You searched for:"Marcelo Zugaib"
We found (76) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2009;31(8):415-422
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800008
The main purpose of using uterulytic in preterm delivery is to prolong gestation in order to allow the administration of glucocorticoid to the mother and/or to accomplish the mother's transference to a tertiary hospital center. Decisions on uterolytic use and choice require correct diagnosis of preterm delivery, as well as the knowledge of gestational age, maternal-fetal medical condition, and medicine's efficacy, side-effects and cost. All the uterolytics have side-effects, and some of them are potentially lethal. Studies suggest that beta-adrenergic receptor agonists, calcium blockers and cytokine receptor antagonists are effective to prolong gestation for at least 48 hours. Among these three agents, atosiban (a cytokine receptor antagonist) is safer, though it presents a high cost. Magnesium sulfate is not efficient to prolong gestation and presents significant side-effects. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors also present significant side-effects. Up till now, there is not enough evidence to recommend the use of nitric oxid donors to inhibit preterm delivery. There is no basis for the use of antibiotics to avoid prematurity in face of preterm labor.
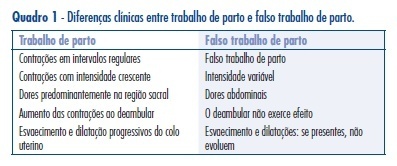
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(9):420-425
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900002
PURPOSE: to compare the patterns of fetal heart rate (FHR) in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective and comparative study performed between January 2008 and July 2009. The inclusion criteria were: singleton pregnancy, live fetus, pregnant women without clinical or obstetrical complications, no fetal malformation, gestational age between 24 and 27 weeks (2nd trimester - 2T) or between 36 and 40 weeks (3rd trimester - 3T). Computerized cardiotocography (System 8002 - Sonicaid) was performed for 30 minutes and the fetal biophysical profile was obtained. System 8002 analyzes the FHR tracings for periods of 3.75 seconds (1/16 minutes). During each period, the mean duration of the time intervals between successive fetal heart beats is determined in milliseconds (ms); the mean FHR and also the differences between adjacent periods are calculated for each period. The parameters included: basal FHR, FHR accelerations, duration of high variation episodes, duration of low variation episodes and short-term variation. The dataset was analyzed by the Student t test, chi-square test and Fisher's exact test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: eighteen pregnancies on the second trimester were compared to 25 pregnancies on the third trimester. There was a significant difference in the FHR parameters evaluated by computerized cardiotocography between the 2T and 3T groups, regarding the following results: mean basal FHR (mean, 143.8 bpm versus 134.0 bpm, p=0.009), mean number of transitory FHR accelerations > 10 bpm (3.7 bpm versus 8.4 bpm, p <0.001) and >15 bpm (mean, 0.9 bpm versus 5.4 bpm, p <0.001), mean duration of high variation episodes (8.4 min versus 15.4 min, p=0.008) and mean short - term variation (8.0 ms versus 10.9 ms, p=0.01). The fetal biophysical profile showed normal results in all pregnancies. CONCLUSION: the present study shows significant differences in the FHR characteristics when the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy are compared and confirms the influence of autonomic nervous system maturation on FHR regulation.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(7):421-428
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700004
Purpose: to evaluate 24 cases of gastroschisis, in relation to the prognostic factors that interfered with postnatal outcome. Patients and Method: twenty-four pregnancies with fetal prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of gastroschisis, during an 8-year period, were analyzed. Gastroschisis was classified into isolated, when there were no other structural abnormalities, or associated, when other abnormalities were present. For both groups the following parameters were examined: ultrasound bowel dilatation (>18 mm), obstetric complications and postnatal outcome. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney and exact Fisher's tests were used for statistical analyses. Results: in 9 cases (37.5%) gastroschisis was associated with other abnormalities, and in 15 cases it was isolated (62.5%). All cases of associated gastroschisis had a letal prognosis, therefore the overall mortality rate was 60.8%. In the group of isolated gastroschisis, all were born alive and were submitted to surgery, but the survival rate after surgical correction was 60%. The median gestational age at birth was 35 weeks and birth weight 2,365 grams. Premature delivery was observed in 10 cases, mainly as a consequence of obstetric complication. Two newborns were small for gestational age, and only 3 had birth weight >2,500 grams. Oligohydramnios was found in 46.6% and it was more frequent in the group of postnatal death (66.7%). Ultrasound assessment of bowel showed bowel dilatation in 86.6%, however, without relation to the prognosis and postnatal bowel findings. There was no significant difference between gestational age at birth and birth weight comparing the survivor and postnatal death groups. Conclusions: isolated gastroschisis had a better prognosis when compared to associated, therefore this prenatal differentiation is important. Isolated gastroschisis was often associated with prematurity, small birth weight and obstetric complications. Prenatal diagnosis allows better monitoring of fetal and obstetric conditions. Delivery should be at term, unless presenting with obstetric complications.
