Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):209-215
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400003
Purpose: to evaluate a populational sample of the screening proposed by the National Program of Uterine Cervical Cancer Control (PNCC), regarding the following issues: frequency of unsatisfactory cytologic results, cytologic frequency of atypical squamous or glandular cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS, AGCUS), low- or high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL), comparing the cytologic results with anatomicopathological results of colposcopically directed biopsies. Methods: through the written, broadcasting television and oral midia, women between 35 and 49 years were requested to have a preventive cytopathological test, to be collected by the authorized public health or other institutions accredited by SUS. The slides were analyzed by the program-authorized laboratories and all those patients from the populational sample from the municipality of Naviraí in the State of Mato Grosso do Sul with cellular alterations were submitted to colposcopy and directed biopsy. Results: the frequency of cytologic alterations of the ASCUS, AGCUS and SIL types was 3.3%, an index that is close to that predicted by the PNCC (4%); the percentage of samples that were unsatisfactory for evaluation was high (12.5%); among the ASCUS, AGCUS or low grade-SIL patients, 27.3% presented intraepithelial lesions of a high grade in the anatomicopathological study; while patients with cytology compatible with high grade-SIL, the directed biopsy revealed that 12.5% presented low-grade intraepithelial lesions. Conclusions: the choice of oncological cytology as the only method for the screening in the program allowed high indexes of false-negatives (27.3%) and of false-positives (12.5%). In the screening of cervical neoplasms, colposcopy has shown to be an important and indispensable method to guide the therapeutical management to be adopted.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):209-214
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400005
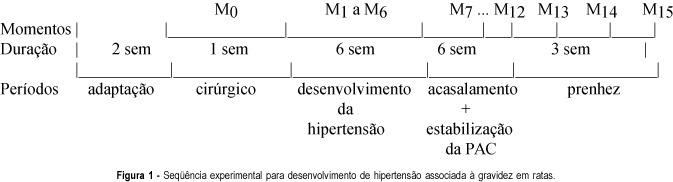
Purpose: to develop an experimental model in rats to study the interaction between hypertension and pregnancy. Methods: the present experiment was divided into 5 periods: adaptation (2 weeks), surgical procedures (1 week), hypertension development (6 weeks), mating and blood pressure stabilization (6 weeks), and gestational period (3 weeks). A total of 82 animals in reproductive age, weighing from 180 to 240 g, were used. They were randomly assigned to the 4 different groups (control, handled, nephrectomy and hypertension) and renal hypertension was produced by a controlled constriction of the main left renal artery, according to the technique described by Goldblatt, and contralateral nephrectomy (Goldblatt I - one kidney, one clip hypertension). They were studied at 15 precise moments. Afterwards, periodic blood pressure determinations were made by the tail plethysmographic method. Results: pregnancy caused a fall in blood pressure levels in the rat. Conclusion: the experimental model was adequate for the purposes of the study, since it proved to be efficient in producing hypertension.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):209-213
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400006
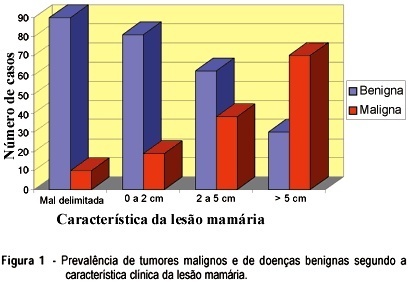
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple method and free from complications, among great value in mastology. Its accuracy can suffer the influence of several factors, among which we can highlight the experience of the physician who performs it. With the objective of verifying the effectiveness of FNAC performed by general gynecologists, 341 patients were studied concerning the relationship between the results of FNAC and the histology of the breast lesion. We obtained sensitivity of 70.87%, specificity of 70.58%, predictive positive value of 92.40%, predictive negative value of 89.36% and accuracy of 70.67%. We concluded that FNAC is of great value in handling breast lesions and can be appropriately performed by general gynecologists. The method, however, may lead to errors of diagnosis. We do not recommend, therefore, the use of the result of FNAC as a definitive diagnosis; instead this result must be interpreted in the context of the clinical diagnosis and mammography.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):209-224
To review the existing recommendations on the prenatal care of women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), based on currently available scientific evidence.
