Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):217-223
To evaluate the effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on fertility in experimental retrocervical endometriosis.
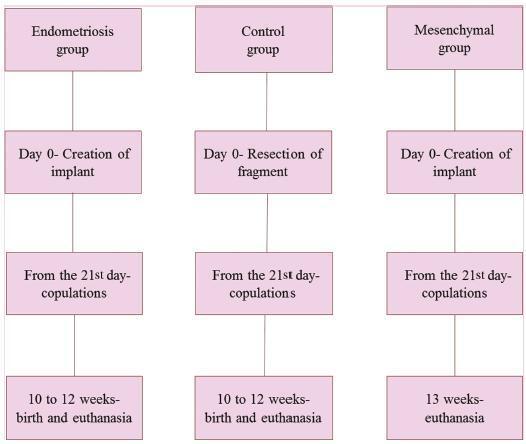
A total of 27 New Zealand rabbits were divided into three groups: endometriosis, in which endometrial implants were created; mesenchymal, in which MSCs were applied in addition to the creation of endometrial implants; and control, the group without endometriosis. Fisher’s exact test was performed to compare the dichotomous qualitative variables among the groups. The quantitative variables were compared by the nonparametric Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis tests. The MannWhitney test was used for post-hoc multiple comparison with Boniferroni correction.
Regarding the beginning of the fertile period, the three groups had medians of 14±12.7, 40±5, and 33±8.9 days respectively (p = 0.005). With regard to fertility (number of pregnancies), the endometriosis and control groups showed a rate of 77.78%, whereas the mesenchymal group showed a rate of 11.20% (p = 0.015). No differences in Keenan’s histological classification were observed among the groups (p = 0.730). With regard to the macroscopic appearance of the lesions, the mesenchymal group showed the most pelvic adhesions.
The use of MSCs in endometriosis negatively contributed to fertility, suggesting the role of these cells in the development of this disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):224-228
This study analyzed the effectiveness of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as a predictor of insulin resistance (IR) and its association with the clinical and metabolic parameters of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) without overt hypothyroidism.
A cross-sectional study was performed. Women with PCOS and without overt hypothyroidism (n = 168) were included.
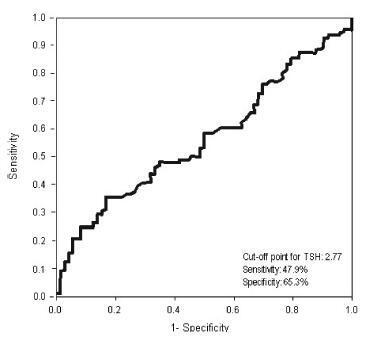
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine the cut-off point for TSH that would maximize sensitivity and specificity for a diagnosis of IR using homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)≥ 2.71. Clinical and metabolic parameters were compared as a function of the TSH cut-off limit and the presence of IR.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone ≥ 2.77 mIU/L was associated with a diagnosis of IR, with sensitivity of 47.9% and specificity of 65.3%. There were no differences in clinical, hormonal or metabolic parameters between TSH < 2.77 and TSH of 2.77 - 10 mIU/L.
In women with PCOS without overt hypothyroidism, TSH ≥2.77 mIU/L is associated with IR; however, with poor sensibility, showing TSH to be a poor predictor of IR in this population. No clinical or metabolic alterations were found that would justify a change in clinical management. Thus, the IR should be investigated in all women with PCOS irrespective of TSH level.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):229-234
Preoperatively identification of malignancy potential of a postmenopausal adnexal masses is important.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the Risk of Malignancy Index-2 in presumably benign adnexal masses in postmenopausal women.
Retrospective, observational study.
119 women with postmenopausal adnexal masses with a preliminary diagnosis of benign tumors according to the Risk of Malignancy Index-2 were included. Age, duration of menopause, ultrasonographic findings, and serum CA-125 levels were recorded preoperatively. The definitive diagnosis was based on postoperative histopathological examination.
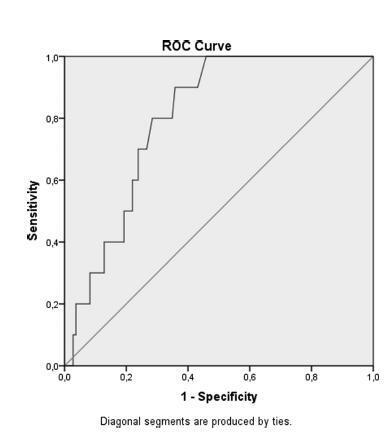
Of 119 adnexal mass, 10 were malignant and 109 were benign. There was no statistically significant difference with regard to age and tumor size between the groups. The two significant ultrasonographic parameter between groups were the presence of solid area in the mass and bilaterality. Moreover, if the cut off point for serum CA-125 was adjusted to 14.75 IU/mL according to ROC curve, a sensitivity value of 80% and a specificity value of 72% could be achieved to discriminate benign and malign cysts.
