Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):415-422
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800006
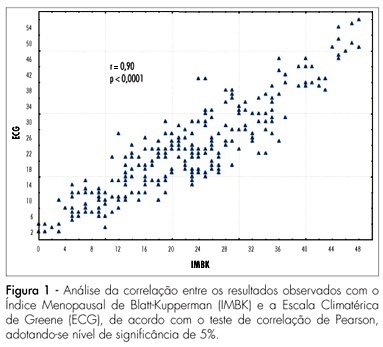
PURPOSE: to evaluate climacteric symptoms and related factors in women living in rural and urban areas of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. METHODS: a cross-sectional study involving 261 women in the climacteric was performed. A total of 130 women from Natal and Mossoró (urban group) and 131 from Uruaçu, in São Gonçalo do Amarante (rural group), were studied. Climacteric symptoms were assessed by the Blatt-Kupperman Menopausal Index (BKMI) and Greene Climacteric Scale (GCE). Statistical analysis involved comparison of median between groups and logistic regression analysis. Patients were defined as "very symptomatic" when the climacteric score was >20 for both questionnaires (dependent variable). Independent variables were: age, living area, schooling, obesity and physical activity. RESULTS: the urban group had significantly higher scores than those of the rural group, both for BKMI (median of 26.0 and 17.0, respectively; p<0.0001) and for GCE (median of 27.0 and 16.0, respectively; p<0.0001). For the entire sample, a total of 56.3% (n=147) of the women were classified as "very symptomatic". This prevalence was significantly higher in urban than in rural women (79.2 and 33.6%, respectively; p<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that the likelihood of belonging to the group defined as "very symptomatic" was greater for urban women [adjusted odds ratio (OR)=7.1; confidence interval at 95% (95%CI)=3.69-13.66] who were literate (OR=2.19; 95%CI=1.16-4.13). Individuals over the age of 60 years had less chance of having significant symptoms (OR=0.38; 95%CI=0.17-0.87). CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of significant climacteric symptoms is less in women from a rural environment, showing that sociocultural and environmental factors are strongly related to the appearance of climacteric symptoms in our population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(9):415-419
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):415-422
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800008
The main purpose of using uterulytic in preterm delivery is to prolong gestation in order to allow the administration of glucocorticoid to the mother and/or to accomplish the mother's transference to a tertiary hospital center. Decisions on uterolytic use and choice require correct diagnosis of preterm delivery, as well as the knowledge of gestational age, maternal-fetal medical condition, and medicine's efficacy, side-effects and cost. All the uterolytics have side-effects, and some of them are potentially lethal. Studies suggest that beta-adrenergic receptor agonists, calcium blockers and cytokine receptor antagonists are effective to prolong gestation for at least 48 hours. Among these three agents, atosiban (a cytokine receptor antagonist) is safer, though it presents a high cost. Magnesium sulfate is not efficient to prolong gestation and presents significant side-effects. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors also present significant side-effects. Up till now, there is not enough evidence to recommend the use of nitric oxid donors to inhibit preterm delivery. There is no basis for the use of antibiotics to avoid prematurity in face of preterm labor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):415-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700008
