Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):280-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000002
PURPOSE: To analyze the results of assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia. METHODS: Data from April 2001 to July 2011 of 96 women with a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy were retrospectively analyzed. We analyzed the following tests performed during the antepartum period for fetal assessment: cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. RESULTS: A total of 96 pregnancies with the following diagnoses were analyzed: gestational thrombocytopenia (n=37, 38.5%) hypersplenism (n=32, 33.3%), immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, n=14, 14.6%), secondary immune thrombocytopenia (n=6, 6.3%), bone marrow aplasia (n=3, 3.1%), and others (n=4, 4.1%). Cardiotocography showed normal results in 94% of cases, a fetal biophysical profile with an index of 8 or 10 in 96.9% and an amniotic fluid index >5.0 cm in 89.6%. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry showed normal results in 96.9% of cases. In the analysis of the major groups of thrombocytopenia, the diagnosis of oligohydramnios was found to be significantly more frequent in the group with ITP (28.6%) compared to the other groups (gestational thrombocytopenia: 5.4% and hypersplenism: 9.4%, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates that in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia, even though the fetal well-being remains preserved in most cases, fetal surveillance is important in pregnant women with ITP, with emphasis on amniotic fluid volume evaluation due to its association with oligohydramnios.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):280-286
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is the standard treatment for locally advanced breast cancer. However, some tumors will not respond to this treatment due to histological and molecular features. The protein EZH2 (enhancer of zest homolog 2) is a histone methyltransferase that is correlated with poorly differentiated breast carcinomas and aggressive tumor behavior.
The present study evaluated the association between EZH2 expression and response to NAC, and its correlation with HER2 overexpression, estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER, PR) and Ki-67 proliferation index.
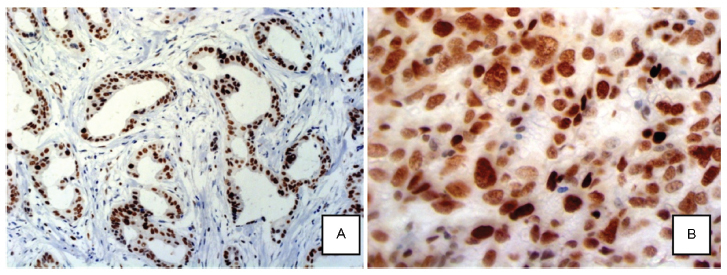
A total of 60 patients with locally advanced breast cancer treated with NAC were selected for this study. Twenty-three paraffin blocks had not enough material for tissue resection, and were not evaluated. A tissue microarray based in immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of EZH2 was performed for the remaining 37 specimens. Patients were divided into two groups based on response to NAC.
EZH2 expression was significantly associated with markers of poor prognosis such as ER negativity (p = 0.001), PR negativity (p = 0.042) and high Ki-67 proliferation index (p = 0.002). High EZH2 expression was not correlated with the response to NAC.
Our data suggested that EZH2 protein expression may not correlate with the clinical response to NAC. Other studies with more patients are needed to confirm this observation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):280-290
To evaluate and compare the prevalence of structural congenital anomalies (CAs) according to maternal body mass index (BMI).
The present cross-sectional study involved pregnant women with fetuses diagnosed with structural CAs through morphological ultrasonography between November 2014 and January 2016. The nutritional status of the pregnant women was classified according to the gross value of the body mass index. The pregnant women were categorized into four groups: low weight, adequate weight, overweight, and obesity. Statistical analysis was performed using Stata/SE version 12.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX), with values of p ≤ 0.05 considered statistically significant.
A total of 223 pregnant women had fetuses diagnosed with CAs. The prevalence of structural CAs in pregnant women with lowweight was of 20.18%, of 43.50% in pregnant women with adequate weight, of 22.87% in pregnant women with overweight, and of 13.45% in pregnant women with obesity. The prevalence of central nervous system (CNS) anomalies and of genitourinary systemanomalieswas high for the four groups of pregnant women. A positive association was observed between multiple anomalies in pregnant women with adequate weight (prevalence ratio [PR] = 1.65; p ≤ 0.004) and between anomalies of the lymphatic system in obese pregnant women (PR = 4.04, p ≤ 0.000).
The prevalence of CNS and genitourinary systemanomalies was high in all of the BMI categories. Obese pregnancies were associated with lymphatic system anomalies. Therefore, screening and identification of the risk factors for CAs are important, regardless of the maternal BMI. Our findings reinforce the importance of discussing with pregnant women maternal nutrition and its effect on fetal development and on neonatal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):280-286
The purpose of this study was to compare the frequency of the occurrence of high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) and abnormal anal cytology in immunocompetent women with and without HPV-induced genital lesions.
