Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):729-744
To review the current state of knowledge on the impact of the surgical treatment on the sexual function and dyspareunia of deep endometriosis patients.
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. We conducted systematic searches in the PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and Web of Science databases from inception until December 2022. The eligibility criteria were studies including: preoperative and postoperative comparative analyses; patients with a diagnosis of deep endometriosis; and questionnaires to measure sexual quality of life.
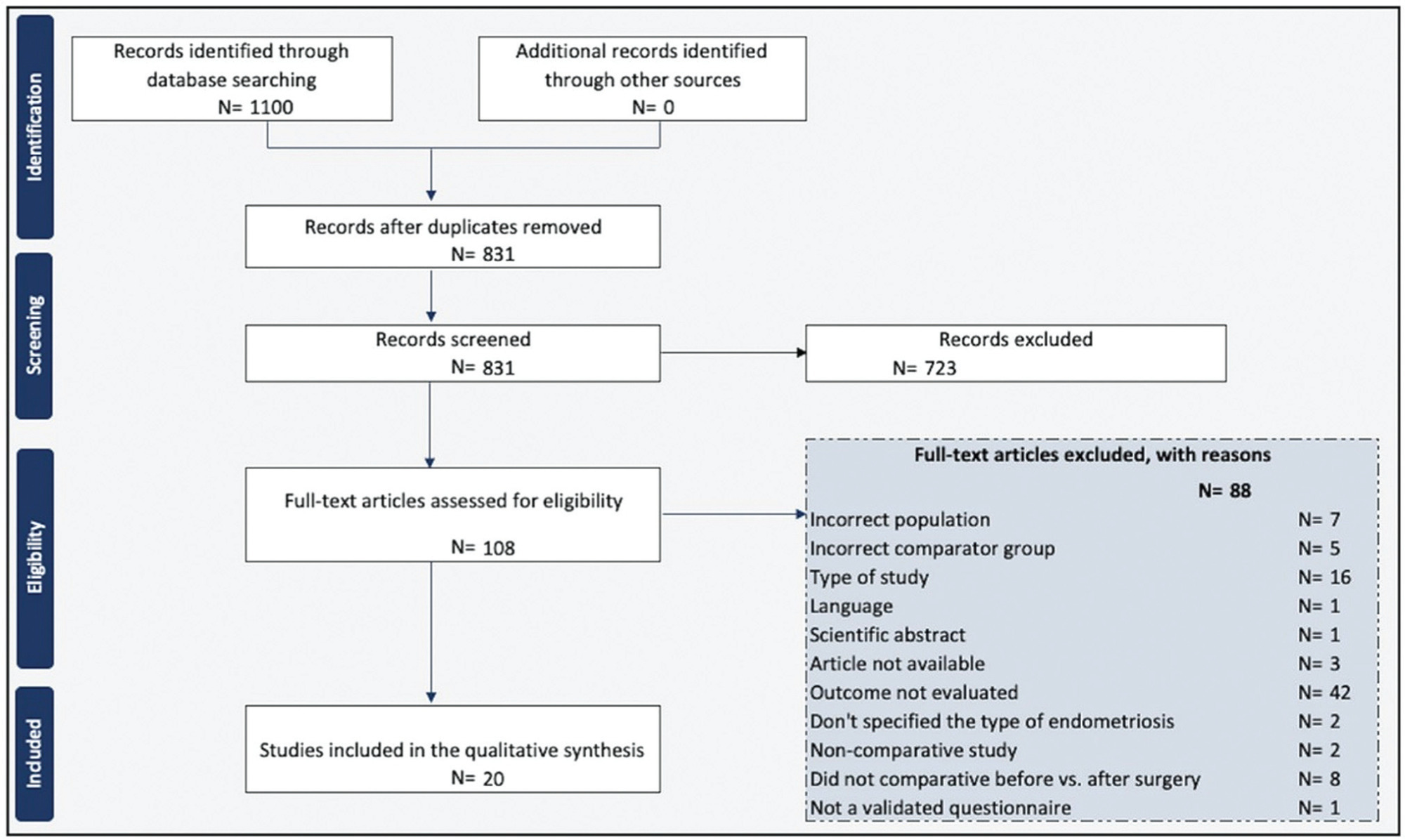
Two reviewers screened and reviewed 1,100 full-text articles to analyze sexual function after the surgical treatment for deep endometriosis. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for randomized controlled trials. The present study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration CRD42021289742).
