Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):390-396
To outline the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with deep intestinal endometriosis submitted to surgical treatment at a tertiary referral center with a multidisciplinary team, and correlate those characteristics with the surgical procedures performed and operative complications.
A prospective cohort from February 2012 to November 2016 of 32 women with deep intestinal endometriosis operations. The variables analyzed were: age; obesity; preoperative symptoms (dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, acyclic pain, dyschezia, infertility, urinary symptoms, constipation and intestinal bleeding); previous surgery for endometriosis; Enzian classification; size of the intestinal lesion; and surgical complications.
Themean age was 37.75 (±5.72) years. A total of 7 patients (22%) had a prior history of endometriosis. The mean of the largest diameter of the intestinal lesions identified intraoperatively was of 28.12 mm (±14.29 mm). In the Enzian classification, there was a predominance of lesions of the rectum and sigmoid, comprising 30 cases (94%). There were no statistically significant associations between the predictor variables and the outcome complications, even after the multiple logistic regression analysis. Regarding the size of the lesion, there was also no significant correlation with the outcome complications (p = 0.18; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]:0.94-1.44); however, there was a positive association between grade 3 of the Enzia classification and the more extensive surgical techniques: segmental intestinal resection and rectosigmoidectomy, with a prevalence risk of 4.4 (p < 0.001; 95%CI:1.60-12.09).
The studied sample consisted of highly symptomatic women. A high prevalence of deep infiltrative endometriosis lesions was found located in the rectum and sigmoid region, and their size correlated directly with the extent of the surgical resection performed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):384-389
The main objective of this study was to examine the diagnostic performance of the first-trimester combined test for aneuploidies in unselected pregnancies from Rio de Janeiro and compare it with the examples available in the literature.
We investigated 3,639 patients submitted to aneuploidy screening from February 2009 to September 2015. The examination is composed of the Fetal Medicine Foundation risk evaluation based on nuchal translucency evaluation, mother’s age, presence of risk factors, presence of the nasal bone and Doppler of the ductus venous in addition to biochemical analysis of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) markers. The cut-off point for high risk for aneuploidies was defined as greater than 1:100, with intermediate risk defined between 1:100 and 1:1,000, and low risk defined as less than 1:1,000. The variable aneuploidy was considered as a result not only of trisomy of chromosome 21 but also trisomy of chromosomes 13 and 18.
Excluding the losses, the results of 2,748 patients were analyzed. The firsttrimester combined test achieved 71.4% sensitivity with a 7.4% false-positive (FP) rate, specificity of 92.6%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 6.91% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 99.76%, when the cut-off point considered was greater than 1:1,000. Through a receiving operating characteristics (ROC) curve, the cut-off point that maximized the sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of aneuploidies was defined as 1:1,860. When we adjusted the false-positive (FP) rate to 5%, the detection rate for this analysis is 72.7%, with a cut-off point of 1:610.
The combined test of aneuploidy screening showed a detection rate inferior to those described in the literature for a higher FP rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):379-383
Perineal trauma is a negative outcome during labor, and until now it is unclear if the maternal position during the second stage of labormay influence the risk of acquiring severe perineal trauma. We have aimed to determine the prevalence of perineal trauma and its risk factors in a low-risk maternity with a high incidence of upright position during the second stage of labor.
A retrospective cohort study of 264 singleton pregnancies during labor was performed at a low-risk pregnancymaternity during a 6-month period. Perineal trauma was classified according to the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (RCOG), and perineal integrity was divided into three categories: no tears; first/ second-degree tears + episiotomy; and third and fourth-degree tears. A multinomial analysis was performed to search for associated factors of perineal trauma.
From a total of 264 women, there were 2 cases (0.75%) of severe perineal trauma, which occurred in nulliparous women younger than 25 years old. Approximately 46% (121) of the women had no tears, and 7.95% (21) performed mediolateral episiotomies. Perineal trauma was not associated with maternal position (p = 0.285), health professional (obstetricians or midwives; p = 0.231), newborns with 4 kilos or more (p = 0.672), and labor analgesia (p = 0.319). The multinomial analysis showed that white and nulliparous presented, respectively, 3.90 and 2.90 times more risk of presenting perineal tears.
