Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):320-327
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004998
To present the cross-cultural adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese language of the Pregnancy and Weight Gain Attitude Scale.
This scale was developed in order to verify whether attitude toward thinness affects weight gain during pregnancy and contains statements that express different attitudes of pregnant women regarding their own weight gain. The procedures were: translation, back translation, comprehension evaluation, preparation of a final version, application of the scale to 180 pregnant women (mean age=29.6, gestational age=25.7 weeks) and psychometric analysis.
Satisfactory equivalence between the versions and satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha 0.7) were detected. The exploratory factor analysis suggested four subscales with 51.4% total variance explained.
The scale proved to be valid and can be used in studies with pregnant women in Brazil to assess attitudes toward weight gain and to detect and prevent dysfunctional behaviors during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(7):321-326
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000700003
PURPOSE: to study the association between hypothyroidism and depression and anxiety symptoms. METHODS: a case-control study was carried out from July 2006 to March 2008 on 100 patients (50 patients with primary hypothyroidism and 50 euthyroid controls) aged 18 to 65 years. Age, race/skin color, marital status, education level, alcohol use, working status, body mass index and menopausal status were evaluated. TSH levels were determined and the Beck Depression and Beck Anxiety Scales were applied to all cases and controls. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software version 14.0. The level of significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: there was no demographic or epidemiologic difference between groups. The concomitant presence of anxiety and depression was five times greater among cases than among controls (20.0 versus 4.0%, p=0.01). Anxiety symptoms were approximately three times more frequent among cases (40.0%) than among controls (14.0%) (p=0.003), while the prevalence of depressive symptoms was 75% higher among cases (28.0%) than among controls (16.0%), but this did not reach statistical significance (p=0.15). We found no association between TSH levels and the prevalence of anxiety or depression symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: this case-control study showed a greater probability for hypothyroid patients to develop anxiety and depression symptoms when compared to euthyroid controls. Due to the high prevalence of hypothyroidism and depression observed in clinical practice, depressive symptoms must be considered in patients with thyroid dysfunction and depressed patients should be tested for TSH.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(7):321-325
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(5):321-327
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000500008
Purpose: to determine the relationship between fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of nonpalpable breast lesions (cystic or solid masses) with the ultrasound and histopathological features of the biopsy lesions. Methods: a total of 617 nonpalpable lesions were analyzed by ultrasound. Fine needle aspiration cytology was guided by ultrasonography and the cysts were distinguished from the solid masses by comparing the biopsies. The cytologic results were compared with the histological results in the case surgical biopsy was carried out. Results: of the 617 nonpalpable lesions 471 were cysts (451 simple cysts with 100% negative cytology and 20 cases were considered complex cysts; 3 (15%) of these had a positive or suspected cytology and in 2 cases malignancy was confirmed. There were 105 solid masses, 63 of them with negative cytology. Fifty-nine cases had a negative biopsy, and 4 cases (0.3%) were false-negative but all of them presented disagreement between the cytological and image features; in 14 cases (13%) there was a suspected cytology and in 5 of them carcinoma was confirmed; in 14 cases (13%), the samples were insufficient, 1 case was carcinoma and in 51 cases, a triple diagnosis was concordant and the lesions were followed-up. Conclusion: cytological analysis of simple cysts is not required, but when they are complex, cytological analysis is mandatery. In the case of nonpalpable solid masses, cytology must be correlated with ultrasound and mammography features. If the results are discordant, the lesion should be followed-up.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):322-331
To establish the Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) scores for each domain before and during pregnancy, and to publish the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI.
Pregnant women were recruited during antenatal care; the PSRI was administered to 244 women prenatally at Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, at Universidade do Estado de São Paulo (UNESP, in the Portuguese acronym). The PSRI scores were estimated based on the Kings Health Questionnaire (KHQ) and the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form survey (SF-36). The raw scale type was used to standardize the minimal value and amplitude of each domain. For each domain, the score varied from 0 to 100, and the composite score was obtained as the domain average. The composite score before and during pregnancy was determined by the sum of the scores of all specific domains for each divided by the full domain number. The categorization of the scale into quartiles was established when all PSRI-specific and composite scores were combined.
The composite and specific scores for each domain were categorized into quartiles: 0 < 25 as “very bad;” 25 < 50 as “bad;” 50 < 75 as “good” and 75 to 100 as “excellent.” The mean scores were lower during pregnancy than before pregnancy in 8 of the 10 domains. The Brazilian Portuguese PSRI version is presented.
This study allowed the establishment of the PSRI composite and specific scores for each domain, and the categorization of scores into quartiles: very bad, bad, good and excellent. In addition, the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI is presented in full for application in the Brazilian population.
