Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):542-548
To assess the relationship involving sexual function (SF), the distress symptoms caused by pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD), and female genital self-image (GSI).
We assessed the GSI, SF and PFD distress symptoms by the Female Genital Self-Image Scale (FGSIS), the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and the Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory (PFDI-20) respectively. Data were analyzed by multiple linear regression.
Among the 216 women (age: 50.92 ± 16.31 years) who participated in the study, 114 were sexually active in the previous 4 weeks. In the total sample (p < 0.001; adjusted R2 = 0.097) and among sexually active women (p = 0.010; adjusted R2 = 0.162), the distress symptoms caused by pelvic organ prolapse (POP) were related to the GSI. Among sexually active women, sexual desire also was related to the GSI (p < 0.001; adjusted R2 = 0.126).
The findings of the present study provide additional knowledge about female GSI and suggest that SF and POP distress symptoms should be investigated together with the GSI in the clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):524-534
To assess the knowledge, attitude, and practice of Brazilian physicians about immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Cross-sectional online survey involving physicians on duty in public Brazilian hospitals. Participants answered an anonymous questionnaire with close-ended questions to assess their knowledge, attitude, and experience on the immediate postpartum and postabortion insertion of copper intrauterine devices.
One hundred twenty-seven physicians working in 23 hospitals in the 5 geographic regions of Brazil completed the questionnaire. Most were female (68.5%) and worked in teaching hospitals (95.3%). The mean (standard deviation) knowledge score (0–10 scale) was 5.3 (1.3); only 27.6% of the participants had overall scores ≥7.0. Most physicians (73.2%) would insert a postpartum intrauterine device in themselves/family members. About 42% of respondents stated that they had not received any training on postpartum or postabortion intrauterine device insertion. In the past 12 months, 19.7%, 22.8%, and 53.5% of respondents stated they had not inserted any intrauterine device during a cesarean section, immediately after a vaginal delivery, or after an abortion, respectively.
Most study participants have a positive attitude toward the insertion of intrauterine devices in the immediate postpartum period, but they have limited knowledge about the use of this contraceptive method. A large percentage of respondents did not have previous training on postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion and had not performed any such insertions in the last 12 months. Strategies are needed to improve the knowledge, training, and experience of Brazilian physicians on immediate postpartum and postabortion intrauterine device insertion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):517-523
Gestational diabetes can cause maternal and neonatal morbidity. Psychological factors, especially stress, play a meaningful role in diabetes management. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the effect of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction counseling on blood sugar and perceived stress in women with gestational diabetes.
The present quasi-experimental interventional study was performed on 78 women with gestational diabetes. In the intervention group, a Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction counseling program was conducted by the researcher in 8 sessions of 90 minutes twice a week. The Cohen stress questionnaire was filled in both groups. Also, fasting blood sugar and 2-hour blood sugar levels were measured in both groups. Statistical analysis was performed using the independent T-Test, the paired T-Test, the Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon Tests using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows version 20 version (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
The mean age of pregnant women in the intervention group was 28.84 ± 6.20 years old and 29.03 ± 5.42 years old in the control group. There was a significant mean difference between the fasting blood sugar score (p = 0.02; - 6.01; and - 11.46) and the 2-hour fasting blood sugar score (p < 0.001;12.35; and - 5.3) and the perceived stress score (p < 0.001; 35.57; and - 49.19) existed between the intervention and control groups after the intervention.
