Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):12-18
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100003
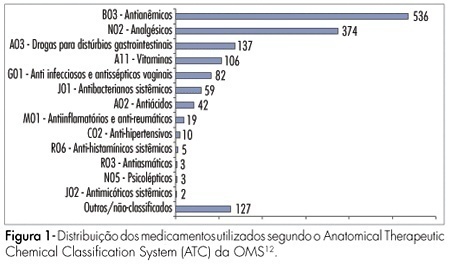
PURPOSE: to study the use of medicines by pregnant women during prenatal care in clinics of the national public health system in the city of Natal, Brazil. METHODS: a total of 610 pregnant women between the first and the third trimesters of pregnancy were interviewed in the public clinics of the four sanitary districts of Natal, from May to July 2006. The data were collected by a structured questionnaire, based in use-oriented and medicine-oriented questions. The drugs were classified according to the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC), in agreement with the gestation risk criteria from the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA). The statistical analysis was made by the chi2 test. RESULTS: a total of 1,505 drugs were used, with an average of 2.4 medications per woman. The use of at least one drug was found in 86.6% of the women. The most frequently used drugs were anti-anemics (35.6%), analgesics (24.9%), drugs for gastrointestinal disorders (9.1%) and vitamins (7%). According to the FDA classification, 42.7% belonged to category A risk, 27.1% to category B, 29.3% to category C, 0.3% to category D and none to category X. The use of medicines during the first trimester of pregnancy amounted to 43.6%. The rate of drug use increased with higher schooling level and family income. Self-medication was found in 12.2% of the drug intake and this rate was higher in the first trimester of gestation and with women with low education level and previous gestations. CONCLUSIONS: pregnant women from Natal are being exposed to a variety of medicines with uncertain safety in pregnancy. Therefore, more careful prescription is needed, to avoid possible fetal damage.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(1):12-19
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000100005
PURPOSE: to evaluate and compare results of female pelvic floor surface electromyography in different positions: lying, sitting and standing. METHODS: twenty-six women with the diagnosis of stress urinary incontinence treated with a protocol of exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscle were evaluated. Pelvic floor surface electromyography was performed with an intravaginal sensor connected to Myotrac 3G TM equipment, as follows: initial rest of 60 s, five phasic contractions, one 10-s tonic contraction and one 20-s tonic contraction. The amplitudes were obtained from the difference between the final contraction amplitude and the amplitude at rest (in µV). Wilcoxon test was applied for nonparametric data (p value <0.05). RESULTS: the amplitudes of contractions were higher in the lying position, decreasing in the sitting and standing positions. In the lying position, the median values of phasic and tonic contractions were 23.5 (5-73), 18.0 (3-58) and 17.0 (2-48), respectively. In the sitting position, they were 20.0 (2-69), 16.0 (0-58) and 15.5 (1-48). In the standing position they were 16.5 (3-67), 12.5 (2-54) and 13.5 (2-41). All amplitude values were significantly lower in the standing position compared to the lying position (p<0.001, p<0.001 and p=0.003). Similar results were also found in comparison to the sitting position. However, there was no significant difference between the lying and the sitting positions. CONCLUSION: all female pelvic floor contraction amplitudes were lower in the standing position, suggesting that the muscle strength should be intensified in that position.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):120-126
To evaluate the precision of both two- and three-dimensional ultrasonography in determining vertebral lesion level (the first open vertebra) in patients with spina bifida.
This was a prospective longitudinal study comprising of fetuses with open spina bifida who were treated in the fetal medicine division of the department of obstetrics of Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade de São Paulo between 2004 and 2013. Vertebral lesion level was established by using both two- and three-dimensional ultrasonography in 50 fetuses (two examiners in each method). The lesion level in the neonatal period was established by radiological assessment of the spine. All pregnancies were followed in our hospital prenatally, and delivery was scheduled to allow immediate postnatal surgical correction.
Two-dimensional sonography precisely estimated the spina bifida level in 53% of the cases. The estimate error was within one vertebra in 80% of the cases, in up to two vertebrae in 89%, and in up to three vertebrae in 100%, showing a good interobserver agreement. Three-dimensional ultrasonography precisely estimated the lesion level in 50% of the cases. The estimate error was within one vertebra in 82% of the cases, in up to two vertebrae in 90%, and in up to three vertebrae in 100%, also showing good interobserver agreement. Whenever an estimate error was observed, both two- and three-dimensional ultrasonography scans tended to underestimate the true lesion level (55.3% and 62% of the cases, respectively).
No relevant difference in diagnostic performance was observed between the two- and three-dimensional ultrasonography. The use of three-dimensional ultrasonography showed no additional benefit in diagnosing the lesion level in the fetuses with spina bifida. Errors in both methods showed a tendency to underestimate lesion level.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):120-125
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300002
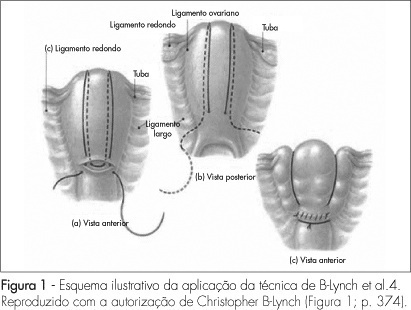
PURPOSE: to present a surgical technique for patients submitted to caesarean section, which evolves to medicine refractory hemorrhage. METHODS: a case report study, of which the including criteria were failure in the pharmacological treatment to control post-partum hemorrhage, and the patients' request to preserve their uterus. Four patients submitted to caesarean section which evolved to immediate post-partum hemorrhage, refractory to the use of ocytocin, ergometrine and misoprostol, were treated with the suture technique described by B-Lynch, without modification. The uterus was transfixed in six points according to the standard procedure, with chrome catgut-2 or polyglactine-1thread. After the assistant's manual compression of the uterus, the thread was pulled by its extremities by the surgeon, and a double knot followed by two simple knots were applied before performing the hysterorraphy. RESULTS: needled chrome catgut-2 thread was used in three cases and needled poluglactine-1 in one case. In the four cases there was immediate discontinuity of the vaginal bleeding, after the suture. The four patients did not present any complication during the procedure or along the immediate and late puerperal period. CONCLUSION: this technique represents a surgical alternative to deal with post-partum hemorrhage and may represent a reduction in the maternal morbidity and mortality in our country.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):121-126
To assess the management chosen by gynecologists after atypical squamous cells (ASCs) cytology results, and to evaluate the outcomes of these cases in Brazilian women.
A prospective observational study evaluated the initial management offered by the gynecologist in the case of 2,458 ASCs cytology results collected between January of 2010 and July of 2016. The outcomes of the cytology, high-risk human papilloma virus (HR-HPV) test and histology were compared in two subgroups: atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) and atypical squamous cells-cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H).
In many cases of ASC-US (36.97%) and ASC-H (40.50%), no clinical actions were taken. Cytology was the most frequent follow-up chosen, including for cases of ASC-H, which goes against the conduct recommended in the national guideline. In women over 30 years of age, the period of time elapsed between an ASC-US result and a new cytology was in 13.03 months, in disagreement with the national guideline recommendations (p< 0.0001). Negative for intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) cytologic (p = 0.0026) and histologic (p = 0.0017) results in the follow-up were associated with prior ASC-US, while negative results for ASC-H were cytologically (p< 0.0001) and histologically associated with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) (p< 0.0001). Two invasive cervical carcinomas (ICCs) were found in the follow-up for ASC-H, and there was a statistically significant association (p = 0.0341). A positive HR-HPV test was associated with ASC-H (p = 0.0075).
The data suggest that even for a population of Brazilian women assisted at private clinics, the national guidelines recommendations for ASCs results are not followed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(2):121-127
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000200008
Purpose: to estimate the performance of ultrasound to detect gestations at risk for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Methods: four hundred and thirty-six patients selected for the study had undergone ultrasound examination and fetal karyotyping, between March 1993 and March 1998. Two hundred and seventy-seven patients had fetal karyotype for fetal malformation detected on ultrasound and 158 for parental anxiety with normal ultrasound examination. Ultrasound sensitivity and specificity were calculated using fetal karyotype as gold standard. The relative risk for each chromosomal abnormality was calculated according to the altered system on ultrasound examination and the risks of the presence of one or more abnormalities on ultrasound, using the Epi-Info 6.0 software package for statistical analysis. Results: the relative risks for chromosomal abnormalities were 89 for face malformations, 53 for abdominal wall and cardiovascular, 49.6 for neck, 44.6 for extremities, 42.4 for lung, 32.7 for gastrointestinal tract, 27.4 for central nervous system and 23.0 for urinary tract malformations. The relative risk for fetal chromosomal anomalies for genital, thorax, spine and muscle and/or skeletal malformations was not appropriate for calculation because they occurred at very low frequencies. An isolated malformation detected by ultrasound is associated with a 7.8 times higher relative risk for chromosomal anomalies than none, and associated morphologic malformations have a 33.8 times higher relative risk for chromosomal abnormalities. Conclusion: ultrasound has good performance to detect gestations at risk for chromosomal abnormalities.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):121-126
To evaluate and compare peripheral, pelvic floor, respiratory muscle strength, and functionality in the immediate puerperium of normal delivery and cesarean section.
This is a cross-sectional study that verified respiratory, pelvic floor, peripheral, and functional muscle strength through manovacuometry, pelvic floor functional assessment (PFF), dynamometry, and the Time Up and Go (TUG) test, respectively. The groups were divided according to the type of delivery, into a cesarean section group and a normal parturition group.
The sample was composed of 72 postpartum puerperae, 36 of normal parturition, and 36 of cesarean section, evaluated before hospital discharge, mean age ranged from 25.56 ± 6.28 and 28.57 ± 6.47 years in puerperae of normal parturition and cesarean section respectively. Cesarean showed higher pelvic floor strength (PFF) compared to normal parturition (p < 0.002), but puerperae from normal delivery showed better functionality (p < 0.001). As for peripheral muscle strength and respiratory muscle strength, there was no significance when comparing the types of parturirion.
There is a reduction in pelvic muscle strength in puerperae of normal delivery and a decrease in functionality in puerperae of cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):121-126
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008005000002
PURPOSE: to compare the frequency of vulvovaginitis in women infected with human imunnodeficiency virus (HIV) with the frequency in non-infected women. METHODS: a transversal study including 64 HIV infected women and 76 non-infected ones. The frequencies of bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and trichomoniasis, diagnosed by Amsel's criteria, culture and fresh exam, respectively, were calculated. Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test and multiple regressions to verify the independence of associations were used to analyze the data. RESULTS: the vaginal infection was more prevalent in HIV infected patients, as compared to the control group (59.4 versus 28.9%, p<0,001; Odds Ratio=2.7, IC95%=1.33-5.83, p=0.007). Bacterial vaginosis occurred in 26.6% of the positive-HIV women; vaginal candidiasis, in 29.7% and trichomoniasis, in 12.5% of them. All the infections were significantly more frequent in the group of HIV infected women (p=0.04, 0.02 e 0.04, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: vulvovaginitis is more frequent in HIV infected women.