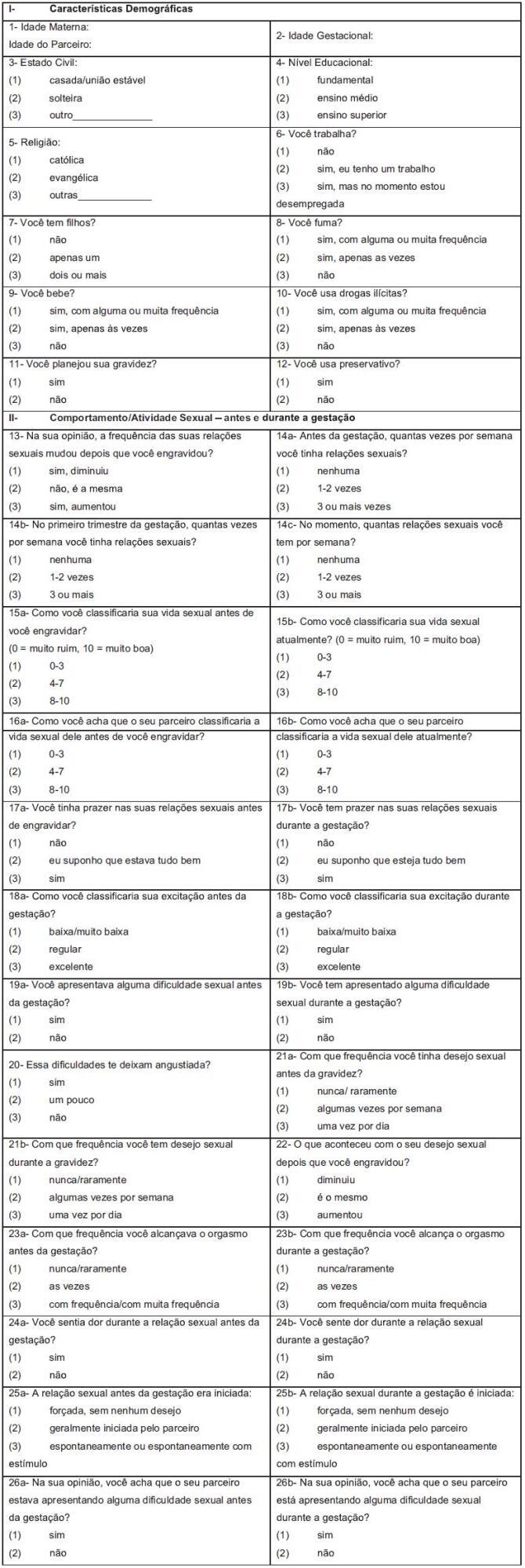
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):322-329
Considering the physical, mental and behavioral problems related to fetal alcohol exposure, prenatal clinical guides suggest a brief evaluation of alcohol consumption during pregnancy to detect alcohol intake and to adjust interventions, if required. Even if any alcohol use should be considered risky during pregnancy, identifying women with alcohol use disorders is important because they could need a more specific intervention than simple advice to abstain. Most screening tests have been developed and validated in male populations and focused on the long-term consequences of heavy alcohol use, so they might be inappropriate to assess consumption in pregnant women.
To analyze the internal reliability and validity of the alcohol screening instruments Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), Alcohol Use Disorders IdentificationTest- Consumption (AUDIT-C), Tolerance, Worried, Eye-Opener, Amnesia and Cut-Down (TWEAK), Rapid Alcohol Problems Screen - Quantity Frequency (RAPSQF) and Tolerance, Annoyed, Cut-Down and Eye-Opener (T-ACE) to identify alcohol use disorders in pregnant women.
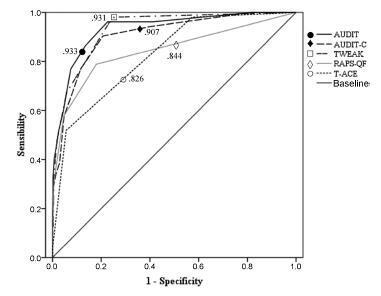
A total of 641 puerperal women were personally interviewed during the 48 hours after delivery. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves and the sensitivity and specificity of each instrument using different cut-off points were analyzed.
All instruments showed areas under the ROC curves above 0.80. Larger areas were found for the TWEAK and the AUDIT. The TWEAK, the T-ACE and the AUDIT-C showed higher sensitivity, while the AUDIT and the RAPS-QF showed higher specificity. Reliability (internal consistency) was low for all instruments, improving when optimal cut-off points were used, especially for the AUDIT, the AUDIT-C and the RAPS-QF.
In other cultural contexts, studies have concluded that T-ACE and TWEAK are the best instruments to assess pregnant women. In contrast, our results evidenced the low reliability of those instruments and a better performance of the AUDIT in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):322-322
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):322-322