The results of the present study showed that mindfulness-based stress reduction counseling is effective in reducing blood sugar levels and reducing perceived stress in women with gestational diabetes treated with diet.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):511-516
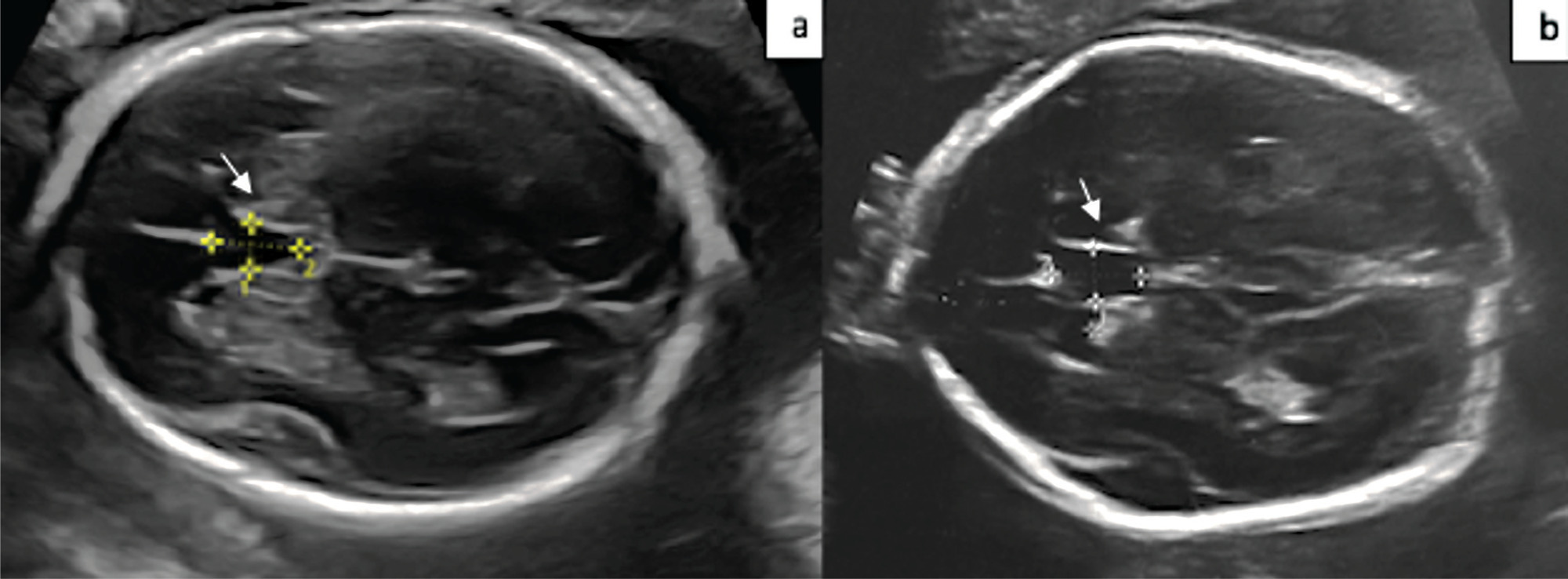
The aim of the present study is to compare the cavum septum pellucidi (CSP) z-score in euploid and aneuploid fetuses and to investigate the performance of the CSP width/length and CSP width/biparietal diameter (BPD) ratios as a diagnostic marker in aneuploidy.
A total of 54 patients, 20 aneuploid and 35 euploid fetuses, between 18 and 37 weeks of gestation, were included in this retrospective study. The CSP width z-score was compared between the two groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated for the CSP width/length and CSP width/BPD ratios to predict aneuploidy.
The median CSP width was 4.8 mm (range, 1.8 to 8.5 mm) in the euploid group, and 5.4 mm (range 3.1 to 8.4 mm) in the aneuploid group. Cavum septum pellucidi width z-score, CSP width/length ratio, and CSP width/BPD ratio were significantly higher in fetuses with aneuploidy than in fetuses with normal karyotype (p = 0.001; p = 0.013; p = 0.028). In the ROC analysis, the CSP width/length ratio had the optimal cutoff value of 0.59, with 72.0% sensitivity and 58.0% specificity, and for the CSP width/BPD ratio, the cutoff value was 0.081 with 83.0% sensitivity and 61.0% specificity for detection of aneuploidy.
