Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):225-231
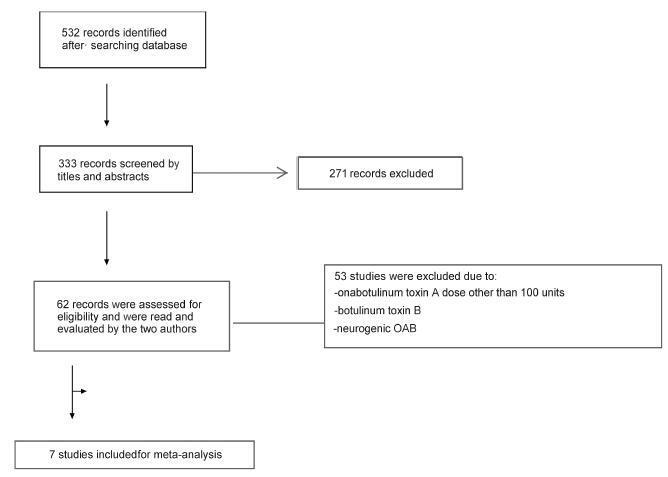
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials that studied non-neurogenic overactive bladder patients who were treated with 100 units of onabotulinumtoxinA or placebo. The primary purpose of our study was to evaluate the clinical effectiveness with regard to urinary urgency, urinary frequency, nocturia, and incontinence episodes. Our secondary purpose consisted of evaluating the adverse effects. Our initial search yielded 532 entries. Of these, seven studies met all the inclusion criteria (prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled studies, ≥ 3 points on the Jadad scale) and were selected for analysis. For all primary endpoints, the toxin was more effective than placebo (p < 0.0001; 95% confidence interval [95CI]), namely: urgency (mean difference = -2.07; 95CI = [-2.55-1.58]), voiding frequency (mean difference = - 1.64; 95CI = [-2.10-1.18]), nocturia (mean difference = -0.25; 95CI = [-0.39-0.11]) and incontinence episodes (mean difference = -2.06; 95CI= [-2.60-1.52]). The need for intermittent catheterization and the occurrence of urinary tract infection (UTI) were more frequent in patients treated with onabotulinumtoxinA than in patients treated with placebo (p < 0.0001). Compared with placebo, onabotulinumtoxinA had significantly and clinically relevant reductions in overactive bladder symptoms and is associated with higher incidence of intermittent catheterization and UTI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):225-234
To evaluate the performance of Intergrowth-21 st (INT) and Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) curves in predicting perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes in newborns weighing below the 3rd percentile.
Pregnant women with a single fetus aged less than 20 weeks from a general population in non-hospital health units were included. Their children were evaluated at birth and in the second or third years of life. Newborns (NB) had their weight percentiles calculated for both curves. Sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV), and area under the ROC curve (ROC-AUC) for perinatal outcomes and neurodevelopmental delay were calculated using birth weight < 3rd percentile as the cutoff.
A total of 967 children were evaluated. Gestational age at birth was 39.3 (± 3.6) weeks and birth weight was 3,215.0 (± 588.0) g. INT and FMF classified 19 (2.4%) and 49 (5.7%) newborns below the 3rd percentile, respectively. The prevalence of preterm birth, tracheal intubation >24 hours in the first three months of life, 5th minute Apgar <7, admission to a neonatal care unit (NICU admission), cesarean section rate, and the neurodevelopmental delay was 9.3%, 3.3%, 1.3%, 5.9%, 38.9%, and 7.3% respectively. In general, the 3rd percentile of both curves showed low sensitivity and PPV and high specificity and NPV. The 3rd percentile of FMF showed superior sensitivity for preterm birth, NICU admission, and cesarean section rate. INT was more specific for all outcomes and presented a higher PPV for the neurodevelopmental delay. However, except for a slight difference in the prediction of preterm birth in favor of INT, the ROC curves showed no differences in the prediction of perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Birth weight below the 3rd percentile according to INT or FMF alone was insufficient for a good diagnostic performance of perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes. The analyzes performed could not show that one curve is better than the other in our population. INT may have an advantage in resource contingency scenarios as it discriminates fewer NB below the 3rd percentile without increasing adverse outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
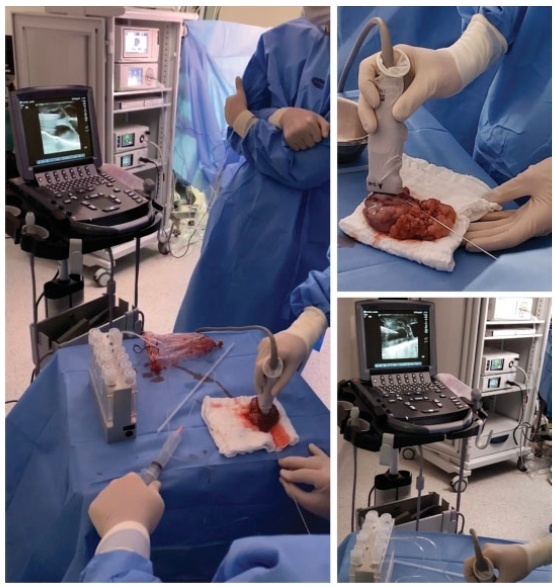
We report a case of ultrasound-guided ex vivo oocyte retrieval for fertility preservation in a woman with bilateral borderline ovarian tumor, for whom conventional transvaginal oocyte retrieval was deemed unsafe because of the increased risk of malignant cell spillage. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins was performed. Surgery was scheduled according to the ovarian response to exogenous gonadotropic stimulation; oophorectomized specimens were obtained by laparoscopy, and oocyte retrieval was performed ~ 37 hours after the ovulatory trigger. The sum of 20 ovarian follicles were aspirated, and 16 oocytes were obtained.We performed vitrification of 12 metaphase II oocytes and 3 oocytes matured in vitro. Our result emphasizes the viability of ex vivo mature oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian stimulation for those with high risk of malignant dissemination by conventional approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):226-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500007