In the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant adnexal masses in postmenopausal women, the presence of a solid component, bilaterallity based on ultrasonography and high CA-125 values may be used as discriminative criteria. There is no direct relation between the size of the adnexal mass and malignancy potential. Therefore, in the malignancy indexes of postmenopausal women, we recommend lower cut-off values of CA-125 to increase the sensitivity of preoperative evaluation tests without having a great impact on negative predictive values.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):14-20
Obesity is associated with an increased risk for breast cancer. Recent studies have shown that aromatase inhibitors may be less effective in women with a high body mass index (BMI). The aim of this study was to establish the relationship between the BMI and plasma estrone and estradiol levels in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer using anastrozole.
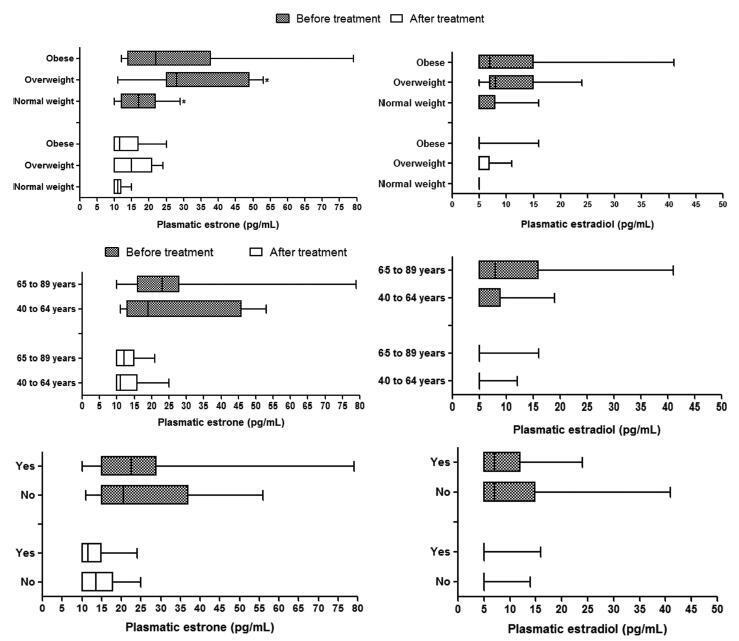
In this cohort study, the patients were divided into three groups according to BMI (normal weight, overweight and obese) to compare and correlate plasma hormone levels before starting anastrozole hormone therapy and three months after treatment. Plasma hormone levels were compared for age and use of chemotherapy.
A statistically significant reduction in estrone and estradiol levels was observed between baseline and three months after starting the anastrozole treatment (p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in plasma estrone and estradiol levels among the BMI groups (p > 0.05), but a significant reduction in plasma estrone levels was observed after three-months' treatment relative to baseline in all groups, as well as a reduction in estradiol in the obese group (p < 0.05). The use of chemotherapy and age > 65 years had no influence on plasma steroid levels.
Changes in estrone and estradiol levels in the studied groups were not associated with BMI, chemotherapy or age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):21-25
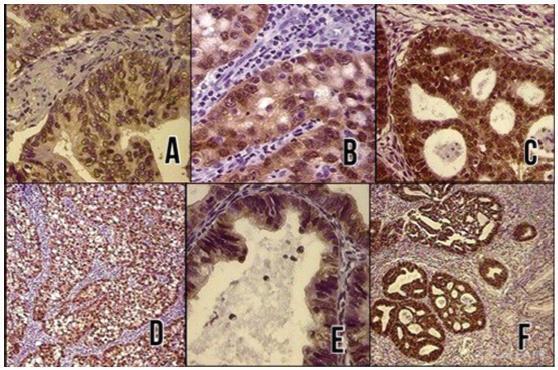
To evaluate the diagnostic utility of the p16ink4a protein expression as a marker for adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
In a cross-sectional study, p16ink4a expression was evaluated in 30 cervical biopsies from patients diagnosed with invasive adenocarcinoma from 2 reference clinics in Brazil, and compared with 18 biopsies of endocervical polyps (control cases). The performance of the tests for p16ink4a was evaluated using a conventional contingency table, and the Kappa (k) index was used to evaluate the agreement of the marker with the tissue diagnosis.