CSP width z-score was found to be increased in aneuploid fetuses. The CSP width /BPD ratio can be used as a new marker for predicting aneuploidy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):503-510
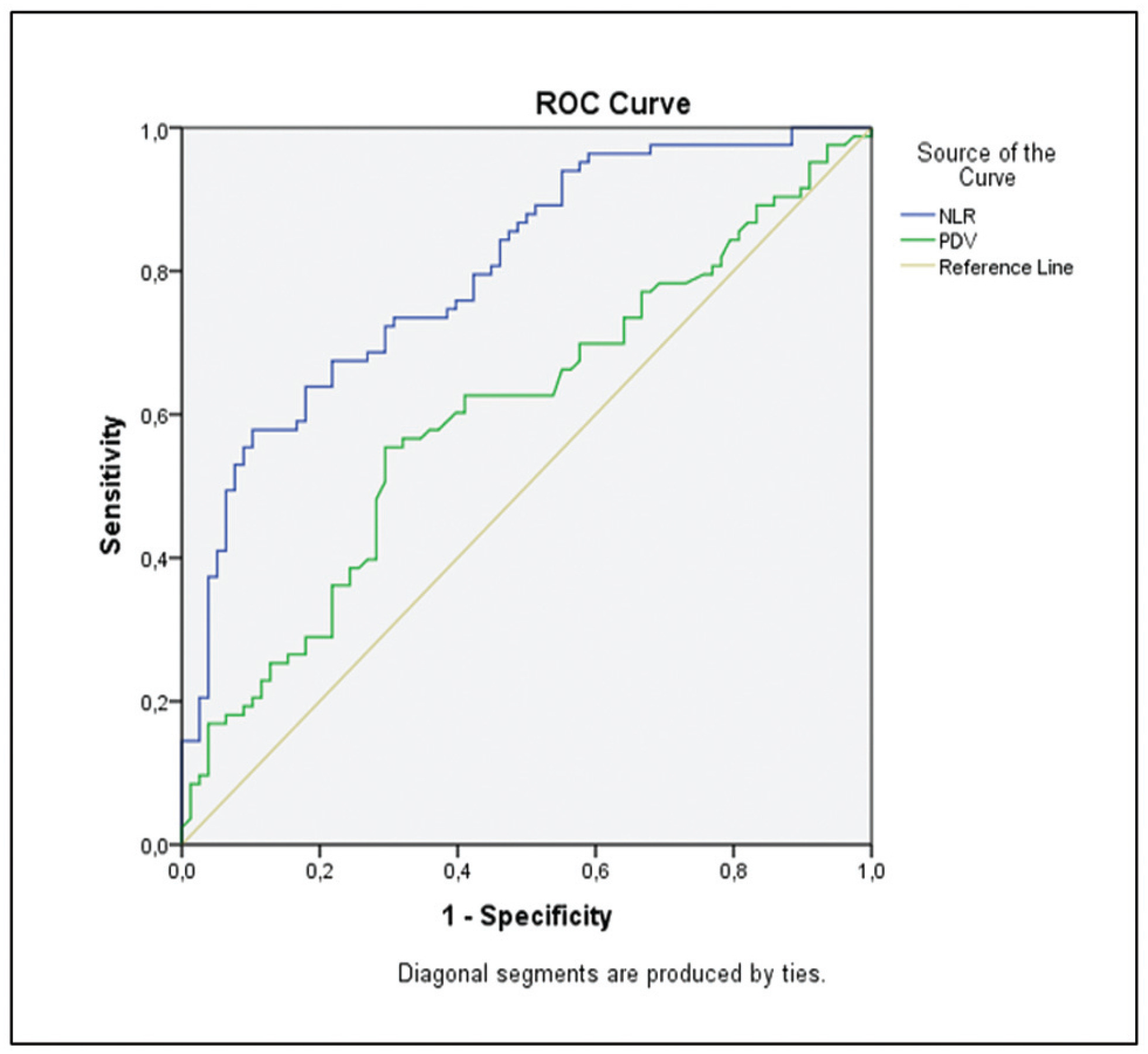
The availability of reliable and inexpensive markers that can be used to determine the risk of rupture during methotrexate (MTX) treatment in ectopic pregnancies (EPs) is considerable. The aim of the present study is to investigate the role of systemic inflammatory markers such as leukocytes (or white blood cells, WBCs), the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet distribution width (PDW), which are among the parameters of the complete blood count (CBC), in the prediction of rupture of EPs under MTX treatment.
A total of 161 patients with tubal EP who underwent a single-dose methotrexate (MTX) protocol were retrospectively analyzed, and the control group (n = 83) included patients cured by MTX, while the ruptured group (n = 78) included patients who were operated on for tubal rupture during the MTX treatment. The features of EP, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels, sonographic findings, and CBC-derived markers such as WBC, NLR, and PDW, were investigated by comparing both groups.
The NLR was found to be higher in the ruptured group, of 2.92 ± 0.86%, and significantly lower in the control group, of 2.09 ± 0.6%. Similarly, the PDW was higher (51 ± 9%) in the ruptured group, and it was significantly lower a (47 ± 13%) in the control group (p < 0.05). Other CBC parameters were similar in both groups (p > 0.05).
