Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):170-175
Endometriosis is a complex disease, and pain is an important component of the syndrome. One of the most used methods to assess pain is the visual analogue scale (VAS). The aim of the present research was to study the pain experienced by patients who referred to our unit for endometriosis, using the VAS to understand the variables that could influence it.
We have conducted a prospective study from February 2012 to December 2016, enrolling 388 patients who referred to a university hospital, in Florence, Italy. We have included in the present study patients during their follow-up for endometriosis; we have also included patients who underwent surgery with a histological diagnosis of endometriosis. We have collected sociodemographic and clinical information regarding age, body mass index (BMI), smoking habit, number of pregnancies, and endometriosis staging. Finally, we have administered the VAS for several symptoms.
Dysmenorrhea was the symptom associated with the highest perception of pain (mean VAS score of 5.76). The logistic regression showed that the stage of endometriosis could influence the pain associated to constipation and to dysuria. The linear regression showed that age couldinfluencethe pain associated to constipation, to dyspareunia,and to dysmenorrhea. A positive correlation was found between dysmenorrhea and chronic pelvic pain(CPP), between dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia, and between constipation and dysuria.
Using a validated method, the VAS, we have studied the pain experienced by a group of patients with a history of endometriosis and observed that smoking habit and BMI did not influence the VAS scores, and that dysmenorrhea was associated with the highest perception of pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):155-163
To evaluate the clinical epidemiological state of women with suspected post partum depression (PPD) in a public maternity hospital in Salvador, state of Bahia, Brazil.
A cross-sectional research was performed with puerperal patients attended at a public maternity hospital in Salvador, Bahia. Data collection was performed from June to September 2017. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale was used as a screening instrument, and, subsequently, women with positive scores answered a questionnaire to identify their clinical and epidemiological status.
Out of 151 postpartum women from the research, 30 (19.8%) presented suspicion of PPD. There was a prevalence of single mothers 13 (43.3%), women with complete fundamental education 15 (50.0%), women with black skin color 14 (46.7%), and those with a monthly family income of up to one minimum wage 18 (40.0%).
Although PPD is an underdiagnosed disease, a high prevalence of the condition was found in our research. It is, then, considered that these results reinforce its significance as a public health problem, requiring prevention strategies, early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):147-154
The objective of the present study was to explore obstetric management in relation to clinical, maternal and child health outcomes by using the Robson classification system.
Data was collected from obstetrics registries in tertiary care hospitals in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE).
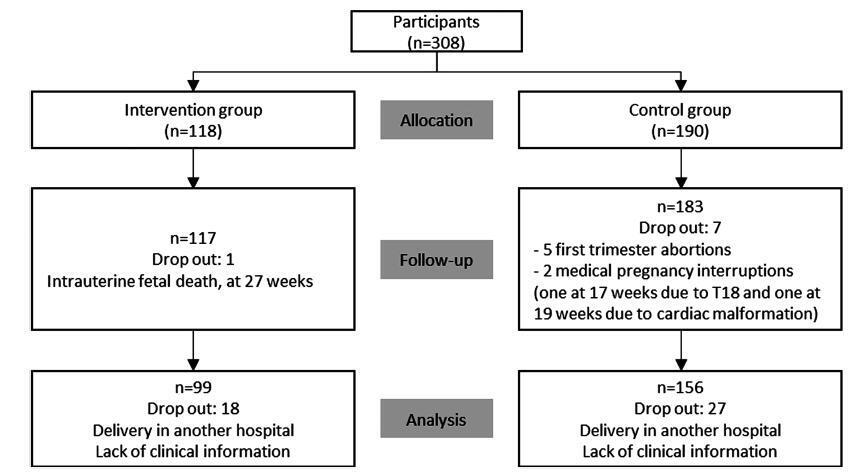
The analysis of > 5,400 deliveries (60% of all the deliveries in 2016) in major maternity hospitals in Dubai showed that groups 5, 8 and 9 of Robson’s classification were the largest contributors to the overall cesarean section (CS) rate and accounted for 30% of the total CS rate. The results indicate that labor was spontaneous in 2,221 (45%) of the women and was augmented or induced in almost 1,634 cases (33%). The birth indication rate was of 64% for normal vaginal delivery, of 24% for emergency CS, and of 9% for elective CS.The rate of vaginal birth after cesarean was 261(6%), the rate of external cephalic version was 28 (0.7%), and the rate of induction was 1,168 (21.4%). The prevalence of the overall Cesarean section was 33%; with majority (53.5%) of it being repeated Cesarean section.
