Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):44-53
To validate the translation and adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese of 36 items from the World Health Organizaton Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 (WHODAS 2.0), regarding their content and structure (construct), in a female population after pregnancy.
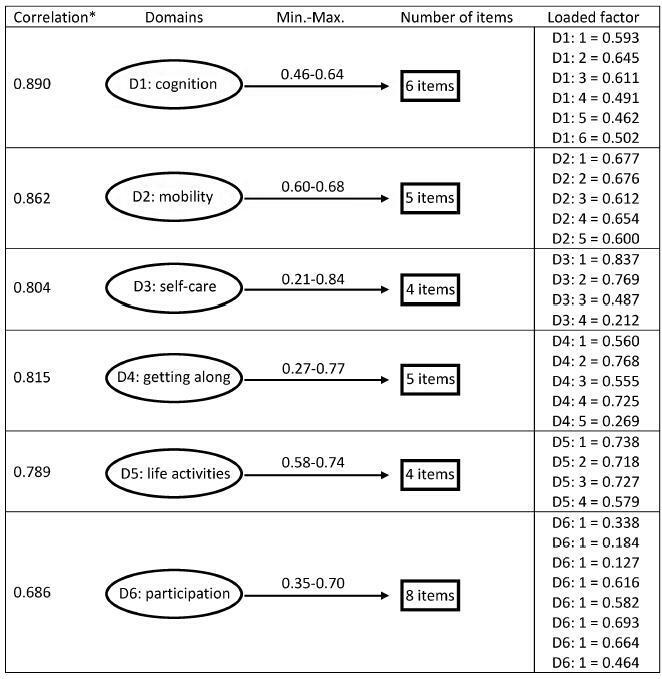
This is a validation of an instrument for the evaluation of disability and functioning and an assessment of its psychometric properties, performed in a tertiary maternity and a referral center specialized in high-risk pregnancies in Brazil. A sample of 638 women in different postpartum periods who had either a normal or a complicated pregnancy was included. The structure was evaluated by exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), while the content and relationships among the domains were assessed through Pearson's correlation coefficient. The sociodemographic characteristics were identified, and the mean scores with their standard deviations for the 36 questions of the WHODAS 2.0 were calculated. The internal consistency was evaluated byCronbach's α.
Cronbach's α was higher than 0.79 for both sets of questons of the questionnaire. The EFA and CFA for the main 32 questions exhibited a total variance of 54.7% (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin [KMO] measure of sampling adequacy = 0.934; p < 0.001) and 53.47% (KMO = 0.934; p < 0.001) respectively. There was a significant correlation among the 6 domains (r = 0.571-0.876), and a moderate correlation among all domains (r = 0.476-0.694).
The version of the WHODAS 2.0 instrument adapted to Brazilian Portuguese showed good psychometric properties in this sample, and therefore could be applied to populations of women regarding their reproductive history.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):53-59
To evaluate blood loss during misoprostol-induced vaginal births and during cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction.
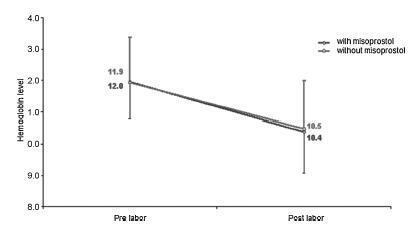
We conducted a prospective observational study in 101 pregnant women indicated for labor induction; pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were measured to estimate blood loss during delivery. Labor was induced by administering 25 μg vaginal misoprostol every 6 hours (with a maximum of 6 doses). The control group included 30 patients who spontaneously entered labor, and 30 patients who underwent elective cesarean section. Pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were evaluated using the analysis of variance for repeated measurements, showing the effects of time (pre- and postpartum) and of the group (with and withoutmisoprostol administration).
Therewere significant differences between pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels (p < 0.0001) with regard to misoprostol-induced vaginal deliveries (1.6 ± 1.4 mg/dL), non-induced vaginal deliveries (1.4 ± 1.0 mg/dL), cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction (1.5 ± 1.0 mg/dL), and elective cesarean deliveries (1.8 ± 1.1 mg/dL). However, the differences were proportional between the groups with and without misoprostol administration, for both cesarean (p = 0.6845) and vaginal deliveries (p = 0.2694).
