Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):599-603
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800009
PURPOSE: the aim was to study Rh-alloimmunized pregnant women and describe the gasometric abnormalities and the fetal acid-base changes before and after intrauterine transfusion. METHODS: between June 2001 and October 2001, before and after intrauterine transfusion in the alloimunized fetuses, gasometric data and acid-base parameters were prospectively studied in the umbilical vein blood. The measurements were performed in 8 samples of 5 fetuses. The fetal blood was obtained by cordocentesis before and after the intrauterine transfusion. The results were compared to the volemic expansion, the gestational age at procedure, the estimated fetal weight and the hemoglobin values (g/dL). RESULTS: all the cases showed pH value reduction, mean of 0.09 (SD=0.02). The fetal hemoglobin value showed a mean improvement of 8.4 g/dL (SD=2.9 g/dL). The pO2 and HCO3- concentrations showed negative variation (mean deltapO2 = -1.28 mmHg, mean deltaHCO3- = -2.25 mEq/L). pCO2 showed improvement (mean deltapCO2 = 3.2 mmHg) and reduced values of base excess occurred (mean = -3.75). CONCLUSION: the gasometric analysis allows to conclude that intrauterine transfusion is followed by pH reduction in the umbilical vein, with relative fetal acidemia after the procedure.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):553-559
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800003
PURPOSE: to verify vitrification techniques using 6 M DMSO to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes, and to assess the effects of the time of exposure to vitrification solutions (VS). METHODS: dilutions of VS were prepared from the stock VS (VS 100%) consisting of 6 M DMSO to give 25 and 65% DMSO solutions. Bovine oocytes were in vitro matured for 18-22 h. Matured oocytes were placed first into 25% VS, at room temperature for 5 min, then transferred to 65% VS, before being pipetted into the 100% VS in plastic straws. Three experimental groups were formed: in the first group, time of pipetting through 65% VS and loading the straw took up to 60 s, in the second group it did not exceed 30 s. For thawing, straws were held in air for 10 s and then in a water bath for 10 s. The contents of each straw were expelled in sucrose solution and held for 5 min. In the third experimental group, oocytes went through all VS, but were not vitrified. All retrieved oocytes were inseminated. For control, fresh, in vitro matured oocytes were inseminated. RESULTS: after vitrification, 69.1 and 59.8% of the oocytes were retrieved from the 30 s and 60 s groups, respectively, and 93 and 89% of these oocytes appeared morphologically normal 24 h after insemination, respectively. In the group of oocytes exposed without vitrification, 75.6% were retrieved and 84.7% were morphologically viable, 24 h after insemination. No fertilization was observed in the experimental groups. Among controls, 65.4% were fertilized. CONCLUSIONS: the vitrification technique using 6 M DMSO is not a feasible approach to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes. Decreasing the time of exposure to VS did not overcome deleterious effects of the procedure on the fertilizability of oocytes. Improvements in the technique are needed to protect the zona pellucida and oolemma.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):563-569
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800004
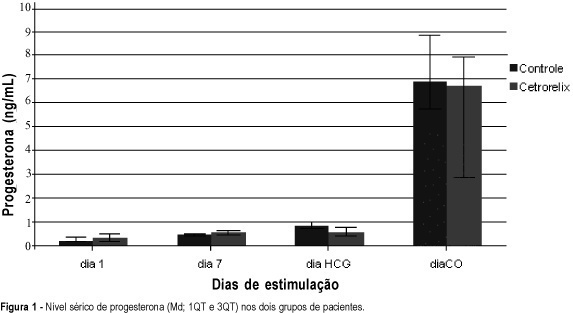
PURPOSE: to verify the efficacy of a single subcutaneous dose of cetrorelix acetate to avoid premature ovulation in assisted fertilization cycles. METHODS: this is a prospective, controlled and randomized study, with 20 women undergoing ovarian stimulation for assisted fertilization, 10 of whom were submitted to classical GnRH agonist protocol (control group) while 10 utilized a 3-mg subcutaneous dose of the GnRH antagonist on the 7th day of ovarian stimulation (cetrorelix group). Serum FSH, LH, estradiol and progesterone concentrations were assessed on the first, seventh, HCG administration and oocyte retrieval days. Both groups were compared for pituitary suppression (progesterone concentration on HCG day) and assisted fertilization cycle performance (gonadotropin ampoules utilized, follicles over 18 mm, retrieved oocytes, fertilization, implantation and pregnancy rates), utilizing Mann-Whitney and Fisher exact tests. RESULTS: no significant difference was observed between control and cetrorelix groups, respectively, for medians of age (31.5 and 34 years), body mass index (24 and 22), gonadotropin ampoles utilized (34 and 32), follicles over 18 mm (3.5 and 3.3), retrieved oocytes (11 and 5), obtained embryos (4 and 3), fertilization (93,7 and 60%, p=0.07) and pregnancy rates (50 and 60%, p=0.07). Efficient pituitary blockade through the ovarian stimulation period was observed for both groups. CONCLUSIONS: these results confirm the efficacy of a 3-mg dose of cetrorelix acetate to prevent premature ovulation in patients undergoing assisted fertilization and suggest a tendency towards a smaller number of embryos and fertilization rates in the cetrorelix group than in the control group. Implantation and pregnancy rates were similar between groups. Other prospective studies with a greater number of patients should be performed to confirm these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):577-583
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800006
PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the Doppler indices of inferior vena cava and ductus venosus and the fetal hemoglobin concentration. METHODS: a cross-sectional prospective study was performed at the "Centro de Medicina Fetal HC UFMG" from January 1998 to July 2001. Thirty-one pregnant women with isoimmunization, detected by an indirect Coombs test >1:8, underwent a protocol for the identification of fetal hemolysis. When intrauterine transfusions were indicated, the umbilical cord hemoglobin concentration was measured at the begining of the procedure. In the other cases, it was measured at delivery. Every single intrauterine transfusion preceded by Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus was defined as one case. Hemocue® (B-Hemoglobin Photometer Hemocue AB; Angelholm, Sweden) was used to measure the fetal hemoglobin concentration. In all cases, inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler examinations were performed before the collection of fetal blood samples. For the inferior vena cava Doppler, the studied indices were pulsatility index for veins (PVI), peak velocity index for veins (PVIV) and atrial/systole ratio (CA/SV ratio or preload index); for ductus venosus, PVI, PVIV and systole/atrial ratio (SV/CA ratio). The relationship between inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices and cord blood hemoglobin concentration was obtained by simple linear regression analysis. Moreover, an association between those indices and the finding of fetal hemoglobin <10 g/dL was shown by the c² test, significant at p<0.05. RESULTS: seventy-four procedures were studied. In twenty-three cases fetal hemoglobin was below 7 g/dL. A significant negative correlation between all studied Doppler indices and fetal concentration of hemoglobin was observed (p<0.05). The highest Doppler index values were observed in severe anemic fetuses. Fetuses with cord blood hemoglobin below 10 g/dL presented inferior vena cava and ductus venosus Doppler indices over the 95 percentile for gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: Doppler flow velocity waveforms from inferior vena cava and ductus venosus may be used as a noninvasive marker of severe fetal anemia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):475-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700003
PURPOSE: to study the effects of low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives (OHC) (<30 mg of ethynylestradiol) on the intraerythrocytic folate levels. METHODS: this was a prospective transversal study with 95 patients treated in the Family Planning Clinic of UNIFESP (Federal University of São Paulo). The control group (Condom group) consisted of patients using condom as their exclusive contraceptive method during the last 12 months, and the study groups consisted of patients using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives, in the following way: OHC 3 group (three to six months of use), OHC 6 group (six to twelve months of use) and OHC 12 group (more than twelve months of use). Intraerythrocytic folate was determined by the ionic capture method. Analysis of variance and c² test were used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: the Condom group showed a rate of 44% of patients with folate lower than 186.0 ng/mL and the users of low-dose oral contraceptives showed a rate of 32% (OHC 3 group), 16% (OHC 6 group) and 31% (OHC 12 group). We did not find in the group using low-dose oral contraceptives a significant reduction in the average level of intraerythrocytic folate compared to the control group and there was no statistically significant difference (p=0.28) regarding time of use. CONCLUSION: we observed reduced levels of intraerythrocytic folate in a significant number (44%) of patients not using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives. Their rates were similar to the lower limit considered to be normal by most authors, which points to a basal folate deficiency in the studied group. We did not observe any alteration in the level of intraerythrocytic folate in patients using low-dose oral hormonal contraceptives.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):483-489
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700004
PURPOSE: to describe the pregnancy outcome of women submitted to cervical cerclage during pregnancy. METHODS: a series of 123 pregnancies in 116 women submitted to elective cervical cerclage by Espinosa-Bahamondes, Palmer and MacDonald techniques and followed at the High-Risk Antenatal Care Unit at CAISM/UNICAMP is described. Variables were analyzed through frequency, mean and standard deviation, comparisons were made using c² or Fisher exact tests. RESULTS: 73% had at least one previous abortion, 17.9% had had 3 prior abortions, and 48% had prior preterm deliveries. The mean gestational age at cerclage was 16 weeks. Cerclage by the Espinosa-Bahamondes technique predominated (94.3%). The overall complication rate was 69%, with preterm labor as the most frequent (31.7%), followed by vaginitis (26%), preterm premature rupture of membranes (10.5%) and fetal death (8.7%). Other clinical complications were less common and included urinary tract infections (5.6%), hypertensive disorders (4%) and gestational diabetes (2.4%). Fetal loss occurred in 8.9% of pregnancies (11 stillbirths). Premature deliveries were present in 18%. History of previous premature deliveries was associated with the occurrence of premature deliveries. CONCLUSION: Obstetrical history compatible with cervical incompetence was frequent, and prior preterm delivery was associated with a preterm delivery in the pregnancy under analysis. The use of cerclage by the Espinosa-Bahamondes technique resulted in 18% of premature newborns, and 104 per thousand rate of perinatal death. Prospective, controlled trials are needed to evaluate the real benefits of cervical cerclage performed during pregnancy.