The incidence of severe perineal trauma was low. The prevalence of upright position during the second stage of labor was 42%. White and nulliparous women were more prone to develop perineal tears.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
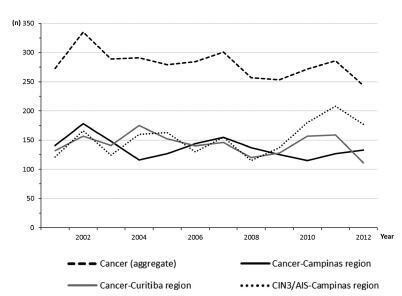
The aim of this study was to assess the time trends and pattern of cervical cancer diagnosed in the period from 2001 to 2012 by means of an opportunistic screening program from two developed regions in Brazil.
An observational study analyzing 3,364 cancer records (n = 1,646 from Campinas and n = 1,718 from Curitiba region) available in hospital-based cancer registries was done. An additional 1,836 records of CIN3/AIS from the region of Campinas was analyzed. The statistical analysis assessed the pooled data and the data by region considering the year of diagnosis, age-group, cancer stage, and histologic type. The Cochran-Armitage trend test was applied and p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
The total annual cervical cancer registered from2001 to 2012 showed a slight drop (273-244), with an age average of 49.5 y, 13 years over the average for CIN3/AIS (36.8 y). A total of 20.6% of the diagnoses (1.6% under 25 y) were done out of the official screening age-range. The biennial rate of diagnoses by age group for the region of Campinas showed an increase trend for the age groups under 25 y (p = 0.007) and 25 to 44 y (p = 0.003). Stage III was the most recorded for both regions, with an annual average of 43%, without any trend modification. There was an increasing trend for stage I diagnoses in the region of Campinas (p = 0.033). The proportion of glandular histologic types registered had an increased trend over time (p = 0.002), higher for the region of Campinas (21.1% versus 12.5% for the region of Curitiba).
The number, pattern and trends of cervical cancer cases registered had mild and slow modifications and reflect the limited effectivity of the opportunistic screening program, even in developed places.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):332-337
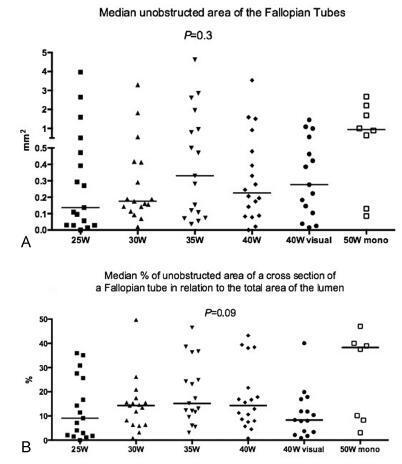
To determine which mode and potency of electrocoagulation, using a modern electrosurgical generator, yields the smallest unobstructed area of the Fallopian tubes.
In an experimental study, tubes from 48 hysterectomies or tubal ligation were evaluated. Tubes were randomly allocated to one of the following groups: group A) 25 W x 5 seconds (n = 17); group B) 30 W x 5 seconds (n = 17); group C) 35 W x 5 seconds (n = 18), group D) 40 W x 5 seconds (n = 20); group E) 40 W x 5 seconds with visual inspection (blanch, swells, collapse) (n = 16); group F) 50 W x 5 seconds (n = 8). Bipolar electrocoagulation was performed in groups A to E, and monopolar electrocoagulation was performed in group F. Coagulation mode was used in all groups. Digital photomicrography of the transversal histological sections of the isthmic segment of the Fallopian tube were taken, and themedian percentage of unobstructed luminal area (mm2) was measured with ImageJ software (ImageJ, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The Kruskal-Wallis test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for statistical analysis.
Ninety-six Fallopian tube sections were analyzed. The smallest median occluded area (%; range) of the Fallopian tube was obtained in the group with 40 W with visual inspection (8.3%; 0.9-40%), followed by the groups 25 W (9.1%; 0-35.9%), 40 W (14.2; 0.9-43.2%), 30 W (14.2; 0.9-49.7%), 35 W (15.1; 3-46.4%) and 50 W (38.2; 3.1-51%). No statistically significant difference was found among groups (p = 0.09, Kruskal-Wallis test).