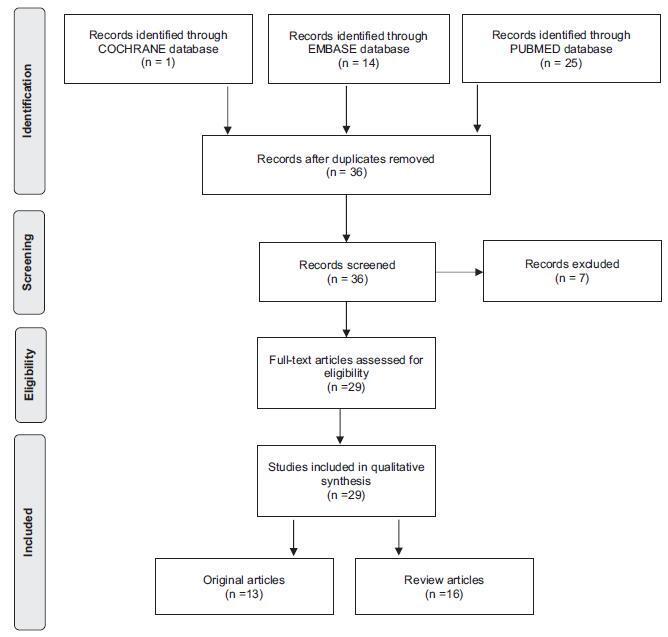
An integrative review was performed by two independent researchers, based on the literature available in the MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE and The Cochrane Library databases, using the medical subject headings (MeSH) terms “systemic lupus erythematosus” AND “high-risk pregnancy” OR “prenatal care.” Studies published in English between 2007 and 2017 were included; experimental studies and case reports were excluded. In cases of disagreement regarding the inclusion of studies, a third senior researcher was consulted. Forty titles were initially identified; four duplicates were excluded. After reading the abstracts, 7 were further excluded and 29 were selected for a full-text evaluation.
Systemic lupus erythematosus flares, preeclampsia, gestation loss, preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and neonatal lupus syndromes (mainly congenital heartblock) were the major complications described. The multidisciplinary team should adopt a specific monitoring, with particular therapeutic protocols. There are safe and effective drug options that should be prescribed for a good control of SLE activity.
Pregnant women with SLE present an increased risk for maternal complications, pregnancy loss and other adverse outcomes. The disease activity may worsen and, thereby, increase the risk of other maternal-fetal complications. Thus, maintaining an adequate control of disease activity and treating flares quickly should be a central goal during prenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):209-216
In 2013, it was estimated that 289,000 maternal deaths occurred worldwide. The maternal mortality ratio has decreased in many countries in the past decades, due to early identification and treatment of obstetric complications, despite the dissimilarities observed in diverse locations and populations. Black women, for instance, have always been more susceptible to the occurrence of maternal mortality and severe morbidity. Therefore, the objective of this study is to assess skin color as a predictive factor for maternal near miss (MNM) in a sample of Brazilian women interviewed in the Brazilian National Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) of 2006.
A secondary analysis of the DHS database, a population-based crosssectional nationally representative study was conducted. This database is of public domain. The risk of maternal complications according to ethnic group and the associated sociodemographic characteristics were evaluated. For the data analysis, the odds ratios and respective 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
In the sample interviewed, 59% of women were black or brown (mixed-race). Approximately 23% of women had some complication, and 2% of these women had at least one MNM pragmatic criterion. The MNM rate was 31 per 1,000 live births, and its occurrence was not statistically different among the ethnic groups. The only factors identified that were considered to be associated with the occurrence of MNM were maternal age above 40 and women not currently attending school, but only among white women.