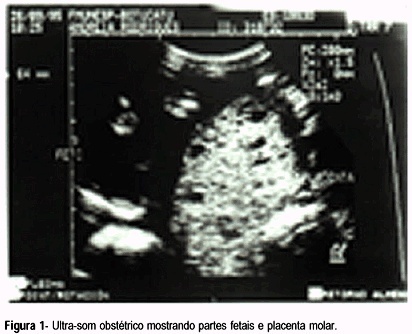
Twin pregnancy in which a normal fetus and a complete mole develop at the same time is a rare event. Clinical complications and malignancy are frequent in this type of disease.This report is about a case of a late diagnosis due to the presence of the fetus. The diagnosis was made when the pregnancy was interrupted and then confirmed by histopathological study and flow cytometry. The pregnancy was terminated transpelvically due to massive uterine hemorrhage. The post-molar follow-up showed the persistence of high levels of bhCG. The patient's complete recovery was achieved after the administration of methotrexate. The diagnosis, natural history, and procedures for this rare disease are discussed in view of this case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):416-422
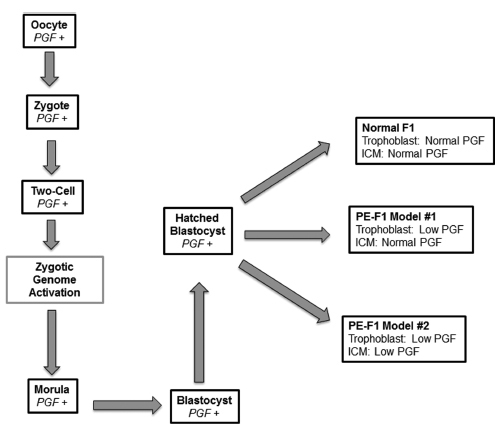
Preeclampsia (PE) is a significant gestational disorder that causes complications in 3- 5% of all human pregnancies. Apart from the immediate risks and complications for mother and fetus, both additionally carry elevated lifelong risks for specific complications. Offspring of PE pregnancies (PE-F1) have higher risks for hypertension, stroke and cognitive impairment compared with well-matched offspring (F1) fromuncomplicated pregnancies. Prior to the clinical onset of PE, placental angiokines secreted into the maternal plasma are deviated. In many PE patients this includes deficits in placental growth factor (PGF). Our laboratory found that mice genetically-deleted for PGF (PGF - / -) have altered cerebrovascular and brain neurological development detectable from midgestation to adulthood. We hypothesized that the PGF deficits seen in human PE, deviate fetal cerebrovascular and neurological development in a manner that impairs cognitive functions and elevates stroke risk. Here we summarize the initial analytical outcomes from a pilot study of 8-10 year old male and female PE-F1s and matched controls. Our studies were the first to report magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and functional brain region assessment by eyemovement control and clinical psychometric testing in PE-F1s. Further studies in larger cohorts are essential to define whether there are image-based biomarkers that describe unique anatomical features in PE-F1 brains.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):416-422
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004995
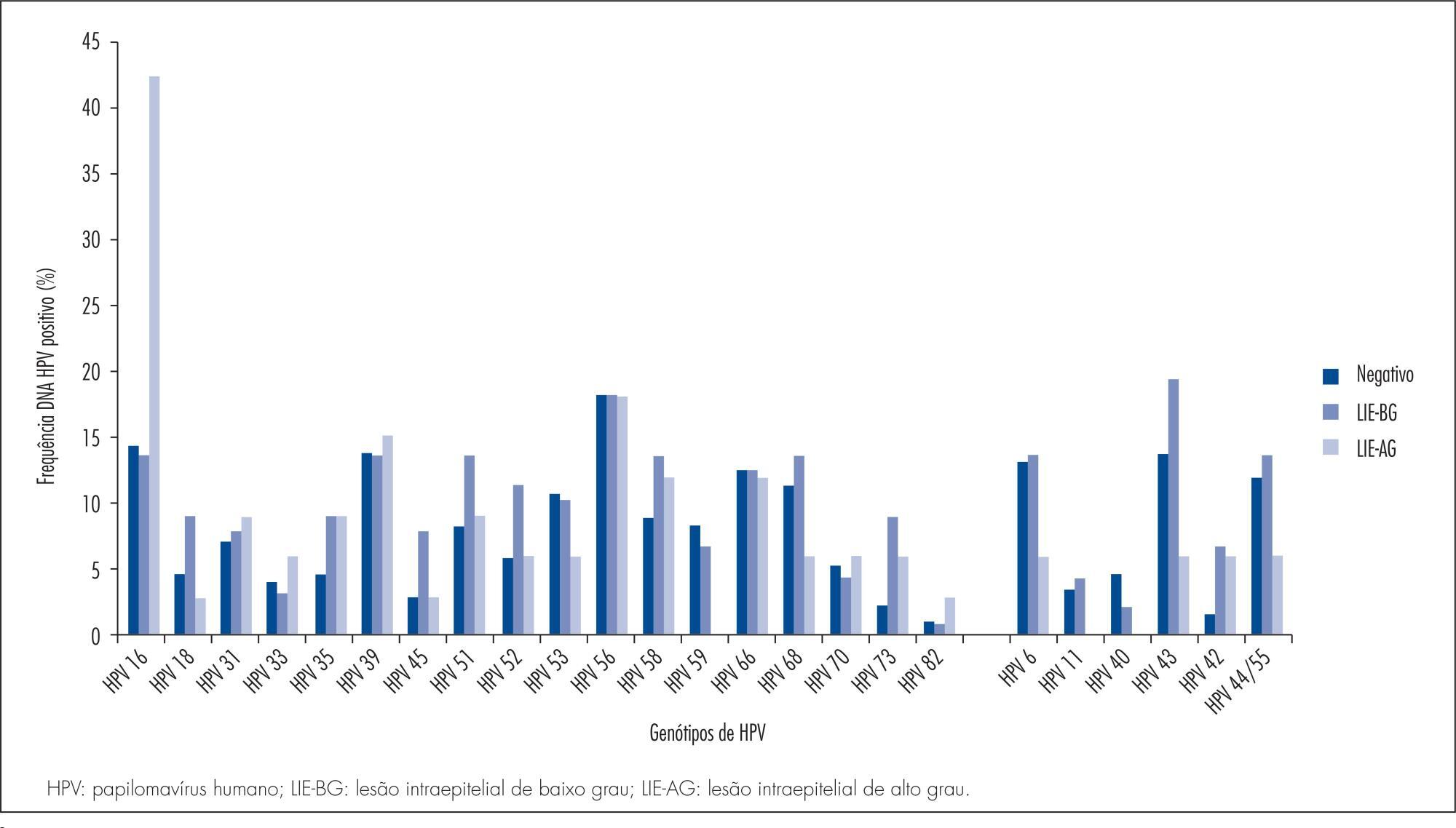
The aim of this study was to evaluate the human papillomavirus genotypes and the frequency of multiple human papillomavirus infections, as well as to assess the association between human papillomavirus genotype, cyto-histopathological abnormalities and age range.