The smallest unobstructed area was obtained with power setting at 40 W with visual inspection using a modern electrosurgical generator. However, no statistically significant difference in the unobstructed area was observed among the groups using these different modes and potencies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):338-346
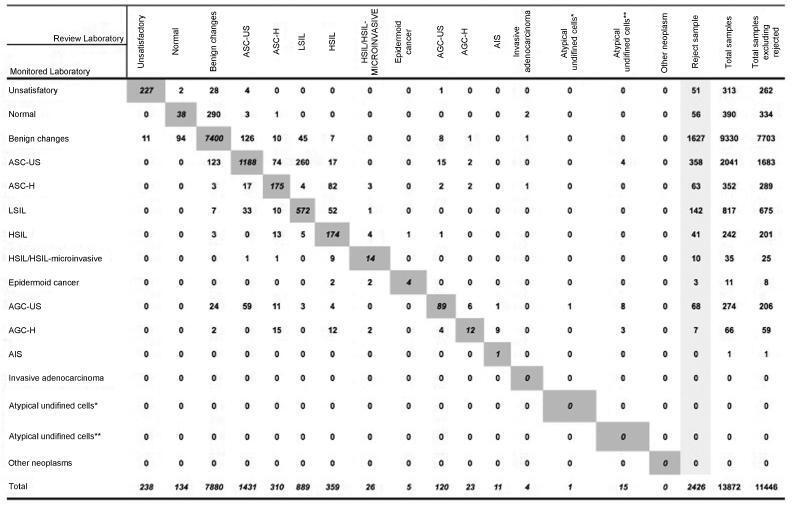
To discuss the implementation and contributions of the External Quality Monitoring in the city of Rio de Janeiro and to analyze the performance of the main providers of cervical cytopathology in this city from September 2013 to March 2017, here referred to as “Alpha laboratory” and “Beta laboratory.”
Observational, cross-sectional, retrospective study using information from the Cervical Cancer Control Information System (SISCOLO, in the Portuguese acronym), municipal coordinationmodule, External QualityMonitoring report. The proportions of false positives, false negatives, unsatisfactory samples and rejected samples were estimated. The agreement among the observers was analyzed through the Kappa index and the reduction of disagreements in the period for each laboratory studied, comparing the results of each cycle.
A total of 19,158 examinations were selected, of which 19,130 (99.85%) were monitored, 16.649 (87, 03%) were reviewed by the External Quality Monitoring Unit, 2,481 (12,97%) were rejected and 441 (2,65%) were considered unsatisfactory. The “Beta laboratory” presented excellent concordance in all cycles; the “Alpha laboratory” had good concordance in the first two cycles (K = 0.76 and 0.79), becoming excellent in the following four cycles. The average Kappa index was 0.85, with median of 0.86. The percentage of diagnostic disagreement was 6.63% of the reviewed exams, of which 5.38% required a change of conduct
External Quality Monitoring is an exercise in diagnostic improvement, and its implementation was fundamental to ensure the reliability of the cytopathological exams in the city of Rio de Janeiro.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):322-331
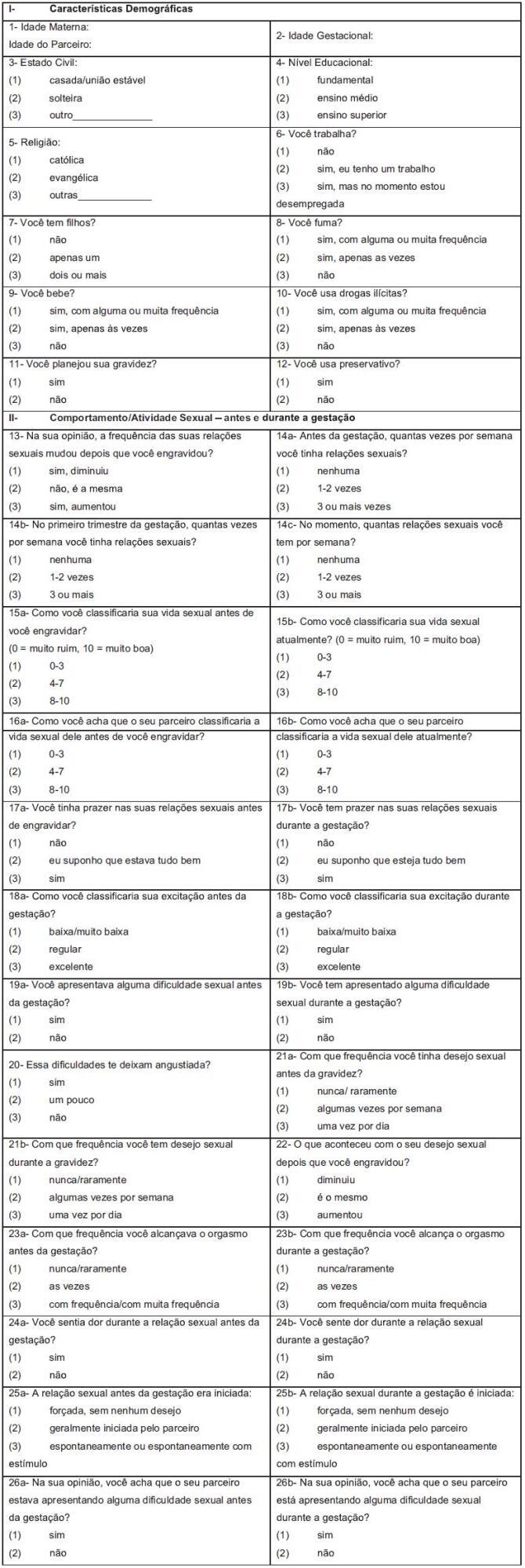
To establish the Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) scores for each domain before and during pregnancy, and to publish the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI.
