You searched for:"Fernanda Garanhani Surita"
We found (38) results for your search.Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(6):567-572
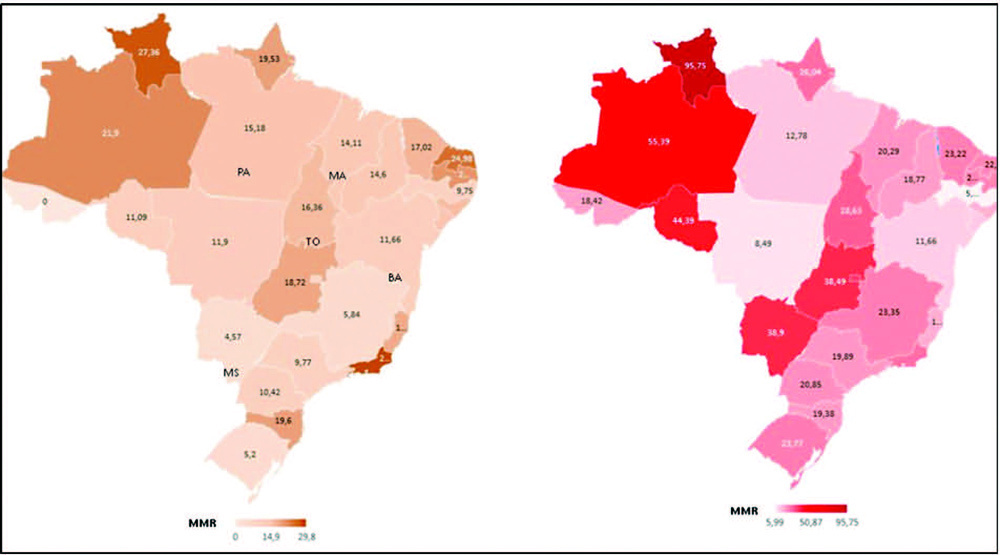
To compare death rates by COVID-19 between pregnant or postpartum and nonpregnant women during the first and second waves of the Brazilian pandemic.
In the present population-based evaluation data from the Sistema de Informação da Vigilância Epidemiológica da Gripe (SIVEP-Gripe, in the Portuguese acronym), we included women with c (ARDS) by COVID-19: 47,768 in 2020 (4,853 obstetric versus 42,915 nonobstetric) and 66,689 in 2021 (5,208 obstetric versus 61,481 nonobstetric) and estimated the frequency of in-hospital death.
We identified 377 maternal deaths in 2020 (first wave) and 804 in 2021 (second wave). The death rate increased 2.0-fold for the obstetric (7.7 to 15.4%) and 1.6-fold for the nonobstetric groups (13.9 to 22.9%) from 2020 to 2021 (odds ratio [OR]: 0.52; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.47–0.58 in 2020 and OR: 0.61; 95%CI: 0.56– 0.66 in 2021; p < 0.05). In women with comorbidities, the death rate increased 1.7-fold (13.3 to 23.3%) and 1.4-fold (22.8 to 31.4%) in the obstetric and nonobstetric groups, respectively (OR: 0.52; 95%CI: 0.44–0.61 in 2020 to OR: 0.66; 95%CI: 0.59–0.73 in 2021; p <0.05). In women without comorbidities, the mortality rate was higher for nonobstetric (2.4 times; 6.6 to 15.7%) than for obstetric women (1.8 times; 5.5 to 10.1%; OR: 0.81; 95%CI: 0.69–0.95 in 2020 and OR: 0.60; 95%CI: 0.58–0.68 in 2021; p <0.05).
There was an increase in maternal deaths from COVID-19 in 2021 compared with 2020, especially in patients with comorbidities. Death rates were even higher in nonpregnant women, with or without comorbidities.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(10):587-592
To evaluate the effects of pregnancy in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients.
