn babies (<37 week's pregnancy) were excluded, there was also a significantly greater proportion (p<0.007) of newborns with low weight (<2,500 g) among the adolescent mothers (11.9%) than among the non-adolescent ones (5.5%). The analysis of logistic regression showed an increased risk for newborns with low weight among the adolescent mothers (OR=2.99; 1.47-6.07), as well as for abortion (OR=2.78; 1.23-6.30) and pregnancy - induced hypertensive disorders (OR=5.16; 1.65-16.12). Conclusions: the present study shows that associated with the psychosocial, familial, and economic impact, already reported in the literature, pregnancy in adolescents is associated with deleterious effects on the conceptus, which requires a cohort study to assess the repercussions at both the medium- and long-term.