Summary
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(8):453-459
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800003
PURPOSE: to analyze the fetal heart rate (FHR) and umbilical artery Dopplervelocimetry between 18th and 20th weeks of gestation in pregnant women complicated by pregestational diabetes mellitus. METHODS: twenty-eight pregnancies with pregestational diabetes and 27 normal pregnant women were analyzed prospectively, in a cross-sectional and case-control study. The inclusion criteria were the following: singleton pregnancy between 18 and 29 weeks, no other associated maternal diseases and no fetal abnormality. Ultrasonography was performed and FHR was calculated by the interval between the beginnings of two consecutive cardiac cycles, in the three umbilical artery Doppler sonograms, obtained in the umbilical cord near to the placental insertion, using color Doppler. Five consecutive FHR cycles from each sonogram were measured, to analyze mean FHR and its variation. The following Doppler indices were studied: systolic/diastolic ratio, pulsatility index (PI) and resistance index (RI). Student's t test and Mann-Whitney Utest were applied to comparative study. p values were considered significant when p<0.05. Results: no significant difference was observed in mean FHR between the studied groups (diabetic group: 149.2 bpm, control group: 147.2 bpm; p = 0.12). FHR variation revealed similar results between the groups (diabetic group: 5.3 bpm; control group: 5.3 bpm; p=0.50). No significant difference was found in the Doppler indices S/D (p=0.79), PI (p=0.25) and RI (p=0.71) between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: the absence of differences in FHR characteristics between the 18th and 20th gestational weeks indicates similar neurological maturation of FHR regulatory systems in this period, between fetuses of diabetic mothers and controls. Abnormalities in the uteroplacental resistance were not identified in the studied period, in pregnancies complicated by pregestational diabetes.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(10):455-459
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005271
To analyze the obstetrical and neonatal outcomes of pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses after 35 weeks based on umbilical cord nucleated red blood cells count (NRBC).
NRBC per 100 white blood cells were analyzed in 61 pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses and normal Doppler findings for the umbilical artery. The pregnancies were assigned to 2 groups: NRBC≥10 (study group, n=18) and NRBC<10 (control group, n=43). Obstetrical and neonatal outcomes were compared between these groups. The χ2 test or Student's t-test was applied for statistical analysis. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The mean±standard deviation for NRBC per 100 white blood cells was 25.0±13.5 for the study group and 3.9±2.2 for the control group. The NRBC≥10 group and NRBC<10 group were not significantly different in relation to maternal age (24.0 versus 26.0), primiparity (55.8 versus 50%), comorbidities (39.5 versus55.6%) and gestational age at birth (37.4 versus 37.0 weeks). The NRBC≥10 group showed higher rate of caesarean delivery (83.3 versus 48.8%, p=0.02), fetal distress (60 versus 0%, p<0.001) and pH<7.20 (42.9 versus 11.8%, p<0.001). The birth weight and percentile of birth weight for gestational age were significantly lower on NRBC≥10 group (2,013 versus 2,309 g; p<0.001 and 3.8 versus 5.1; p=0.004; respectively). There was no case described of 5th minute Apgar score below 7.
An NRBC higher than 10 per 100 white blood cells in umbilical cord was able to identify higher risk for caesarean delivery, fetal distress and acidosis on birth in small for gestational age fetuses with normal Doppler findings.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(7):463-468
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000700006
Purpose: to evaluate, in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, the correlation between cervical length and spontaneous preterm delivery. Methods: cervical length was evaluated in 641 pregnant women between 11-16 weeks' and 23-24 weeks' gestation. Cervical assessment was performed by a transvaginal scan with the patient with empty bladder in a gynecological position. Cervical length was measured from the internal to the external os. The gestational age at delivery was correlated with the length of the cervix. To compare the means in groups of pregnant women who had a term or preterm delivery, we used Student's t test. Sensitivity, specificity, false-positive and false-negative rates, and accuracy were calculated for cervical length of 20 mm or less, 25 mm or less and 30 mm or less in the prediction of preterm delivery. Results: the measurement of cervical length, between 11 and 16 weeks of pregnancy, did not show any statistically significant difference on comparing women who had preterm and term delivery (40.6 mm and 42.7 mm, respectively, p=0.2459). However, the difference between the two groups at 23 to 24 weeks was significant (37.3 mm in the group who delivered prematurely and 26.7 mm in the term group, p=0.0001, Student's t test). Conclusion: there was no significant difference in cervical length, at 11 to 16 weeks, between pregnant women who had a preterm and term delivery. However, at 23 to 24 weeks, cervical length was significantly different between the two groups, and this measurement might be used as a predictor for prematurity.