Labor induction using misoprostol did not affect blood loss during delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
The aim of this study was to evaluate which risk factors may lead patients with gestational diabetes mellitus to cesarean delivery.
This was a retrospective, descriptive study. The subjects of the study were pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus attending a public maternity hospital in the south of Brazil. The primary outcomes assessed were based on maternal and fetal characteristics. The data were correlated using an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), calculated using multinomial logistic regression.
A total of 392 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were analyzed, and 57.4% of them had cesarean deliveries. Among the maternal characteristics, the mean age of the patients and the pregestational body mass index were greater when a cesarean delivery was performed (p = 0.029 and p < 0.01 respectively). Gestational age at birth, newborn weight, weight class according to gestational age, and Apgar score were not significant. The analysis of the OR showed that the chance of cesarean delivery was 2.25 times (95%CI = 1.49-2.39) greater if the pregnant woman was obese, 4.6 times (95%CI = 3.017-7.150) greater if she was a primigravida, and 5.2 times (95% CI = 2.702-10.003) greater if she had a previous cesarean delivery. The other parameters analyzed showed no differences.
The factors that led to an increase in the occurrence of cesarean deliveries included history of a prior cesarean section, first pregnancy, and obesity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):66-71
To investigate the association between the intensity of climacteric symptoms and sexual dysfunction in women aged 40 to 65 years.
Observational, analytic, cross-sectional study conducted with 63 women aged 40 to 65 treated at the gynecology outpatient clinic of a public hospital in northeastern Brazil. A questionnaire was used to collect identification data, clinical information, gynecological-obstetric data, lifestyle traits and information on chronic diseases. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were evaluated by means of the Blatt-Kupperman index and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) respectively. The association between the two indices was investigated using the chi-squared test; the difference in mean scores on the FSFI as a function of menopausal status was evaluated by Student's t-test. The significance level was set to p < 0.05.
The mean value of the Blatt-Kupperman index was 26.42 (standard deviation [SD]: 4.52); 36.51% of the women exhibited severe symptoms. The mean score on the FSFI was 21.84 (SD: 4.11). More than half of the analyzed women (58.73%) exhibited sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.5). Regarding the association between the Blatt- Kupperman index and the FSFI, the greater the intensity of the climacteric symptoms (Blatt-Kupperman), the higher the frequency of sexual dysfunction (FSFI). Sexual dysfunction was exhibited by 100% of the participants with severe climacteric symptoms, 70.59% of those with moderate symptoms, and only 9.09% with mild symptoms (p < 0.001).
The application of the Blatt-Kupperman index and of the FSFI allowed the detection of an association between the severity of climacteric symptoms and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):72-79
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of elastography for breast cancer identification in patients with indeterminate lesions on ultrasound.
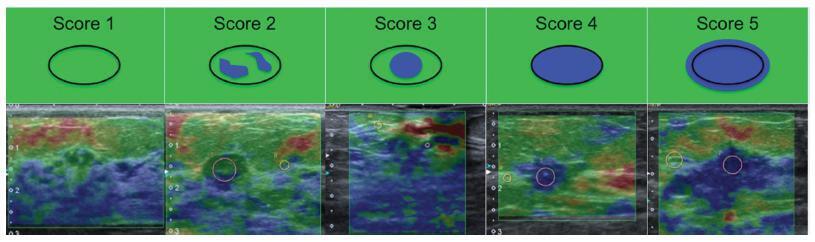
This prospective, descriptive study included patients with indeterminate breast lesions in the ultrasound and with indication for percutaneous or surgical biopsy. The elastography was evaluated by qualitative analysis and by two methods for the semi quantitative analysis.
