Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):79-85
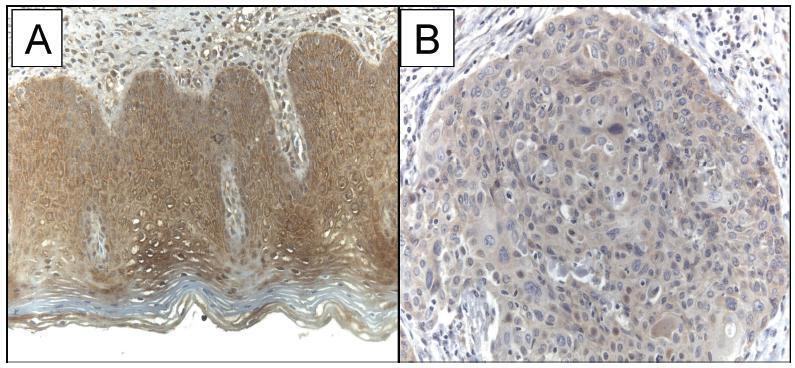
The current study evaluated the expression of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX), its association with clinicopathological features and with p53, Ki-67 (cell proliferation) and CD31 (angiogenesis) expression in patients with invasive cervical squamous cell carcinoma (ICSCC). To the best of our knowledge, no other study has evaluated this association.
Women with IB stage-ICSCC (n = 20) and women with uterine leiomyoma (n = 20) were prospectively evaluated. Patients with ICSCC were submitted to type BC1 radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. Patients in the control group underwent vaginal hysterectomy. Tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation and protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry studies.
The WWOX expression was significantly lower in the tumor compared with the expression in thebenign cervix (p = 0.019). TheWWOXexpressionwas inversely associated with the CD31 expression in the tumor samples (p = 0.018). There was no association betweentheWWOXexpression with the p53 expression (p = 0.464)or the Ki-67expression (p = 0.360) in the samples of invasive carcinoma of the cervix. There was no association between the WWOX expression and tumor size (p = 0.156), grade of differentiation (p = 0.914), presence of lymphatic vascular invasion (p = 0.155), parametrium involvement (p = 0.421) or pelvic lymph node metastasis (p = 0.310) in ICSCC tissue samples.
The results suggested that WWOX may be involved in ICSCC carcinogenesis, and this marker was associated with tumor angiogenesis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):86-91
To compare the quality of cervicovaginal samples obtained from basic health units (BHUs) of the Unified Health System (SUS) and those obtained fromprivate clinics to screen precursor lesions of cervical cancer.
It was an intervention study whose investigated variables were: adequacy of the samples; presence of epithelia in the samples, and cytopathological results. A total of 940 forms containing the analysis of the biological samples were examined: 470 forms of women attended at BHUs of the SUS and 470 forms of women examined in private clinics in January and February of 2016.
All the unsatisfactory samples were collected at BHUs and corresponded to 4% of the total in this sector (p < 0.0001). There was a higher percentage of samples containing only squamous cells in the SUS (43.9%). There was squamocolumnar junction (SJC) representativeness in 82.1% of the samples from the private clinics (p < 0.0001). Regarding negative results for intraepithelial lesions and/or malignancies, the percentages obtained were 95.9% and 99.1% (p < 0.0049) in the exams collected in the private system and SUS, respectively. Less serious lesions corresponded to 0.89% of the samples from the SUS and 2.56% of the tests from the private sector; more serious lesions were not represented in the samples obtained from BHUs, whereas the percentage was 1.49% in private institutions.
Unsatisfactory cervical samples were observed only in exams performed at the SUS. There is a need for guidance and training of professionals who perform this procedure to achieve higher reliability in the results and more safety for women who undergo this preventive test.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):04-10
External cephalic version (ECV) is a maneuver that enables the rotation of the non-cephalic fetus to a cephalic presentation. The Newman-Peacock (NP) index, which was proposed by Newman et al. in a study published in 1993, was described as a prediction tool of the success of this procedure; it was validated in a North-American population, and three prognostic groups were identified.
To evaluate the value of the NP score for the prediction of a successful ECV in a Portuguese obstetrical population, and to evaluate maternal and fetal safety.
We present an observational study conducted from 1997-2016 with pregnant women at 36-38 weeks of pregnancy who were candidates for external cephalic version in our department. Demographic and obstetrical data were collected, including the parameters included in the NP index (parity, cervical dilatation, estimated fetal weight, placental location and fetal station). The calculation of the NP score was performed, and the percentages of success were compared among the three prognostic groups and with the original study by Newman et al. The performance of the score was determined using the Student t-test, the Chi-squared test, and a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
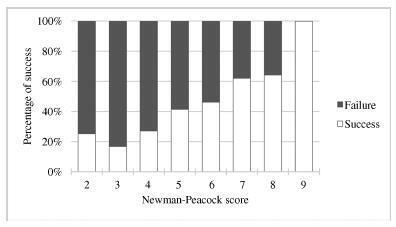
In total, 337 women were included. The overall success rate was of 43.6%. The univariate analysis revealed that multiparity, posterior placentation and a less engaged fetus were factors that favored a successful maneuver (p < 0.05). Moreover, a higher amniotic fluid index was also a relevant predictive factor (p < 0.05). The Newman-Peacock score had a poorer performance in our population compared with that of the sample of the original study, but we still found a positive relationship between higher scores and higher prediction of success (p < 0.001). No fetal or maternal morbidities were registered.