In total, 66% of the invasive adenocarcinoma cases were positive for p16ink4a. All of the adenomatous polyps cases used as negative controls were shown to be negative for p16ink4a. The marker showed a high sensitivity and a high negative predictive value. The Kappa index was good for p16ink4a (k 1/4 0.6).
Considering the strong association between the p16ink4a marker and the cervical adenocarcinoma, its use represents an important tool for reducing incorrect diagnoses of adenocarcinoma and thereby avoiding overtreatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):26-30
To evaluate the long-term effectiveness of perineal Thiele massage in the treatment of women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles.
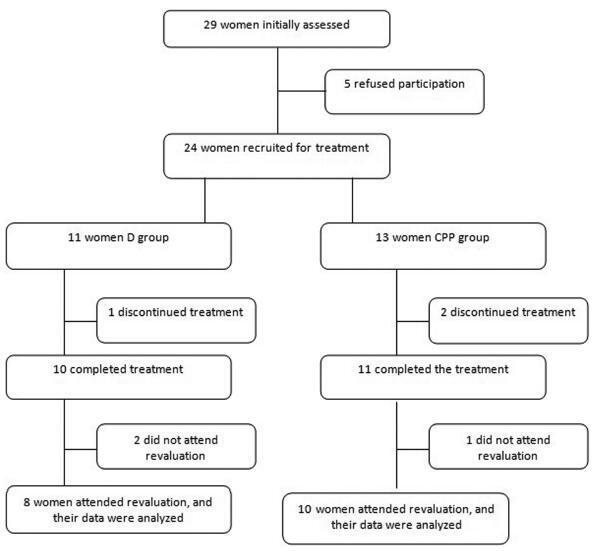
A total of 18 women with diagnoses of dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles were included in the study. The women were divided in two groups: the dyspareunia (D) group - 8 women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles; and the chronic pelvic pain group (CPP) group - 10 women with dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles associated with CPP. Each patient filled out the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), the McGill Pain Index, the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). After an evaluation, the women underwent transvaginal massage using the Thiele technique over a period of 5 minutes, once a week for 4 weeks.
All women had significant improvements in their dyspareunia according the VAS and the McGill Pain Index (p < 0,001), but the HADS scores did not show significant differences. Regarding sexual function, the D group showed improvements on all aspects of sexual function, while the CPP group showed differences only in the pain domain.
Thiele massage is effective in the treatment of dyspareunia caused by tenderness of the pelvic floor muscles with a long-term pain relief.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):4-8
This study aims to give information about the relationship between different types of factor deficiencies and maternal/obstetric outcomes.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of eight women with factor deficiency disorders. The demographic and clinical features of the patients after their last pregnancies were registered retrospectively.
There were 29 pregnancies among the 8 patients. The spontaneous abortion rate was relatively high in two patients with factor XIII deficiency (80% and 57.1%) compared with the other factor deficiency groups. There were 16 births, which included 1 set of twins, and 2 deaths (1 stillbirth and 1 postpartum exitus occurred in the same patient). Intrauterine growth restriction was noted in five cases; four of these occurred in factor X deficiency cases. The mean decrease in hemoglobin level of all patients after birth was 1.7 g/dL (range, 0.2-3.6 g/dL). Red blood cell transfusion was required only in one case of factor XIII deficiency.
There is currently no consensus on the pregnancy management of women with factor deficiencies because of the limited knowledge due to the rarity of such disorders. Labor should be managed in a dedicated unit with a team consisting of an obstetrician, a hematologist, an anesthesiologist, a midwife, and a pediatrician to minimalize the complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(1):9-13
To evaluate the prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) in fetuses of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in the beginning of the treatment.
A cross-sectional study was performed between July 1, 2013, and Decem-ber 20, 2013, in a public maternity clinic in southern Brazil. The subjects were 63 fetuses of mothers with gestational diabetes, with a single pregnancy and no other associated pathologies. We diagnosed HCM through a fetal echocardiography before treatment and evaluated the maternal and fetal characteristics.
The average age of the pregnant women was 32.32 (±6.2) years, and the average gestational age at the time of the evaluation was 30.59 (±2.27) weeks. The interventricular septum thickness showed a standard deviation of more than two in 50.8% of the fetuses (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 38.1-63.5%). The left ventricular wall thickness showed a standard deviation of more than 2 in 13 (20.6%) fetuses (95%CI: 11.1-30.2%). The HCM was confirmed in 54% of the fetuses (95%CI: 41.3-65.1%). The fetal abdominal circumference was normal in 46 (73%) fetuses, and 50% of these fetuses had HCM.
The prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in fetuses of pregnant women with GDM before treatment was of 54% (95%CI: 41.3-65.1%).