The 2006 DHS results did not show a higher occurrence of maternal complications, and specifically of MNM associated with black/brown skin color.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):21-25
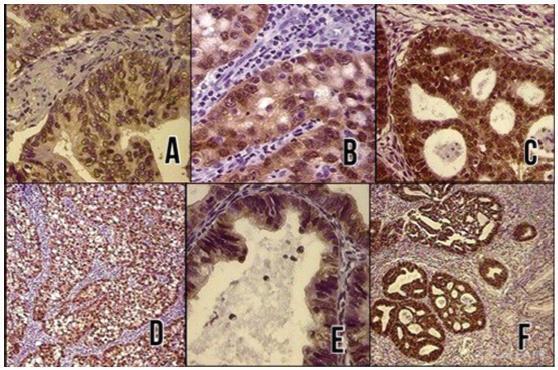
To evaluate the diagnostic utility of the p16ink4a protein expression as a marker for adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
In a cross-sectional study, p16ink4a expression was evaluated in 30 cervical biopsies from patients diagnosed with invasive adenocarcinoma from 2 reference clinics in Brazil, and compared with 18 biopsies of endocervical polyps (control cases). The performance of the tests for p16ink4a was evaluated using a conventional contingency table, and the Kappa (k) index was used to evaluate the agreement of the marker with the tissue diagnosis.
In total, 66% of the invasive adenocarcinoma cases were positive for p16ink4a. All of the adenomatous polyps cases used as negative controls were shown to be negative for p16ink4a. The marker showed a high sensitivity and a high negative predictive value. The Kappa index was good for p16ink4a (k 1/4 0.6).
Considering the strong association between the p16ink4a marker and the cervical adenocarcinoma, its use represents an important tool for reducing incorrect diagnoses of adenocarcinoma and thereby avoiding overtreatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):21-29
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100004
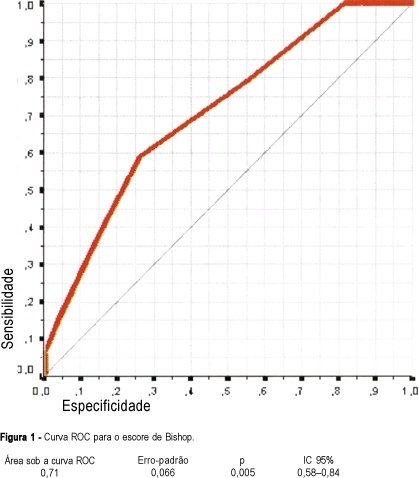
PURPOSE: to determine the main factors associated with vaginal delivery in high-risk pregnant women submitted to labor induction with vaginal misoprostol (50 µg). METHODS: this is a secondary analysis of an open nonrandomized clinical trial that included 61 high-risk pregnant women admitted at the "Maternidade-Escola Assis Chateaubriand", Fortaleza (Ceará). All women had singleton pregnancies with alive fetuses, gestational age >37 weeks and Bishop scores <7. Misoprostol was vaginally administered at doses of 50 µg every 6 h for a maximum of four doses. Univariate and multiple logistic regression analyses were performed to determine association between vaginal delivery (dependent variable) and independent variables (predictive), and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed for parity and Bishop scores. RESULTS: parity (one or more previous deliveries), Bishop scores >4 and interval induction to delivery <6 h were significantly associated with vaginal delivery, while tachysystole reduced the probability of vaginal delivery. A multivariate stepwise logistic regression was then performed to evaluate each of these as independent predictors. Parity (OR = 5.41, 95% CI = 4.18-6.64) and Bishop score >4 (OR = 3.30, 95% CI = 2.15-4.45) were significant independent predictors for vaginal delivery. In the ROC curve for parity and Bishop score, sensitivity of 63.2% and positive predictive value of 100% were found. The area under the ROC curve was 86.8%, significantly higher than 50% (p=0.023). CONCLUSIONS: the most important predictive factors for vaginal delivery after induction with misoprostol were parity and Bishop score. These characteristics should be considered when choosing schemes and doses of misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction.