You searched for:"Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori"
We found (29) results for your search.-
Original Article
Efficacy of Sacrospinous Fixation or Uterosacral Ligament Suspension for Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Stages III and IV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):584-593
Summary
Original ArticleEfficacy of Sacrospinous Fixation or Uterosacral Ligament Suspension for Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Stages III and IV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):584-593
Views3Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and outcomes of the surgical treatment for pelvic organ prolapse (POP) in stages III and IV by sacrospinous ligament fixation (SSLF) or uterosacral ligament suspension (USLS) by comparing anatomical and subjective cure rates and quality-of-life parameters (through the version validated for the Portuguese language of the Prolapse Quality of Life [P-QoL] questionnaire) under two definitions: genital prolapse Ba, Bp, and C< −1 (stage I) and Ba, Bp, and C ≤ 0 (stage II).
Materials and Methods
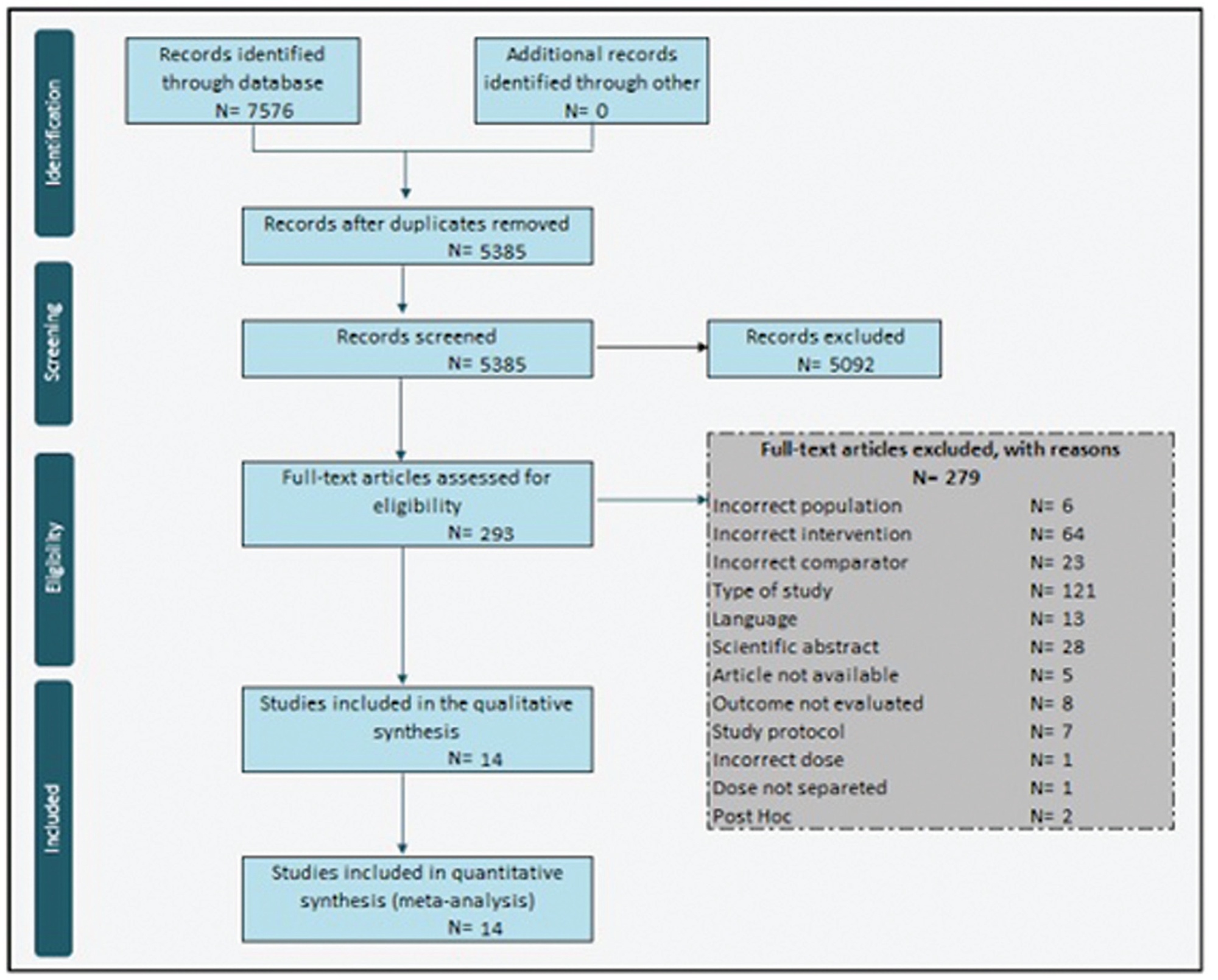
After we obtained approval from the Ethics Committee (under CAAE 0833/06) and registered the study in ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT 01347021), 51 patients were randomized into two groups: the USLS group (N = 26) and the SSLF group (N = 25), with follow-up 6 and 12 months after the procedures.
Results
There was a significant improvement in the P-QoL score and anatomical measurements of all compartments in both groups after 12 months (p< 0.001). The anatomical cure rates in the USLS and SSLF groups, considering stage 1, were of 34.6% and 40% (anterior) respectively; of 100% both for groups (apical); and of 73.1% and 92% (posterior) respectively. The rates of adverse outcomes were of 42% (N = 11) and 36% (N = 11) for the USLS and SSLF groups respectively (p = 0.654), and those outcomes were excessive bleeding, bladder perforation (intraoperative) or gluteal pain, and urinary infection (postoperative), among others, without differences between the groups.
Conclusion
High cure rates in all compartments were observed according to the anatomical criterion (stage I), without differences in P-QoL scores and complications either with USLS or SSLF for the surgical treatment of accentuated POP.
Key-words patient health questionnairepatient-reported outcome measurespelvic floor disorderspelvic organ prolapsereconstructive surgical proceduresSee more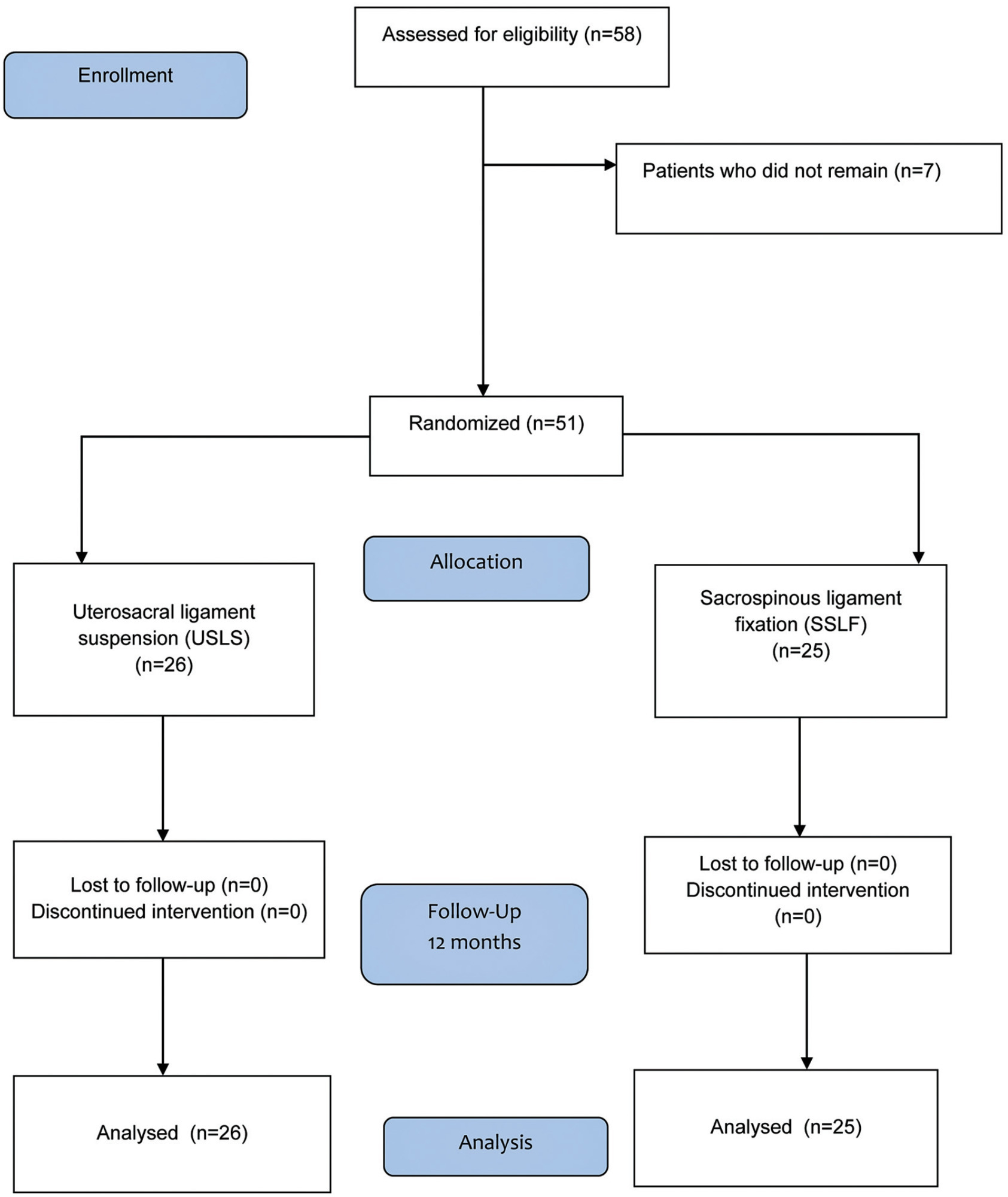
-
Original Article/Teaching and Training
Effectiveness of an Educational Intervention with Guidelines from the Total Acceleration of Postoperative Recovery Project (ACERTO) in Gynecology
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(11):699-705
Summary
Original Article/Teaching and TrainingEffectiveness of an Educational Intervention with Guidelines from the Total Acceleration of Postoperative Recovery Project (ACERTO) in Gynecology
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(11):699-705
Views2Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effectiveness of an educational intervention among gynecologists about recommendations of the Total Acceleration of Postoperative Recovery (ACERTO, in the Portuguese acronym) project derived from the solid foundations of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) guidelines to optimize hospital care for surgical-gynecological patients.
Methods
Educational intervention through monthly 1-hour long meetings (3 months), with the application of an objective questionnaire about specific knowledge of the ACERTO project between before and after educational intervention phases, for gynecologists, after approval by the ethics committee and signature of informed consent by participants, in a federal university hospital.
Results
Among the 25 gynecologists who agreed to participate, the educational intervention could be effective with a statistically significant difference between the phases before and after the intervention for the main recommendations of the ACERTO project, such as abbreviation of preoperative fasting (p = 0.006), venous thromboembolism prophylaxis (p = 0.024), knowledge and replication of ACERTO (p = 0.034), and multimodal analgesia (p = 0.021).
Conclusion
An educational intervention, through clinical meetings with exposition and discussion of the recommendations of the ACERTO project based on the ERAS protocol can be effective for the knowledge and possibility of practical application of the main measures, such as abbreviation of preoperative fasting, multimodal analgesia, and prophylaxis of thrombosis among gynecologists.
Key-words enhanced recovery after surgeryperioperative carepreoperative caresurgical procedures in gynecologySee more
-
Original Article
Three-dimensional Printer Molds for Vaginal Agenesis: An Individualized Approach as Conservative Treatment
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(12):1110-1116
Summary
Original ArticleThree-dimensional Printer Molds for Vaginal Agenesis: An Individualized Approach as Conservative Treatment
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(12):1110-1116
Views1See moreAbstract
Objective
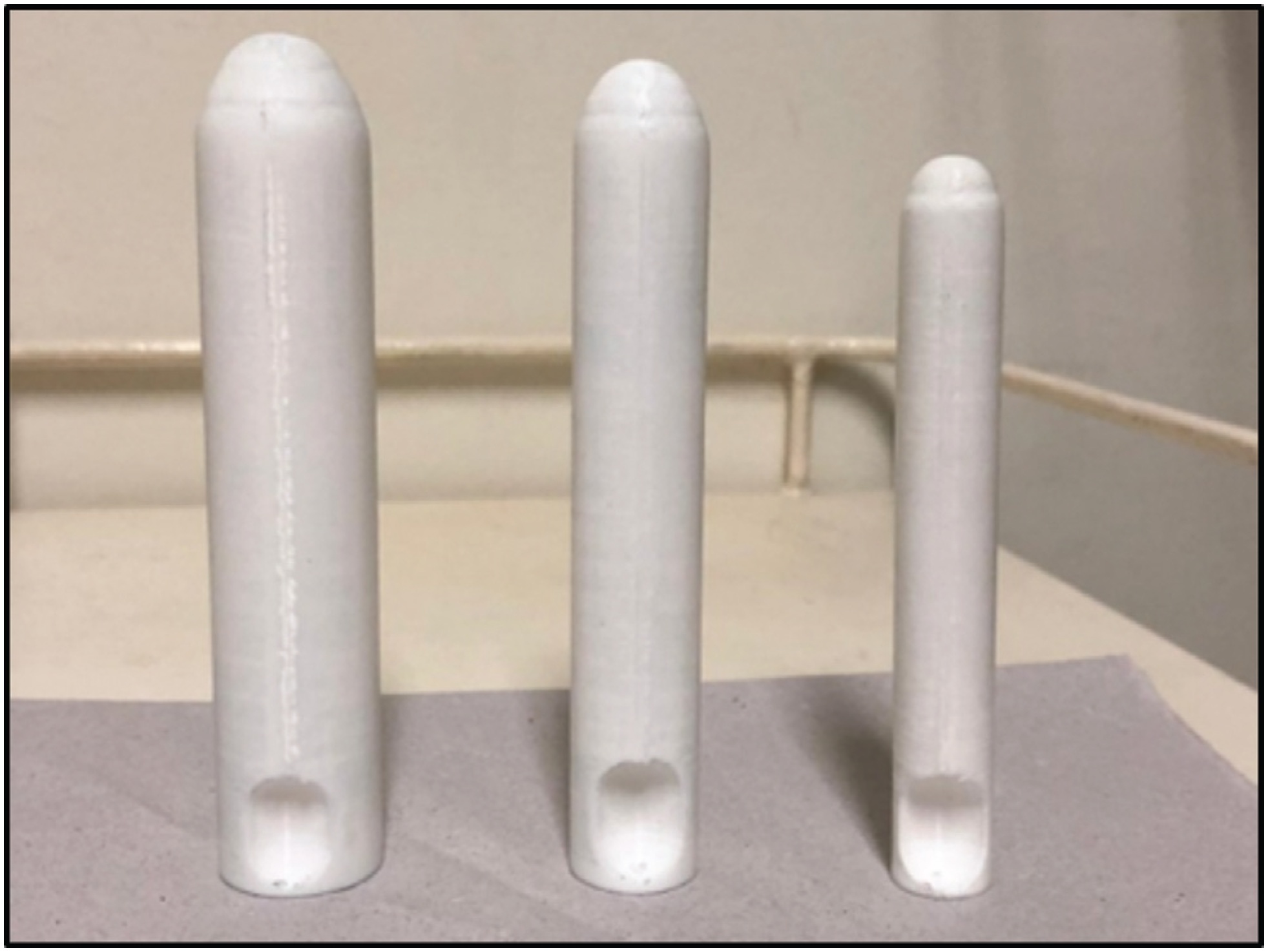
The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of vaginal molds, made with three-dimensional (3D) printing, for conservative treatment through vaginal dilation in patients with vaginal agenesis (VA).
Methods
A total of 16 patients with a diagnosis of VA (Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome, total androgen insensitivity syndrome, and cervicovaginal agenesis) from the Federal University of São Paulo were selected. Device production was performed in a 3D printer, and the polymeric filament of the lactic polyacid (PLA) was used as raw material. A personalized treatment was proposed and developed for each patient.
Results
There were 14 patients who reached a final vaginal length of 6 cm or more. The initial total vaginal length (TVL) mean (SD) was 1.81(1.05) and the final TVL mean (SD) was 6.37 (0.94); the difference, analyzed as 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was 4.56 (5.27–3.84) and the effect size (95% CI) was 4.58 (2.88–6.28).
Conclusion
The 3D printing molds for vaginal dilation were successful in 87.5% of the patients. They did not present any major adverse effects and offered an economical, accessible, and reproducible strategy for the treatment of VA.
-
Editorial
The Use of Three-dimensional Printer Molds for Treatment of Vaginal Agenesis
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(12):1081-1082
Summary
EditorialThe Use of Three-dimensional Printer Molds for Treatment of Vaginal Agenesis
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(12):1081-1082
Views1Although rare, vaginal agenesis is a relevant condition for gynecologists, who must be familiar with its current treatment.It results from agenesis of the Mullerian ducts, known as Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome (MRKHS), and the incidence is 1:5000 women. In this congenital malformation, genetic alterations affect the development of Mullerian ducts during the embryonic period and there is […]See more -
Review Article
Burch Procedure: A Historical Perspective
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(5):511-518
Summary
Review ArticleBurch Procedure: A Historical Perspective
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(5):511-518
Views5See moreAbstract
Introduction
The Burch procedure (1961) was considered the gold standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) before the midurethral slings (MUSs) were introduced, in 2001.
Objective
This historical perspective of the Burch’s timeline can encourage urogynecological surgeons to master the Burch technique as one of the options for surgical treatment of SUI.
Search Strategy and Selection
Criteria A bibliographic search was performed in the PubMed and National Library of Medicine (NIH) databases with the terms Burch colposuspension AND history AND stress urinary incontinence in the last 20 years. The original article by Burch (1961) was included. The references were read by three authors. The exclusion criterion was studies in non-English languages. Biomedical Library Special Collections were included as historical relevant search.
Data Collection, Analysis and Main Results
Some modifications of the technique have been made since the Burch procedure was first described. The interest in this technique has been increasing due to the negative publicity associated with vaginal synthetic mesh products. Twenty-nine relevant articles were included in the present review article, and numerous trials have compared Burch colposuspension with MUS.
Conclusion
This historical perspective enables the scientific community to review a standardized technique for SUI. Burch colposuspension should be considered an appropriate surgical treatment for women with SUI, and an option in urogynecological training programs worldwide.

-
Review Article
Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Gynecological Health: An Integrative Review
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(2):194-200
Summary
Review ArticleEffects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Gynecological Health: An Integrative Review
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(2):194-200
Views3Abstract
Objective
To analyze the existing scientific literature to find out if the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has an effect on gynecological health.
Search Strategy
We performed an integrative review of articles published between April 2020 and April 2021 on the PubMed, SciELO, and LILACS databases, using COVID-19 and the following relevant terms: Menstrual change; Ovarian function; Violence against women; Contraception; HPV; Mental health; and Urogynecology.
Selection Criteria
Among the eligible studies found, editorials and primary research articles, which describe the dynamics between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection (the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic) and gynecological health, were included.
Data Collection and Analysis
Through qualitative synthesis, data were extracted from the included publications and from guidelines of national and international societies of gynecology.
Main Results
The 34 publications included in the present study showed that some factors of the SARS-CoV-2 infection, and, consequently, the COVID-19 pandemic, might be associated with menstrual abnormalities, effects on contraception, alterations in steroid hormones, changes in urogynecological care, effects on women’s mental health, and negative impact on violence against women.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the health of women. The scientific community encourages the development of recommendations for specialized care for women and strategies to prevent and respond to violence during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key-words contraceptionCOVID-19 pandemicmenstrual changeovarian functionSARS-CoV-2urogynecologyviolence against womenSee more -
Original Article
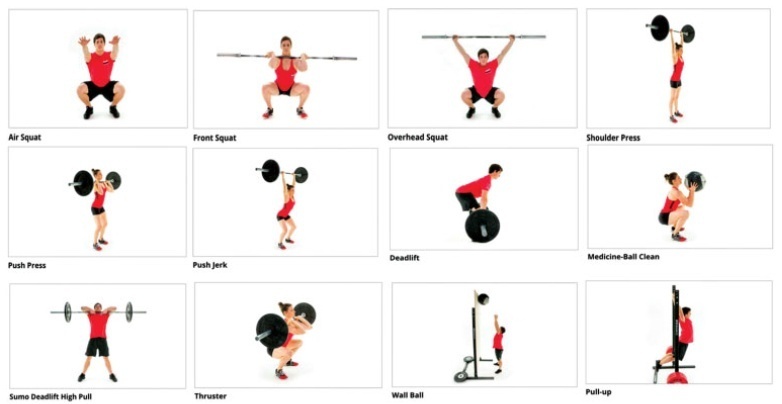
Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in CrossFit Practitioners before and during the COVID-19 Quarantine and its Relationship with Training Level: An Observational Study
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(11):847-852
Summary
Original ArticlePrevalence of Urinary Incontinence in CrossFit Practitioners before and during the COVID-19 Quarantine and its Relationship with Training Level: An Observational Study
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(11):847-852
Views1See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare the prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) before and during the COVID-19 quarantine in CrossFit women and their relationship with training level.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed among 197 women practicing CrossFit. The inclusion criteria were nulliparous women, between 18 and 45 years old, who had trained, before quarantine, in accredited gyms. The exclusion criteria were not following the COVID-19 prevention protocols and having UI on other occasions than just sport. An online questionnaire was emailed containing questions about frequency, duration, and intensity of training and data related to the COVID-19 pandemic. The participants were invited to answer whether they were infected with COVID-19 and what treatment/recommendation they have followed. Whether UI stopped among participants, they were asked about the possible reasons why this happened. The training intensity was categorized as “the same,” “decreased” or “increased.”
Results
The mean age of the participants was 32 years old and most (98.5%) could practice CrossFit during the pandemic. There was a decrease in training intensity in 64% of the respondents. Exercises with their own body weight, such as air squat (98.2%), were the most performed. Urinary incontinence was reported by 32% of the participants before the COVID-19 pandemic, and by only 14% of them during the pandemic (odds ratio [OR]=0.32 [0.19-0.53]; p<0.01; univariate analysis). Practitioners reported that the reason possibly related to UI improvement was the reduction of training intensity and not performing doubleunder exercise.
Conclusion
The reduction in the intensity of CrossFit training during the COVID-19 quarantine decreased the prevalence of UI among female athletes.

Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)