Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):523-528
To assess cases of labor induction with vaginal 25-μg tablets of misoprostol and maternal outcomes in a tertiary hospital in southeastern Brazil.
This was a retrospective cohort study of 412 pregnant women with indication for labor induction. Labor induction was performed with vaginal 25-μg tablets ofmisoprostol in pregnant women with Bishop scores < 6. Stepwise regression analysis was used to identify the factors present at the beginning of induction that could be used as predictors of successful labor induction.
A total of 69% of the pregnant women who underwent labor induction progressed to vaginal delivery, and 31% of the women progressed to cesarean section. One or two misoprostol tablets were used in 244 patients (59.2%). Of the 412 patients, 197 (47.8%) required oxytocin later on in the labor process, after induction with misoprostol. The stepwise regression analysis showed that only Bishop scores of 4 and 5 and previous vaginal delivery were independent factors with statistical significance in the prediction of successful vaginal labor induction (β = 0.23, p < 0.001, for a Bishop score of 4 and 5, and β = 0.22, p < 0.001, for previous vaginal delivery).
Higher Bishop scores and previous vaginal delivery were the best predictors of successful labor induction with vaginal 25-μg tablets of misoprostol.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):529-533
To evaluate the efficacy of an outpatient protocol with vaginal misoprostol to treat delayed miscarriage.
Retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data on women medically treated for missed abortion with an outpatient protocol. The inclusion criteria were: ultrasound-based diagnosis of missed abortion with less than 10 weeks; no heavy bleeding, infection, inflammatory bowel disease ormisoprostol allergy; nomore than 2 previous spontaneous abortions; the preference of the patient regarding the medical management. The protocol consisted of: 1) a single dose of 800 μg of misoprostol administered intravaginally at the emergency department, after which the patients were discharged home; 2) clinical and ultrasonographic evaluation 48 hours later - if the intrauterine gestational sac was still present, the application of 800 μg of vaginal misoprostol was repeated, and the patients were discharged home; 3) clinical and ultrasonography evaluation 7 days after the initiation of the protocol - if the intrauterine gestational sac was still present, surgical management was proposed. The protocol was introduced in January 2012. Every woman received oral analgesia and written general recommendations. We also gave them a paper form to be presented and filled out at each evaluation.
Complete miscarriage with misoprostol occurred in 340 women (90.2%). Surgery was performed in 37 (9.8%) patients, representing the global failure rate of the protocol. Miscarriage was completed after the first misoprostol administration in 208 (55.2%) women, with a success rate after the second administration of 78.1% (132/169). The average age of the women with complete resolution using misoprostol was superior to the average age of those who required surgery (33.99 years versus 31.74 years; p = 0.031). Based on the ultrasonographic findings in the first evaluation, the women diagnosed with fetal loss achieved greater success rates compared with those diagnosed with empty sac (p = 0.049).
We conclude this is an effective and safe option in the majority of delayed miscarriage cases during the first trimester, reducing surgical procedures and their consequences.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):534-540
The presence of bacteria in urine is called bacteriuria, which may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The manipulation of the urinary tract during urodynamic study (UDS), which is an invasive procedure, can result in urinary tract infection (UTI). Studies on the use of prophylactic antibiotics for UDSs are contradictory. Some investigators concluded that they were valuable and others did not. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis before UDS. This is a placebo-control randomized double-blind study.
Two-hundred and seventeen women affected by urinary incontinence were eligible for this study. All patients had presented negative urine culture previous to the UDS. They were randomized in four groups: group A received placebo, group B received 500 mg of levofloxacin, group C received 80 mg trimethoprim and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and group D received 100 mg of nitrofurantoin. A urine culture was performed 14 days after the UDS.
We observed asymptomatic bacteriuria after the UDS in five patients in group A, one in group B, one in group C and one in group D. Only one patient on group A had symptomatic bacteriuria.We didn’t observe statistical difference between the groups. When we recategorized the patients in two groups, the incidence of bacteriuria was significantly higher in the placebo group compared with the antibiotic group.
The conclusion is that antibiotic prophylaxis before the UDS did not reduce the incidence of UTI in women within the target population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):545-551
To assess the clinical characteristics of subjects with gender dysphoria (GD).
A cross-sectional study of adults with GD. Symptoms of anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Sociodemographic data, clinical data and life habits were recorded.
Total of 44 subjects participated in the study: 36 (82%) trans women and 8 (18%) trans men. Forty-three (98%) of the GD patients had anxiety (36 [100%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men), and 36 (82%) had depression (29 [80.5%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men). Suicide had been attempted by 32 (73%) subjects. The rates of depression were lower among the subjects living with partners, parents, or other people than among those living alone (p = 0.03), and it was also lower among the subjects who were married compared to those who were dating or single (p = 0.03).
Improving the relationship status may reduce the prevalence of depressive symptoms in GD patients. There was a high rate of attempted suicide in this sample.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):552-559
Resident doctors usually face the task to communicate bad news in perinatology without any formal training. The impact on parents can be disastrous. The objective of this paper is to analyze the perception of residents regarding a training program in communicating bad news in perinatology based on video reviews and setting, perception, invitation, knowledge, emotion, and summary (SPIKES) strategy.
We performed the analysis of complementary data collected from participants in a randomized controlled intervention study to evaluate the efficacy of a training program on improving residents’ skills to communicate bad news. Data were collected using a Likert scale. Through a thematic content analysis we tried to to apprehend the meanings, feelings and experiences expressed by resident doctors in their comments as a response to an open-ended question. Half of the group received training, consisting of discussions of video reviews of participants’ simulated encounters communicating a perinatal loss to a “mother” based on the SPIKES strategy. We also offered training sessions to the control group after they completed participation. Twenty-eight residents who were randomized to intervention and 16 from the control group received training. Twenty written comments were analyzed.
The majority of the residents evaluated training highly as an education activity to help increase knowledge, ability and understanding about breaking bad news in perinatology. Three big categories emerged fromresidents’ comments: SPIKES training effects; bad news communication in medical training; and doctors’ feelings and relationship with patients.
Residents took SPIKES training as a guide to systematize the communication of bad news and to amplify perceptions of the emotional needs of the patients. They suggested the insertion of a similar training in their residency programs curricula.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):443-452
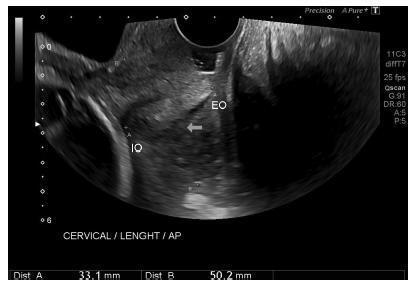
To define transvaginal ultrasound reference ranges for uterine cervix measurements according to gestational age (GA) in low-risk pregnancies.
Cohort of low-risk pregnantwomen undergoing transvaginal ultrasound exams every 4 weeks, comprisingmeasurements of the cervical length and volume, the transverse and anteroposterior diameters of the cervix, and distance fromthe entrance of the uterine artery into the cervix until the internal os. The inter- and intraobserver variabilities were assessed with the linear correlation coefficient and the Student t-test. Within each period of GA, 2.5, 10, 50, 90 and 97.5 percentiles were estimated, and the variation by GA was assessed with analysis of variance for dependent samples. Mean values and Student t-test were used to compare the values stratified by control variables.
After confirming the high reproducibility of the method, 172 women followed in this cohort presented a reduction in cervical length, with an increase in volume and in the anteroposterior and transverse diameters during pregnancy. Smaller cervical lengths were associated with younger age, lower parity, and absence of previous cesarean section (C-section).
In the studied population, we observed cervical length shortening throughout pregnancy, suggesting a physiological reduction mainly in the vaginal portion of the cervix. In order to better predict pretermbirth, cervical insufficiency and premature rupture of membranes, reference curves and specific cut-off values need to be validated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):453-463
To assess the knowledge and compliance of health professionals regarding the diagnostic and treatment practices for syphilis in patients admitted for childbirth in public maternity hospitals in the city of Teresina, in the state of Piauí, Northeastern Brazil.
A cross-sectional study was performed in 2015 with obstetricians and nurses working in the public maternity hospitals in Teresina (n = 159) using a selfadministered questionnaire, with 5% of losses and 10% of refusals. The study used 21 evaluation criteria: 13 of them were related to knowledge (5 on serological tests and 8 on treatment adequacy); 8 were related to practices (3 on diagnosis, 4 on treatment, and 1 on post-test counseling). The knowledge of and compliance to the practices was estimated as the proportion of health professionals’ answers that were in agreement with Brazilian Ministry of Health protocols.
The obstetricians were in agreement with twocriteria concerning the knowledge of serological tests, one for diagnostic practices, and one for treatment practice. Among nurses, no single match between actual procedures and guidelines was observed.
Low compliance with the protocols results in missed opportunities for the diagnosis and treatment of pregnant and postpartum women and their partners. Strategies for training and integrating the various professional groups, improved data recording on prenatal cards, and greater accountability of the hospital team in managing the women’s partners are needed to overcome the barriers identified in the study and to interrupt the syphilis transmission chain.