You searched for:"Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade"
We found (21) results for your search.Summary
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(12):779-786
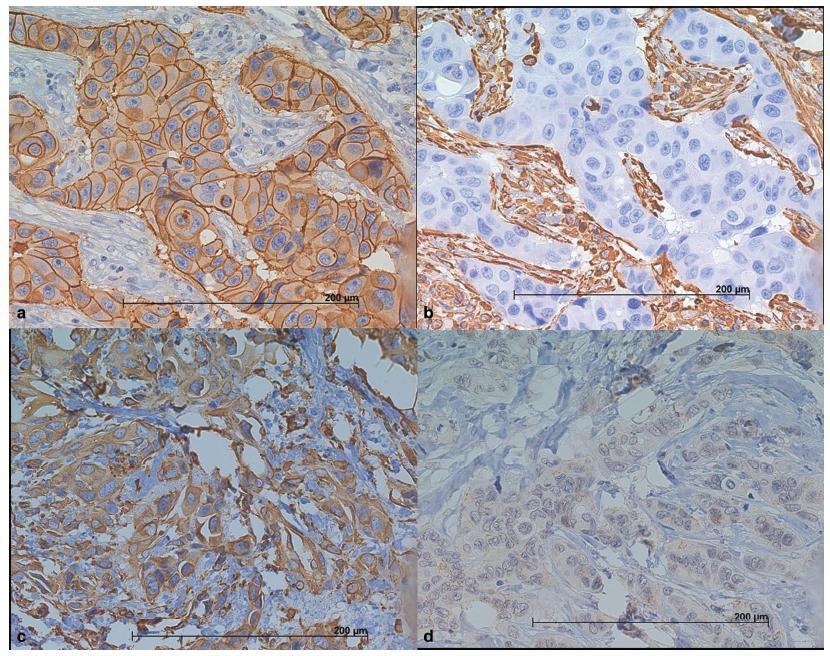
The use of molecular markers can identify a subgroup of tumors with distinct recurrence patterns. The present study aimed to characterize the immunohistochemical expression of vimentin (VIM), of E-cadherin (CDH1), and of cytokeratin 5 (CK5) in patients with invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs).
We have constructed a tissuemicroarray (TMA) from87 patients with IDC of the breast. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to study the expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER and PgR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), VIM, CDH1, CK5, and Ki67. The tumors were classified as luminal A and B (n = 39), HER2 enriched (n = 25), and triple-negative (TNBC) (n = 23), based on the IHC expression.
We have observed that luminal A and B tumors lack the VIM+/CDH1-/low phenotype. This phenotype was observed in 16.5% of the HER2+ tumors and in 60% of the TNBC tumors (p = 0.0001). Out of a total of 20 TNBC tumors, the CK5 (basal-like marker) was positive in 11 of them. The VIM+/CDH1-/low phenotype was observed in 5 CK5+ TNBC tumors (45%) and in 7 out of 9 CK5- TNBC tumors (78%) (p = 0.02). The median Ki67 index in the VIM+/CDH1-/low tumors was 13.6 (range: 17.8-45.4) compared with 9.8 (range: 4.1-38.1) in other tumors (p = 0.0007). The presence of lymph nodemetastasis was less frequent in patients with VIM+/CDH1-/low tumors (23% versus 61%; X2 test; p = 0.01).
Our findings suggest that the expression of VIM and CDH1 can identify a subset of IDCs of the breast with a mesenchymal phenotype associated with poor prognosis, high-grade lesion, and high mitotic index.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2000;22(2):79-87
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200004
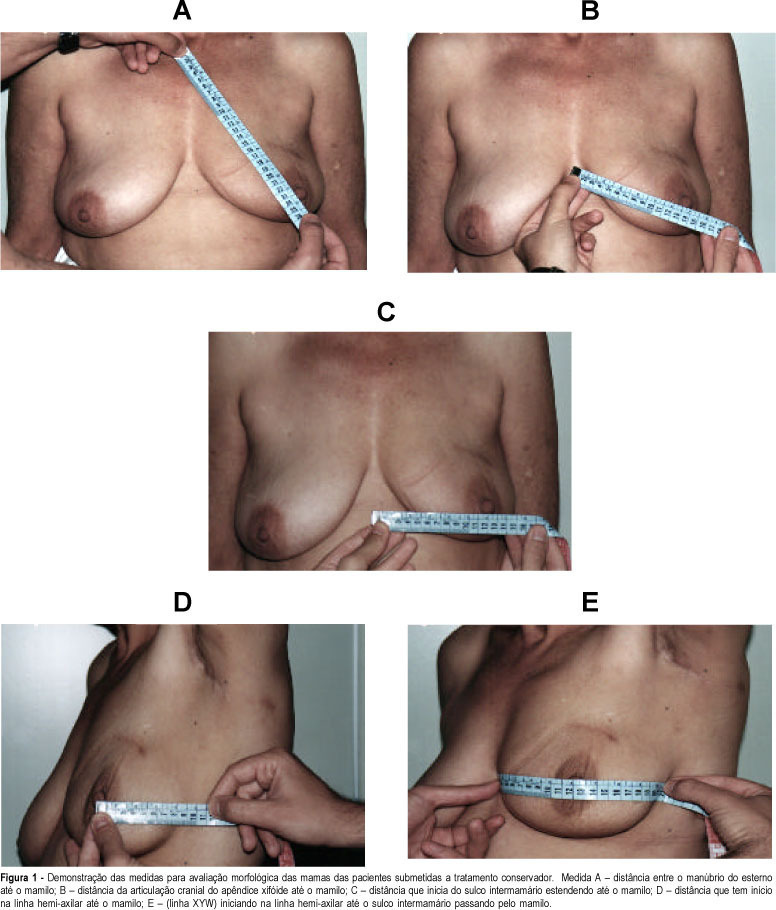
Purpose: to assess the esthetic results and personal satisfaction of patients submitted to conservative surgery for cancer of the breast. The study was conducted on 44 patients with breast cancer diagnosed at the mastology outpatient clinic of HCFMRP-USP from January 1990 to December 1994, who fulfilled inclusion criteria according to a previously established protocol. The study consisted of analysis of the esthetic results after conservative treatment of breast cancer and analysis of the degree of patient satisfaction, with a comparison of the morphometry of the treated breast to that of the normal breast. The results were obtained on the basis of five previously established parameters using the esthetic evaluation score proposed by Westreich¹. Methods: of the 44 patients studied, 10 had been submitted to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (CT) because they presented locally advanced tumors, and 2 because of an unfavorable tumor/breast ratio for conservative treatment. Mean follow-up time was 65 months. All 27 patients followed-up at the outpatient clinic received a convocation letter. An evaluation questionnaire was applied to the 20 patients who came to the clinic, followed by breast measurement. Fifteen of these patients had been submitted to surgery with separate incisions and 5 to surgery with a single incision. Results: according to morphometry, the results were classified as excellent in 17 cases (85%), as good in two (10%), and as poor in only one case (5%), an evaluation comparable to the subjective evaluation made by the patients themselves. Considered separately, both measurement "A" (distance from the manubrium of the sternum to the nipple) and measurement "B" (distance from the cranial articulation of the xyphoid appendix to the nipple) showed a greater discriminative power than the measurements as a whole, since with these measurements the cases classified as poor by the patients would have also been classified as poor according to these same criteria separately (A and/or B). Conclusion: there was a significant difference in esthetic results between surgical treatment with a single incision or separate incisions, with the separate incision providing better results. There was high agreement between the classification made by the patients and the morphometric results obtained by us.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2009;31(2):94-101
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200008
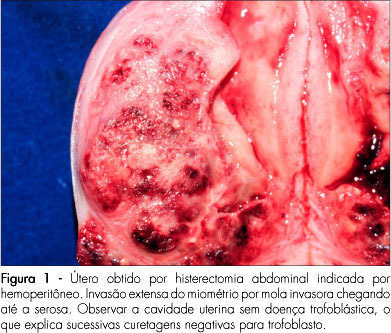
The hydatiform mole is a relatively rare pregnancy complication, but with potential to evolve to forms which need systemic treatment and can be a threat to life. There are two histopathological and clinical entities under the name of hydatiform mole: the partial and the complete mole. The differences between the two forms are important due to risk of evolution to persistent forms, which is higher for the complete moles. The diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of hydatiform mole have been under important changes in the last years. The number of asymptomatic patients has increased, due to the use of ultrasonography at the onset of pregnancy. The use of medication that induces uterine contractions must be avoided, and vacuum aspiration should be used. Soon after emptying the mole, a hormonal contraceptive method should be prescribed. Follow-up should be based on weekly serial dosages of chorionic gonadotropin. It is important that the method employed detects all the forms of chorionic gonadotropins (intact molecule, with hyper glycol, free β subunit, and central fragment β subunit).