The Newman-Peacock score had a poorer performance among our population compared to its performance in the original study, but the results suggest that this score is still a useful tool to guide our clinical practice and counsel the candidate regarding ECV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):11-19
To evaluate the relation between changes the body mass index (BMI) percentile, reflected in the Atalah curve, and perinatal outcomes.
A cross-sectional study with 1,279 women was performed. Data regarding gestational weight, sociodemographic characteristics and perinatal outcomes were collected through medical charts, prenatal card and interviews in the postpartum period. Women could be classified according to the Atalah curve in the following categories: low weight, adequateweight, overweight, and obese. The BMIwas calculated at the first and at the last prenatal care visits, and these values were compared.
An increase in the BMI category according to the Atalah classification occurred in 19.9% of pregnant women, and an increase of 3.4, 5.8 and 6.4 points of BMI were found for women respectively classified in the adequate weight, overweight and obese categories at the first prenatal visit. Women with high school education presented a lower chance of increasing their BMI (odds ratio [OR] 0:47 [0.24- 0.95]). Women who evolved with an increase in the the Atalah classification were associated with cesarean section (OR 1.97-2.28), fetalmacrosomia (OR 4.13-12.54) and large for gestational age newborn (OR 2.88-9.83).
Pregnant women who gained enough weight to move up in their BMI classification according to the Atalah curve had a higher chance of cesarean section and macrosomia. Women classified as obese, according to the Atalah curve, at the first prenatal visit had a high chance of cesarean section and delivering a large for gestational age newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered "normal" (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):26-31
A vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesion is deemed to be a preceding lesion to vulvar cancer, especially in women aged under 40 years, holders of an acquired or idiopathic immunosuppression. Several treatments have been used to treat these lesions. One of the aesthetically acceptable therapeutic methods is the CO2 laser vaporization.
In a transversal study, 46 records of immunosuppressed women bearing a vulvar low grade and/or high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion were selected out of the retrospective analysis, computing age, date of record, date of vulvar lesion treatment with CO2 laser, the time elapsed between the first and the last visit (in months), the number of visits, the presence or absence of condylomatous lesions in other female lower genital tract sites and whether or not recurrences and persistence of intraepithelial lesions have been noticed during the follow-up.
Patients bearing vulvar high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion and immunosuppressed (serumpositive forhumanimmunodeficiency virus [HIV] or with solid organs transplantation) have shown a higher level of persistence of lesions and a higher chance of having other areas of the female lower genital tract involved.
While the CO2 laser vaporization is the most conservative method for the treatment of vulvar high-grade intraepithelial lesions, it is far frombeing the ideal method, dueto the intrinsic infection features considered. The possibility of persistence, recurrences and spontaneous limited regression indicates that a closer surveillance in the long-term treated cases should be considered, in special for immunosuppressed patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):202-208
To evaluate the perception of health professionals involved in the labor process and theassistanceto normal delivery, comparing two hospitals in the cityof Goiânia, Brazil, regarding the perception of theseprofessionals when they are performing the routines and practices recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).
This is an analytical comparative study with a quantitative approach, performed in two public hospitals in the city of Goiânia, in the state of Goiás, Brazil. The study included 86 professionals working in assistance to immediate labor in two hospitals. A questionnaire containing 40 questions was applied. The questionnaire related to the Program for the Humanization of Prenatal and Childbirth Care (PHPN, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Brazilian Ministry of Health, the presence of a companion, and the procedures performed. For the data analysis, we used the chisquare and Fisher’s exact tests.
Most of the professionals claimed to know about the PHPN proposed by Brazilian Ministry of Health in the two hospitals. With regard to good practices, most professionals said that they are performed in maternity ward 2, while on maternity 1, although many of them are present, there are still many unnecessary interventions.
When comparing the two maternity hospitals, maternity 2, which was created as a routine humanization model, manages to better adhere to the WHO recommendations. In maternity 1, there was a series of interventions considered by the WHO as ineffective, or used in an inappropriate manner.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):209-216
In 2013, it was estimated that 289,000 maternal deaths occurred worldwide. The maternal mortality ratio has decreased in many countries in the past decades, due to early identification and treatment of obstetric complications, despite the dissimilarities observed in diverse locations and populations. Black women, for instance, have always been more susceptible to the occurrence of maternal mortality and severe morbidity. Therefore, the objective of this study is to assess skin color as a predictive factor for maternal near miss (MNM) in a sample of Brazilian women interviewed in the Brazilian National Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) of 2006.
A secondary analysis of the DHS database, a population-based crosssectional nationally representative study was conducted. This database is of public domain. The risk of maternal complications according to ethnic group and the associated sociodemographic characteristics were evaluated. For the data analysis, the odds ratios and respective 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
In the sample interviewed, 59% of women were black or brown (mixed-race). Approximately 23% of women had some complication, and 2% of these women had at least one MNM pragmatic criterion. The MNM rate was 31 per 1,000 live births, and its occurrence was not statistically different among the ethnic groups. The only factors identified that were considered to be associated with the occurrence of MNM were maternal age above 40 and women not currently attending school, but only among white women.
The 2006 DHS results did not show a higher occurrence of maternal complications, and specifically of MNM associated with black/brown skin color.