A retrospective cross-sectional study was carried out between June 2010 and October 2013 in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. We analyzed 351 results of positive human papillomavirus genotyping performed using the PapilloCheck(r) test, designed to detect 24 human papillomavirus types. The cyto-histopathological abnormalities were classified as negative (negative cytology and histopathology), low-grade lesions (cytologic low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion diagnosis or histopathologic cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 1 or vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia 1 diagnosis) and high-grade lesions (cytologic high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion diagnosis or histopathologic cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2+ or vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia 2+ diagnosis).
The most frequently detected high risk human papillomavirus genotype was HPBV 16, with 18.5%, 95% confidence interval (95%CI) 14.6-23.0, followed by HPV 56 (14%; 95%CI 10.5-18.0) and HPV 39 (13.4%; 95%CI 9.5-16.8). HPV 18 (5.4%; 95%CI 3.3-8.3) was among the least frequent types. Among the low risk types, HPV 42 (15.7%; 95%CI 12.0-20.0), HPV 6 (11.4%; 95%CI 8.3-15.2) and HPV 44/55 (11.1%; 95%CI 8.0-14.9) were the most frequent, while HPV 11 (2.8%; 95%CI 1.4-5.2) was the least common. The proportion of HPV 16-positive women increased with severity of cyto-histopathological abnormalities: 13.8% (12/87) in low-grade lesion and 42.4% (14/33) in high-grade lesion. There was association between low- or high-grade cyto-histopathological lesion and the high risk genotypes, HPV16, HPV 52, HPV 73 and HPV 82, and the low risk type, HPV 43. Women under 30 years showed a significantly higher frequency of HPV 16 (22.2 versus 12.9%, p =0.01), HPV 42 (19.7 versus 10.9%, p=0.01) and HPV 45 (6.6 versus 1.4%, p=0.01), and multiple human papillomavirus infections (58.1 versus 47.4%, p=0.04).
We observed variability of human papillomavirus genotype distribution in women from the state of Bahia. HPV 16 was the most frequently detected high risk human papillomavirus, as also reported for other geographic areas of Brazil and for the world in general. HPV 56 and HPV 39 were the second and the third most common genotypes, whereas HPV 18 was among the least frequent types. HPV 42, 6 and 44/55 were the most frequently detected low risk human papillomavirus, and HPV 11 was the least common.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):416-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700007
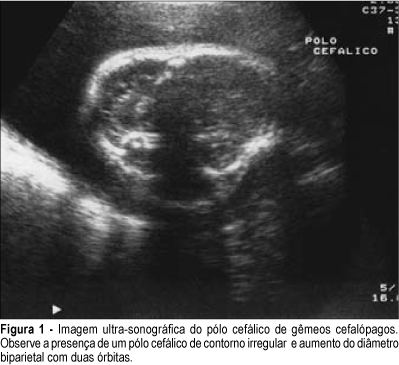
Conjoined twins have a rare prevalence and special curiosity among physicians and the general population. The reported frequency varies from 1:50,000 to 1:200,000 pregnancies. Its early diagnosis becomes very important when we think about pregnancy management, method of delivery and neonatal care. We describe two cases of conjoined twins diagnosed by ultrasound and magnetic resonance during prenatal care with the aim to better studying the fetus anatomy. The first conjoined twins were cephalopagus sharing head, thorax and abdominal wall and with two pelvis and four arms and four legs. The second were thoracopagus, united by thorax and part of abdomen. Magnetic resonance imaging contribution was not important to diagnose conjoined twins. However, it was useful to describe the shared organs, contributing to define fetal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):417-417