General variables about the studies, the surgical technique, complementary treatments, and questionnaires were inserted in an Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, United States) spreadsheet.
We included 20 studies in which the videolaparoscopy technique was used for the excision of deep infiltrating endometriosis. A meta-analysis could not be performed due to the substantial heterogeneity among the studies. Classes III and IV of the revised American Fertility Society classification were predominant and multiple surgical techniques for the treatment of endometriosis were performed. Standardized and validated questionnaires were applied to evaluate sexual function.
Laparoscopic surgery is a complex procedure that involves multiple organs, and it has been proved to be effective in improving sexual function and dyspareunia in women with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):724-728
To determine if the use of lubricating gel on the speculum during the cervicovaginal cytology examination interferes with the results obtained, as well as whether it reduces reported discomfort in patients.
A systematic review was carried out according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations, with a search in the Pubmed/Medline, Scielo, Cochrane Library, Embase databases of articles published between January 2011 and May 2022. The keywords used were cytology, speculum, lubricant, result, and pain.
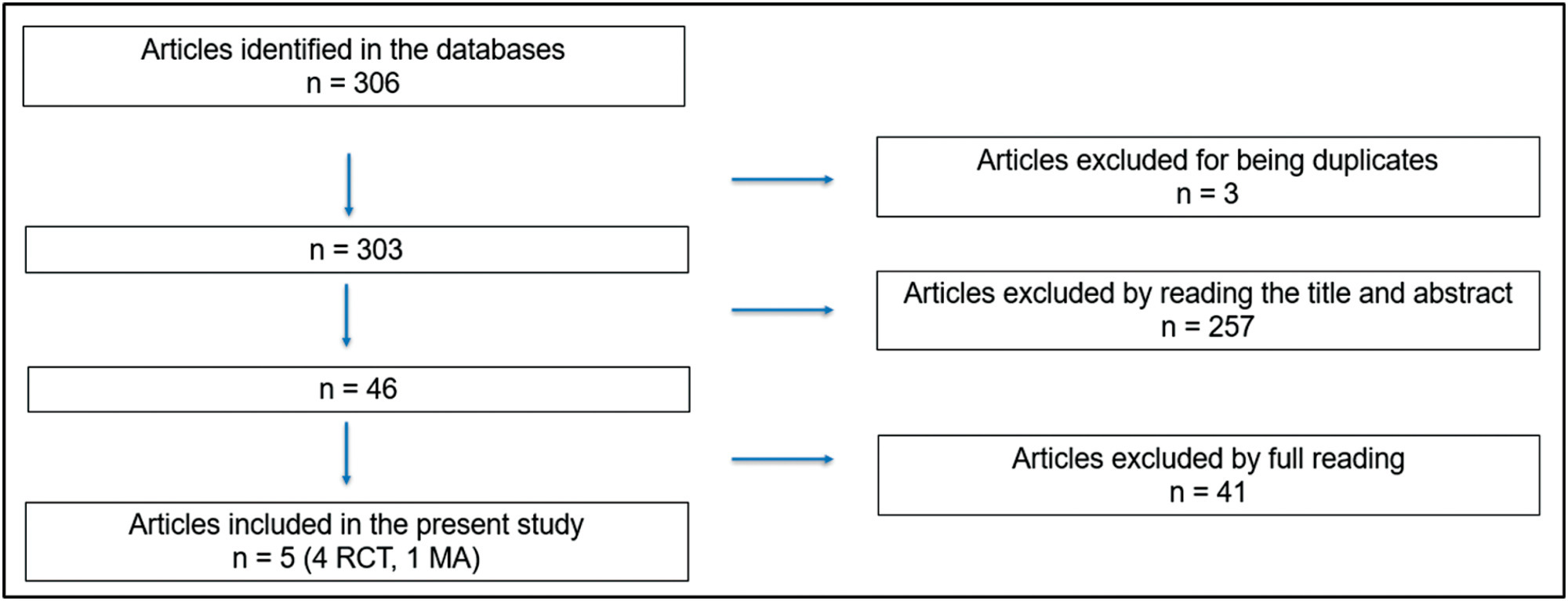
The initial search resulted in 306 articles, of which were excluded three because they were duplicates, 257 after reading the title and abstract and 41 after reading the full text. Thus, five articles were selected for the study: four randomized clinical trials and one metanalysis.