Systemic inflammation markers derived from CBC can be easily applied to predict the risk of tubal rupture in Eps, since the CBC is an inexpensive and easy-to-apply test, which is first requested from each patient during hospitalization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):134-141
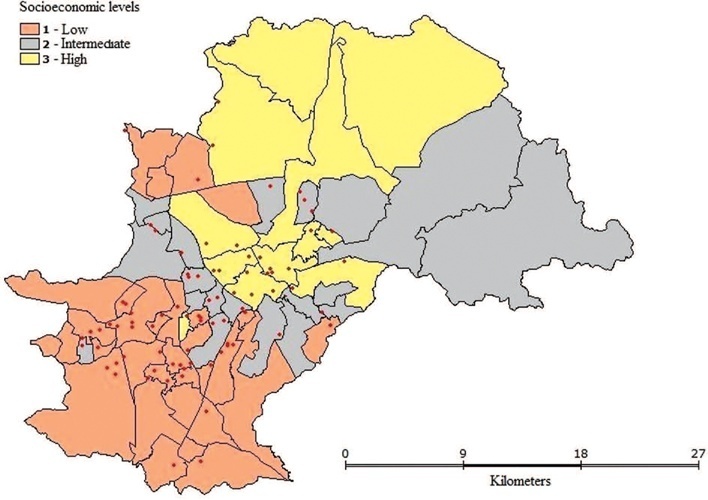
This study assessed maternal mortality (MM) and related factors in a large-sized municipality in the Southeastern region of Brazil (Campinas, São Paulo) during the period 2000-2015.
This study consisted of two phases: 1. An analytical nested case-control phase that assessed the impact of individual and contextual variables on MM; and 2. an ecological phase designed to contextualize maternal deaths by means of spatial analysis. The case group consisted of all maternal deaths (n = 87) and the control group consisted of 348 women who gave birth during the same period. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, association, and multiple logistic regression (MLR) tests at p < 0.05 as well as spatial analysis.
Maternal Mortality Ratio was 37 deaths per 100.000 live births. Deaths were dispersed throughout the urban territory and no formation of cluster was observed. MLR showed that pregnant women aged > 35 years old (OR = 2.63) or those with cesarean delivery (OR = 2.51) were more prone to maternal death.
Maternal deaths were distributed dispersedly among the different socioeconomic levels and more prone to occur among older women or those undergoing cesarean deliveries.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):121-126
To evaluate and compare peripheral, pelvic floor, respiratory muscle strength, and functionality in the immediate puerperium of normal delivery and cesarean section.
This is a cross-sectional study that verified respiratory, pelvic floor, peripheral, and functional muscle strength through manovacuometry, pelvic floor functional assessment (PFF), dynamometry, and the Time Up and Go (TUG) test, respectively. The groups were divided according to the type of delivery, into a cesarean section group and a normal parturition group.
The sample was composed of 72 postpartum puerperae, 36 of normal parturition, and 36 of cesarean section, evaluated before hospital discharge, mean age ranged from 25.56 ± 6.28 and 28.57 ± 6.47 years in puerperae of normal parturition and cesarean section respectively. Cesarean showed higher pelvic floor strength (PFF) compared to normal parturition (p < 0.002), but puerperae from normal delivery showed better functionality (p < 0.001). As for peripheral muscle strength and respiratory muscle strength, there was no significance when comparing the types of parturirion.
There is a reduction in pelvic muscle strength in puerperae of normal delivery and a decrease in functionality in puerperae of cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):113-120
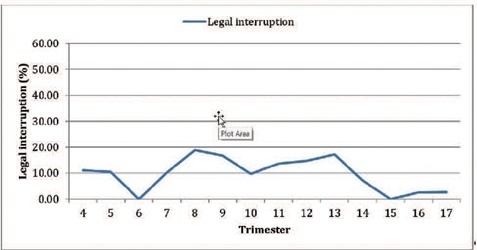
To evaluate the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the care of patients with miscarriage and legal termination of pregnancy in a university hospital in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of women admitted for abortion due to any cause at Hospital da Mulher Prof. Dr. J. A. Pinotti of Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), Brazil, between July 2017 and September 2021. Dependent variables were abortion-related complications and legal interruption of pregnancy. Independent variables were prepandemic period (until February 2020) and pandemic period (from March 2020). The Cochran-Armitage test, Chi-squared test, Mann-Whitney test, and multiple logistic regression were used for statistical analysis.
Five-hundred sixty-one women were included, 376 during the prepandemic period and 185 in the pandemic period. Most patients during pandemic were single, without comorbidities, had unplanned pregnancy, and chose to initiate contraceptive method after hospital discharge. There was no significant tendency toward changes in the number of legal interruptions or complications. Complications were associated to failure of the contraceptive method (odds ratio [OR] 2.44; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.23–4.84), gestational age (OR 1.126; 95% CI 1.039–1.219), and preparation of the uterine cervix with misoprostol (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.01–3.96).
There were no significant differences in duration of symptoms, transportation to the hospital, or tendency of reducing the number of legal abortions and increasing complications. The patients’ profile probably reflects the impact of the pandemic on family planning.