PURPOSE: To determine the HPV prevalence and genotypes and to identify factors associated with infection in pregnant and non-pregnant women with positive or negative HIV-1, treated in Gynecology and Obstetrics Ambulatories and in Health Primary Units, in Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. METHODS: Cervical cells samples from 302 patients were analyzed for HPV presence and genotypes were determined by nested and sequencing polymerase chain reaction. We calculated prevalence ratios associated with the studied variables by Fisher's exact or χ² tests, and Poisson's regression. Women with insufficient material were excluded from the study. RESULTS: HPV was detected in 55 of the 302 women included in the study (18.2%); of these, 31 were pregnant, showing a significant association for HPV (p=0.04) when compared to non-pregnant ones. Risk factors for the infection were: patients aged <20 years-old (p=0.04), early initiation of sexual life (p=0.04), absence of cytological test (p=0.01), diagnosis of altered cytology (p=0.001), and counting <349 cells/mm³ (p=0.05). However, multi-parity was found to be a protective factor for the infection (p=0.01). Multivariate analysis showed that age <20 years-old (PR=2.8; 95%CI 1.0 - 7.7, p=0.04) and an altered cytological result (PR=11.1; 95%CI 3.0 - 4.1, p=0.001) were significantly associated with infection. HPV genotype was determined in 47 samples (85.4%) presenting one genotype per infection: eight HPV 16 and 58; six HPV 6; four HPV 18 and 33; three HPV 53 and 82; two HPV 83 and 61; one HPV 31, 35, 45, 64, 68, 71 and 85. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of HPV detection was 18.2%, the most frequent genotypes were 16 and 58, and sociodemographic and gynecological factors were associated with viral infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):227-233
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000900002
PURPOSE: To evaluate the coping strategies of women facing a diagnosis of fetal heart disease. METHODS: We interviewed 50 women who had received a diagnosis of fetal heart disease. For data collection we used a semi-directed and Coping Strategy Inventory. The interview was conducted, on average, 22 days after the diagnosis. RESULTS: When asked how they felt about the baby, 56.0% reported concern and fragility, while the remaining 44.0% said they were happy and well. The strategies most used by women were problem solving (73.0%), social support (69.1%) and escape/avoidance (62.7%), and the least used strategy was removal (17.3%). It was found that women with partners, as well as those with 1 or 2 children, used more the problem-solving strategy (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: The active coping strategies, focused on problem solving and seeking social support, coupled with the responsibility and the need for specific care for the survival and welfare of the baby, brought about a closer relationship with the pregnancy, strengthening the maternal-fetal bond.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):227-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400008
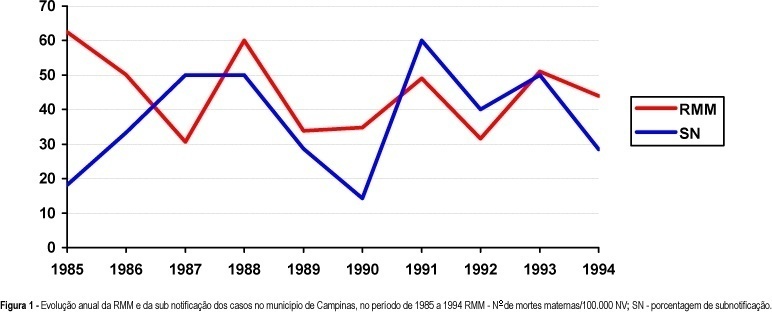
Purpose: to identify and investigate the causes of maternal death that occurred in Campinas from 1992 to 1994. Methods: a total of 204 death certificates (DC) whose causes of death were maternal (declared and/or presumed) were selected among the 1032 DC's of 10 to 49 year-old women. A complementary investigation was performed consulting hospital records, Death Survey Units, and households. Results: a total of 20 maternal deaths were confirmed, corresponding to a maternal mortality ratio of 42.2 deaths per 100,000 live births. The direct obstetrical causes were responsible for 85% of the deaths (17 cases). Abortion complications were the main causes of death (7 cases), followed by hemorrhage (4 cases), preeclampsia (3 cases) and puerperal infection (3 cases). Conclusions: despite the apparent progress concerning the reduction in deaths due to hypertensive syndromes during pregnancy, that were the main causes in earlier periods, there was no improvement in the maternal mortality ratio for this studied period. Unfortunately, this lack of progress was due to abortion complications. A better coverage and efficiency of family planning programs, besides the need for implementation of a real epidemiological surveillance of maternal deaths, as well as a better social protection of the pregnant woman, the mother, and the newborns, could reduce their occurrence and specially those due to abortions.