The selection of articles was performed by two investigators. The 5 selected articles were read in full and submitted to a comparative analysis.
Screening through cervicovaginal cytology allows for early diagnosis and reduction of associated mortality, but the procedure can be associated with pain. A small amount of aqueous lubricating gel in the speculum can be used to reduce the discomfort associated with performing cervicovaginal cytology.
The use of lubricating gel in the speculum does not seem to be associated with a change in the cytology result and reduces the discomfort associated with its insertion into the vagina.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):415-421
The aim of the present study was to identify how the transition of care from the hospital to the community occurs from the perspective of puerperal women at risk. An integrative literature review was performed, with the question: “How does the transition of care for at-risk puerperal women from the hospital to the community occur?” The search period ranged from 2013 to 2020, in the following databases: PubMed, LILACS, SciELO, and Scopus. MESH, DeCS and Boolean operators “OR” and “AND” are used in the following crossover analysis:patient transfer ORtransition care ORcontinuity of patient care ORpatient discharge ANDpostpartum period, resulting in 6 articles. The findings denote discontinuity of care, given the frequency of non-adherence to the puerperal consultation. Transition studies of care in the puerperium were not found, which requires proposing new studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):281-288
Female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) can affect women’s lives through various physical, psychological, social and even sexual mechanisms. According to the World Health Organization guidelines for managing the health effects of FGM/C, further research into its psychological effects and preventative measures is required. In this study, a comprehensive review of the mental health consequences of circumcised women of reproductive age has been conducted with a special focus on providing preventive solutions.
A comprehensive search of the Web of Science, PubMed(MEDLINE), Proquest ,Scopus and Google scholar was carried outfrom 2000 to 2022. The second stage of search was conducted in grey literature. To facilitate a systematic approach to search the literature, the PECO framework, was adopted.
The result of this narrative review study showed that, the most common mental health disorder in reproductive age circumcised women were depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. Some studies found a significant relationship between parents’ education level and circumcised girls, so that parents of the circumcised women had a low level of education. Two studies considered religious beliefs, tradition, cleanness, sexual desire control and virginity as the reasons for FGM/C.
All forms of FGM/C may be harmful to one’s health. Women, who have undergone widespread forms of circumcision, are more likely to develop mental disorders. As the psychosocial effects of circumcision can affect the sexual experience of circumcised women, addressing this issue, emphasizing its legal aspects, and providing preventative solutions can improve physical, mental, social, and even sexual health in circumcised women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):347-355
To review the literature and synthesize evidence on pathophysiological interactions attributed to the simultaneous occurrence of COVID-19 and preeclampsia.
A systematic review was conducted from November (2021) to January (2022) to retrieve observational studies published on the PubMed, LILACS, SciELO Brazil and Google Scholar databases. The search was based on the descriptors [(eclampsia OR preeclampsia) AND (COVID-19)]. Quantitative studies that pointed to pathophysiological interactions were included. Literature reviews, studies with HIV participants, or with clinical approach only were excluded. The selection of studies was standardized and the evaluation was performed by pairs of researchers.
In this review, 155 publications were retrieved; 16 met the inclusion criteria. In summary, the physiological expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptors is physiologically increased in pregnant women, especially at the placental site. Studies suggest that the coronavirus binds to ACE-2 to enter the human cell, causing deregulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and in the ratio between angiotensin-II and angiotensin-1-7, inducing manifestations suggestive of preeclampsia. Furthermore, the cytokine storm leads to endothelial dysfunction, vasculopathy and thrombus formation, also present in preeclampsia.