We evaluated 125 female patients with 159 lesions, with a mean age of 47 years, and a range of 20-85 years. Ultrasound has shown to be a method with good sensitivity (98.1%), but with a lower specificity (40.6%). On the elastography qualitative analysis, the specificity and accuracy were of 80.2% and 81.8% respectively. The mean size of the lesions showed no difference in classification by elastography. For the semiquantitative elastography, the mean values of the malignant lesions were statistically higher when compared with the subcutaneous tissue or the adjacent fibroglandular tissue. The analysis of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for these two semiquantitativemethods showed that both are considered satisfactory, with an area under the curve above 0.75 and statistical significance (p < 0.0001). The best results were obtained when using the findings of combined conventional ultrasound and qualitative elastography, with 100% sensitivity and 63.2% specificity.
Elastography can be a useful complementary method, increasing the specificity and diagnostic accuracy of conventional ultrasound for the diagnosis of breast cancer in patients with indeterminate breast lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):80-85
To evaluate the association of age at first sexual intercourse with the results of the cervicovaginal cytology.
Observational analytical study about the prevalence of altered cervicovaginal cytology results in women aged between 18 and 34 years from a densely populated area in Brazil, during 10 years. The patients were stratified into 2 categories according to their age at first sexual intercourse (13-16 years and 17-24 years).
From the total of 2,505,154 exams, 898,921 tests were in accordance with the inclusion criteria. Considering women with 4 years or less from the first sexual intercourse as a reference, those with 5 to 9 years and 10 years or more showed a higher prevalence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs). Women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse (13-16 years) showed higher prevalence ratios for atypical squamous cells (ASC), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and HSIL. The prevalence ratio for HSIL adjusted by age at diagnosis and by age at first sexual intercourse was higher only for women with an earlier onset of sexual intercourse.
The age of first sexual intercourse could be a variable that might qualify the selection among young women who are really at a higher risk for HSIL.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):585-588
Analyzing if the sonographic evaluation of the cervix (cervical shortening) is a prognostic marker for vaginal delivery.
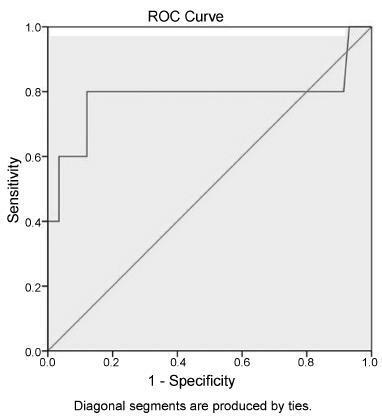
Women who underwent labor induction by using dinoprostone were enrolled. Before the induction and three hours after it, the cervical length was measured by ultrasonography to obtain the cervical shortening. The cervical shortening was introduced in logistic regression models among independent variables and for calculating receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Each centimeter in the cervical shortening increases the odds of vaginal delivery in 24.4% within 6 hours; in 16.1% within 24 hours; and in 10.5% within 48 hours. The best predictions for vaginal delivery are achieved for births within 6 and 24 hours, while the cervical shortening poorly predicts vaginal delivery within 48 hours.
The greater the cervical shortening 3 hours after labor induction, the higher the likelihood of vaginal delivery within 6, 24 and 48 hours.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):589-592
We speculate that genetic racial disparity exists in fetal life and can be detected by modern computerized cardiotocography (cCTG) .
This is a retrospective study comparing the results of the cCTG of pregnant patients at 37-42 weeks according to the parental ethnicity (black versus white). A cCTG was performed to analyze the variables of fetal heart rate (FHR). The cCTG variables analyzed were: percentage of signal loss; number of contractions; basal FHR; number of accelerations; number of decelerations; length of high variation episodes; short-term variability (STV); total trace duration time; and number of fetal active movements. Non-stress test (NST) parameters in the two groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney test for continuous data, and the Chi-square test for categorical variables.
We found a significantly lower number of active fetal movements (p 1/4 0.007) and longer periods of low variation (p 1/4 0.047) in the cCTG of black patients when compared with white patients.
In conclusion, identifying the factors responsible for the variance in the objective analysis of CTG results is important to improve the outcomes of patients. Our study lends further evidence as to the importance of ethnicity in clinical cCTG interpretation.