The CS rate in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is higher than the global average rate and than the average rate in Asia, which highlights the need for more education of pregnant women and of their physicians in order to promote vaginal birth. A proper planning is needed to reduce the number of CSs in nulliparous women in order to prevent repeated CSs in the future. Monitoring both CS rates and outcomes is essential to ensure that policies, practices, and actions for the optimization of the utilization of CS lead to improved maternal and infant outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):97-101
To analyze the prescription of antimicrobial agents for pregnant women admitted into the obstetrics service who presented with acute pyelonephritis.
Three cross-sectional studies were performed comparing the prescription of antimicrobials for pyelonephritis in pregnant women in the time periods evaluated (2010-2011: 99 patients evaluated; 2013: 116 patients evaluated; 2015: 107 patients evaluated), at the Hospital Fêmina, Porto Alegre, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The analysis was performed before and after the promotion of an institutional protocol for the treatment of pyelonephritis during pregnancy, and on a third occasion after the introduction of a smartphone-based mobile educational tool.
The evaluation of the prescribing physicians and the adequacy of the prescriptions between the different periods studied revealed a significant increase in appropriate conduct for the choice of antimicrobial (2010: 83.8%; 2013: 95.7%; and 2015: 100%), route of administration (2010: 97%; 2013: 100%; and 2015: 100%), and interval (2010: 91.9%; 2013: 95.7%; and 2015: 100%), following the introduction of the protocol, and again after the implementation of the softwareapplicationwithorientationsontheantimicrobial treatment.
The use of specific mobile applications should be encouraged to attain a better quality and accuracy in prescriptions and to include strategies that not only reduce the risk of negative outcomes, but also improve the quality of care and treatment for maintaining the health both of the mother and of the baby.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
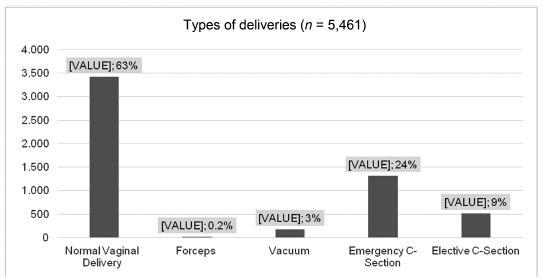
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births - this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):84-89
To compare low doses of pethidine with dipyrone in labor analgesia.
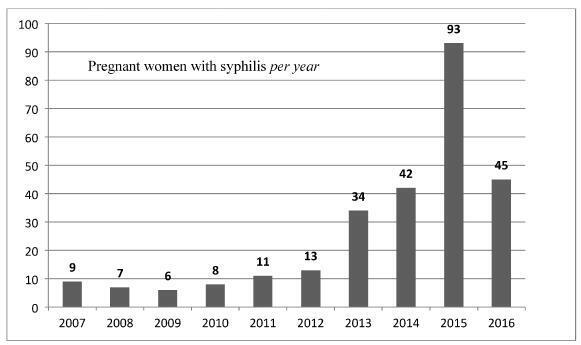
In a randomized prospective study conducted by Universidade de Fortaleza, in the state of Ceará, Brazil, between May and December 2016, 200 full-term parturients, with very painful uterine contractions and exhibiting uterine cervix dilatation ≥ 5 cm, were selected to receive a single intravenous dose of either 0.25 mg/kg of pethidine (n = 100) or of 25 mg/kg of dipyrone (n = 100). Pain was assessed using the visual analogue scale. The data were analyzed using the Student t-test, the chi-square test and the likelihood ratio.
There was a significant improvement in pain in 35% of the parturients. Both drugs presented a similar analgesic effect 1 hour after the intervention (p = 0.692). There was no analgesic effect during the evaluation of the second hour after the intervention with pethidine or dipyrone. There were no adverse effects, such as maternal drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, related to the drugs used.
Pethidine in low doses and dipyrone presented equivalent analgesia during labor. Public Registry of Clinical Trials.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):68-75
To access the benefits or harms of an exercise program, based on the current American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, on the mode of delivery, duration and onset of labor.
A study performed at the Hospital Senhora da Oliveira between October 2015 and February 2017. This was a quasi-experimental study involving 255 women divided into two groups: an intervention group engaged in a controlled and supervised exercise program during pregnancy (n = 99), and a control group that did not participate in the exercise program (n = 156). Data were collected in two stages: during the 1st trimester biochemical screening (before the beginning of the program), through a written questionnaire, and after delivery, from the medical files of the patients. The significance level in the present study was 5% (p = 0.05).
The control group had higher odds of induced labor (odds ratio [OR] 2.71; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.42-5.17; p = 0.003), when compared with women who underwent the intervention. No differences were found between the groups in instrumental vaginal deliveries, cesarean rate, time until the beginning of the active phase, duration of the active phase, and duration of the second stage of labor.
The implementation of a controlled and supervised exercise program in pregnancy was associated with significantly lower odds of induced deliveries.