The studies retrieved in this review suggest that there is a possible overlap of pathophysiological interactions between COVID-19 and preeclampsia, which mainly involve ACE-2 and endothelial dysfunction. Given that preeclampsia courses with progressive clinical and laboratory alterations, a highly quality prenatal care may be able to detect specific clinical and laboratory parameters to differentiate a true preeclampsia superimposed by covid-19, as well as cases with hypertensive manifestations resulting from viral infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):096-103
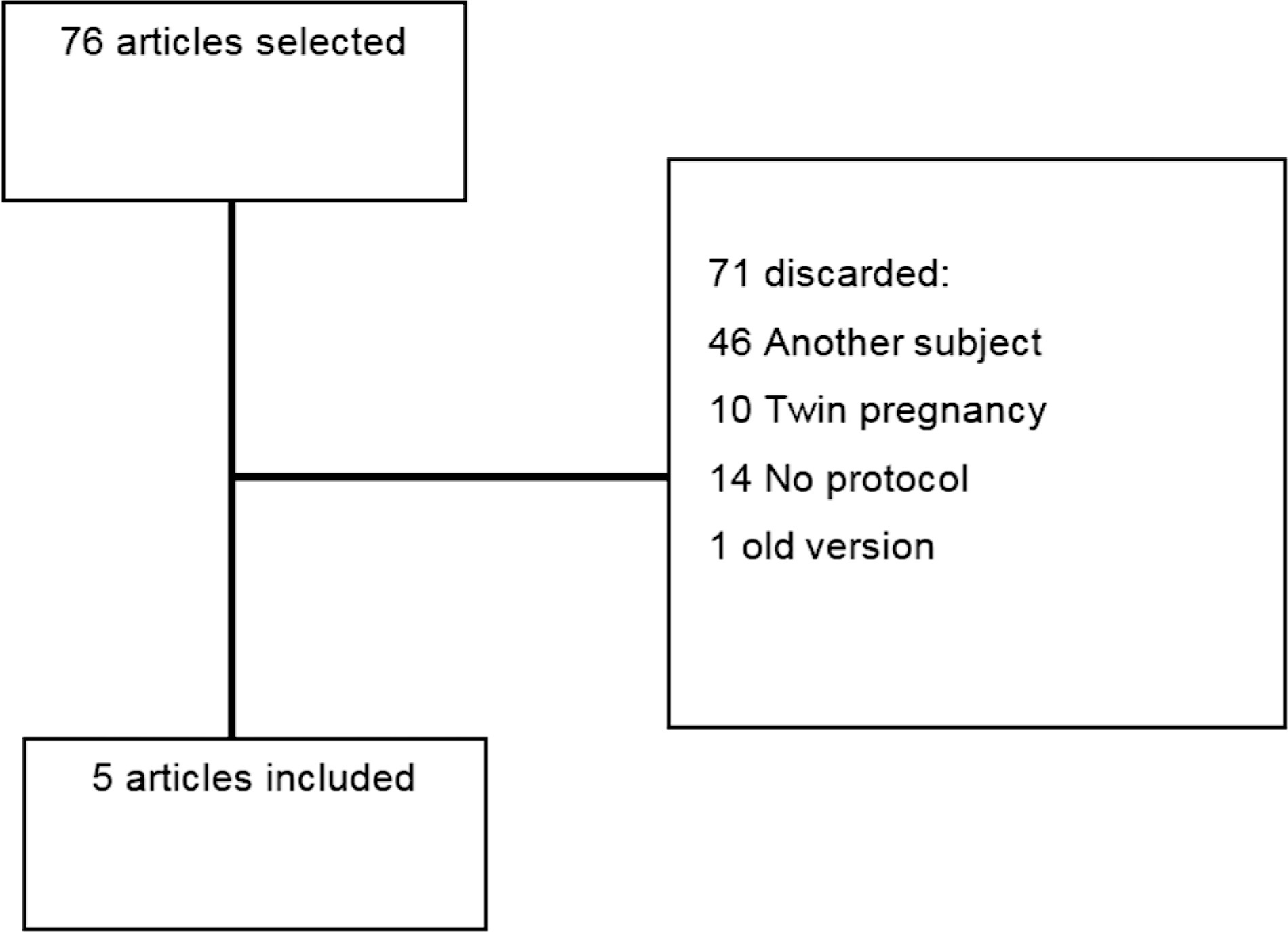
This comprehensive review compares clinical protocols of important entities regarding the management of fetal growth restriction (FGR), published since 2015. Five protocols were chosen for data extraction. There were no relevant differences regarding the diagnosis and classification of FGR between the protocols. In general, all protocols suggest that the assessment of fetal vitality must be performed in a multimodally, associating biophysical parameters (such as cardiotocography and fetal biophysical profile) with the Doppler velocimetry parameters of the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, and ductus venosus. All protocols reinforce that the more severe the fetal condition, the more frequent this assessment should be made. The timely gestational age and mode of delivery to terminate the pregnancy in these cases can vary much between the protocols. Therefore, this paper presents, in a didactic way, the particularities of different protocols for monitoring FGR, in order to help obstetricians to better manage the cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.