The present article is a retrospective cohort study. Datawere collected from medical records of pregnant women with SLE from January 2002 to December 2012 at Universidade Estadual de Campinas, in the city of Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Systemic lupus erythematosus and disease activity were defined according to the American College of Rheumatology and the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) criteria respectively. The means, standard deviations (SDs), percentages and correlations were performed using the SAS software, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, US).
We obtained data from 69 pregnancies in 58 women. During pregnancy, a new flare was observed in 39.2% (n = 27). The manifestations were most common in patients with prior kidney disease, and mainly occurred during the third quarter and the puerperium. Renal activity occurred in 24.6% (n = 17), and serious activity, in 16% (n = 11). Of all deliveries, 75% (n = 48) were by cesarean section. Twomaternal deaths occurred (3%). Preterm birth was themain complication in the newborns. The abortion rate was 8.7%. Severe SLEDAI during pregnancy was associated with prematurity (100%) and perinatal death (54%).
Thematernal-fetal outcome is worse in SLE when thewomen experience a flare during pregnancy. The best maternal-fetal outcomes occur when the disease is in remission for at least 6 months before the pregnancy.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(6):593-601
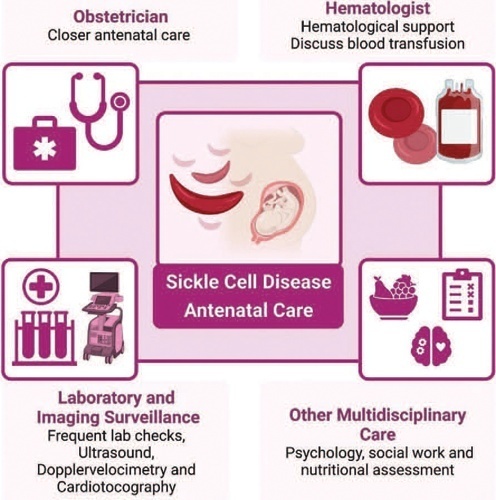
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most common monogenic disease worldwide, with a variable prevalence in each continent. A single nucleotide substitution leads to an amino-acid change in the β-globin chain, altering the normal structure of hemoglobin, which is then called hemoglobin S inherited in homozygosity (HbSS) or double heterozygosity (HbSC, HbSβ), and leads to chronic hemolysis, vaso-occlusion, inflammation, and endothelium activation. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing maternal and perinatal complications. We performed a narrative review of the literature considering SCD and pregnancy, the main clinical and obstetrical complications, the specific antenatal care, and the follow-up for maternal and fetal surveillance. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing clinical and obstetric complications such as pain episodes, pulmonary complications, infections, thromboembolic events, preeclampsia, and maternal death. Their newborns are also at an increased risk of developing neonatal complications: fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, stillbirth. Severe complications can occur in patients of any genotype. We concluded that SCD is a high-risk condition that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. A multidisciplinary approach during pregnancy and the postpartum period is key to adequately diagnose and treat complications.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(10):607-612
Almost 80% of adolescent pregnancies are unplanned, and between 28 and 63% of adolescent mothers had a repeated pregnancy within 18 months. Among girls with repeated pregnancies, two-thirds reported that the pregnancy was unplanned. We aim to assess contraceptive use by adolescent mothers with increasing choice for long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) methods in postpartum consultation after a semistructured group intervention involving adolescent mothers.
Retrospective observational study conducted at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil, involving new antenatal and postpartum education groups for adolescents. At postpartum consultations, the adolescents chose their contraceptive. The datawas compared with previous series followed in a period before the implementation of the education group - a historical control group.