Pregnant women were recruited during antenatal care; the PSRI was administered to 244 women prenatally at Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, at Universidade do Estado de São Paulo (UNESP, in the Portuguese acronym). The PSRI scores were estimated based on the Kings Health Questionnaire (KHQ) and the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form survey (SF-36). The raw scale type was used to standardize the minimal value and amplitude of each domain. For each domain, the score varied from 0 to 100, and the composite score was obtained as the domain average. The composite score before and during pregnancy was determined by the sum of the scores of all specific domains for each divided by the full domain number. The categorization of the scale into quartiles was established when all PSRI-specific and composite scores were combined.
The composite and specific scores for each domain were categorized into quartiles: 0 < 25 as “very bad;” 25 < 50 as “bad;” 50 < 75 as “good” and 75 to 100 as “excellent.” The mean scores were lower during pregnancy than before pregnancy in 8 of the 10 domains. The Brazilian Portuguese PSRI version is presented.
This study allowed the establishment of the PSRI composite and specific scores for each domain, and the categorization of scores into quartiles: very bad, bad, good and excellent. In addition, the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI is presented in full for application in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):313-321
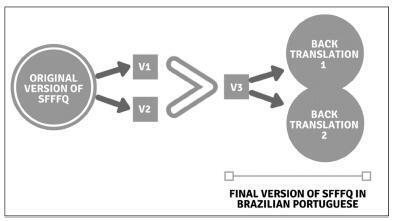
To translate and culturally adapt the short-formFood Frequency Questionnaire (SFFFQ) for pregnant women, which contains 24 questions, into Brazilian Portuguese.
Description of the process of translation and cultural adaptation of the SFFFQ into Brazilian Portuguese. The present study followed the recommendation of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research for translation and cultural adaptation with the following steps: 1) preparation; 2) first translation; 3) reconciliation; 4) back translation; 5) revision of back translation; 6) harmonization; 7) cognitive debriefing; 8) revision of debriefing results; 9) syntax and orthographic revision; and 10) final report. Five obstetricians, five dietitians and five pregnant women were interviewed to contribute with the language content of the SFFFQ.
Few changes were made to the SFFFQ compared with the original version. These changes were discussed with the research team, and differences in language were adapted to suit all regions of Brazil.
The SFFFQ translated to Brazilian Portuguese can now be validated for use in the Brazilian population.