This analytical cross-sectional, observational study was conducted between July 2017 and December 2018 in a specialized outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital in Fortaleza, CE. Fifty-seven immunocompetent women with and without genital intraepithelial lesions were assessed; they were divided into two groups: group 1 was comprised of women with HPV-associated genital lesions (n=26), and group 2 was comprised of those without HPV-associated genital lesions (n=31). Samples for liquidbased cytology and high-risk DNA-HPV polymerase chain reaction real-time tests were collected from the cervix and anus. All cases were evaluated using high-resolution anoscopy; biopsies were performed when required. The Fisher exact and chi-squared tests were applied for consolidated data in the contingency table, and the Student ttest and Mann-Whitney U-test for independent variables.
Anal high-risk HPV infections were more frequent in group 1 (odds ratio [OR], 4.95; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34-18.3; p=0.012), along with concomitant highrisk HPV infections in the uterine cervix and the anus (OR 18.8; 95% CI, 2.20-160; p<0.001). The incidence of high-risk cervical HPV infection was associated with highrisk anal HPV infection (OR, 4.95; 95% CI, 1.34-18.3; p=0.012). There was no statistical difference concerning abnormal anal cytology or anoscopy between the groups, and no anal intraepithelial lesion was found in either group.
Immunocompetent women with HPV-associated genital lesions and high-risk cervical HPV were more likely to have high-risk anal HPV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):281-284
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500006
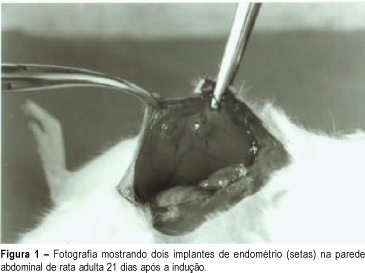
Purpose: to demonstrate the experimental endometriosis induction in animals. Method: we used adult female Wistar rats weighing 200 - 250 g anesthetized with ethyl ether to open the abdominal cavity. After identifying the uterine horns, we removed an approximately 4 cm fragment from the right uterine horn. This fragment was placed in physiological saline and, with the aid of a stereoscopic magnifying glass, the endometrium was separated from the myometrium and cut into rectangles of approximately 4 x 5 mm. These rectangles were fastened to the lateral abdominal wall near great blood vessels, taking care that the free portion of the endometrium was directed towards the lumen of the abdominal cavity. After 21 days the animals were again operated to observe the size of the implants and to remove the ectopic endometrium for microscopic analysis. Results: we macroscopically observed a significant growth of the endometrial implants. Microscopic examination showed presence of glandular epithelium and stroma similar to topic epithelium. Conclusion: this model reproduces endometriosis in the female rat allowing a better study of this pathology, mainly the action of drugs on these implants.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):281-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600008
PURPOSE: It was to describe and compare the preference of nulliparous and primiparous women for a particular mode of delivery and to determine whether the previous experience of childbirth influences the delivery process. METHODS: We conducted a prospective cross-sectional study. One-hundred interviews were held with 56 nulliparous and 44 primiparous women using previously prepared questionnaires. The quantitative and categorical data were evaluated by the chi-square or Fisher's Exact Test. RESULTS: 60.7% of nulliparous women and 70.5% of primiparous women reported to prefer vaginal delivery. When analyzing the answers about receiving sufficient information about the type of delivery, the presence or absence of influence on the choice of route of delivery and the preferred route of delivery by the partner, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. The level of significance used for the tests was 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: This study permitted us to conclude that the previous experience of delivery does not influence the expectation of the delivery process or the choice for a specific mode of delivery. When choosing the route of delivery, women seek to ensure the health of mother and neonate, as well as to avoid the process of pain and suffering.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):281-288
Female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) can affect women’s lives through various physical, psychological, social and even sexual mechanisms. According to the World Health Organization guidelines for managing the health effects of FGM/C, further research into its psychological effects and preventative measures is required. In this study, a comprehensive review of the mental health consequences of circumcised women of reproductive age has been conducted with a special focus on providing preventive solutions.
A comprehensive search of the Web of Science, PubMed(MEDLINE), Proquest ,Scopus and Google scholar was carried outfrom 2000 to 2022. The second stage of search was conducted in grey literature. To facilitate a systematic approach to search the literature, the PECO framework, was adopted.
The result of this narrative review study showed that, the most common mental health disorder in reproductive age circumcised women were depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. Some studies found a significant relationship between parents’ education level and circumcised girls, so that parents of the circumcised women had a low level of education. Two studies considered religious beliefs, tradition, cleanness, sexual desire control and virginity as the reasons for FGM/C.
All forms of FGM/C may be harmful to one’s health. Women, who have undergone widespread forms of circumcision, are more likely to develop mental disorders. As the psychosocial effects of circumcision can affect the sexual experience of circumcised women, addressing this issue, emphasizing its legal aspects, and providing preventative solutions can improve physical, mental, social, and even sexual health in circumcised women.