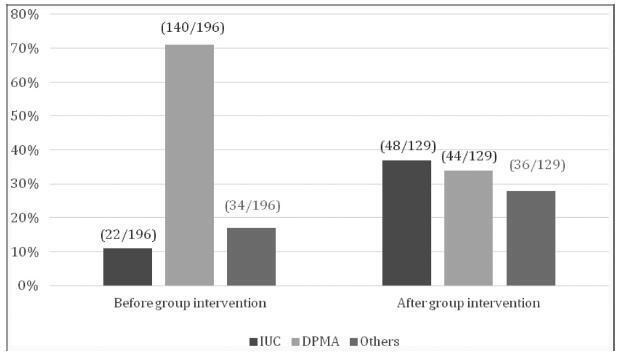
We included 129 adolescent after childbirth from January 1st, 2015 through July 31st, 2017. Out of this total, 63% had ever used contraceptive methods before pregnancy, and the most frequent method was combined oral contraceptives (33%) followed by condoms (21%). At the first postpartum consultation, the most common contraceptive chosen was intrauterine contraception (IUC) (37.2%) and depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) (34.1%).When comparing the rates before and after the education interventions, there was a 3-fold increase in the use of IUCs.
Antenatal and postpartum education have shown a significant increase in the choice for LARC methods among adolescent mothers, with very high acceptability after a period using the method. The educational groups performed during the antenatal care and beyond the gestational period are easy to be applied worldwide with low dependence on funding.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(11):622-631
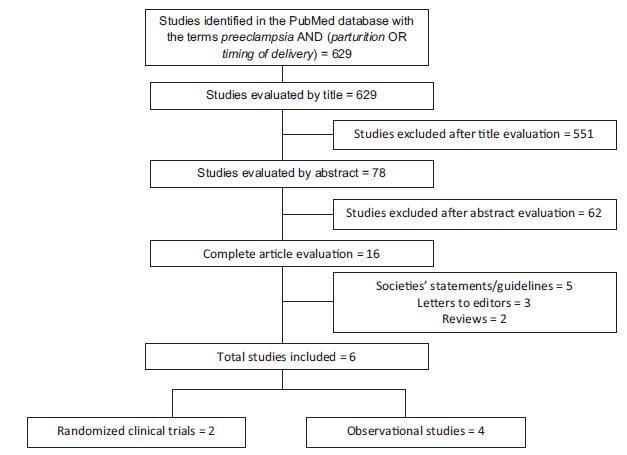
Preeclampsia, a multifactorial disease with pathophysiology not yet fully understood, is a major cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, especially when preterm. The diagnosis is performed when there is an association between arterial hypertension and proteinuria or evidence of severity. There are unanswered questions in the literature considering the timing of delivery once preterm preeclampsia has been diagnosed, given the risk of developingmaternal complications versus the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes associated with prematurity. The objective of this systematic review is to determine the best timing of delivery for women diagnosed with preeclampsia before 37 weeks of gestation.
Systematic literature review, performed in the PubMed database, using the terms preeclampsia, parturition and timing of delivery to look for studies conducted between 2014 and 2017. Studies that compared the maternal and perinatal outcomes of women who underwent immediate delivery or delayed delivery, in the absence of evidence of severe preeclampsia, were selected.
A total of 629 studies were initially retrieved. After reading the titles, 78 were selected, and their abstracts, evaluated; 16 were then evaluated in full and, in the end, 6 studies (2 randomized clinical trials and 4 observational studies) met the inclusion criteria. The results were presented according to gestational age range (< 34 weeks and between 34 and 37 weeks) and by maternal and perinatal outcomes, according to the timing of delivery, considering immediate delivery or expectant management. Before 34 weeks, thematernal outcomeswere similar, but the perinatal outcomes were significantly worse when immediate delivery occurred. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the progression to severe maternal disease was slightly higher among women undergoing expectant management, however, with better perinatal outcomes.
When there is no evidence of severe preeclampsia or impaired fetal wellbeing, especially before 34 weeks, the pregnancy should be carefully surveilled, and the delivery, postponed, aiming at improving the perinatal outcomes. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the decision on the timing of delivery should be shared with the pregnant woman and her family, after providing information regarding the risks of adverse outcomes associated with preeclampsia and prematurity.
