-
Original Article
Betatrophin Levels were Increased in Pregnant Women with or without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Associated with Beta Cell Function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):287-292
06-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleBetatrophin Levels were Increased in Pregnant Women with or without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Associated with Beta Cell Function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):287-292
06-01-2016Views94See moreAbstract
Purpose
betatrophin has been reported to boost β cell expansion in insulin resistant states. Pregnancy is a well-recognized physiological state of insulin resistance. Betatrophin levels in pregnant women and their relationships with metabolic variables remain to be elucidated.
Methods
A total of 49 pregnant women and 31 age-matched unpregnant women with normal glucose regulation (UP-NGR) were included. Among these subjects, according to results from 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), 22 women were diagnosed as having gestational diabetes mellitus ( GDM ).
Results
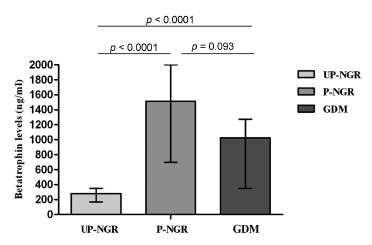
Our study found that pregnant women, regardless of their glucose regulation status, had remarkably higher triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β). However, GDM patients had much lower HOMA-β compared with those of pregnant women with normal glucose regulation (P-NGR). Participants of the P-NGR group had almost 4 times higher levels of betatrophin than those of the UP-NGR group. Although betatrophin levels were lower in the GDM group than those of the P-NGR group, the difference did not reach statistical significance. Spearman correlation analysis showed that betatrophin levels were positively and significantly associated with total cholesterol, triglycerides, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), FINS and HOMA-β. However, adjustments of TC, TG and HDL-c eliminated the association between HOMA-β and betatrophin.
Conclusions
Pregnant women have significantly higher betatrophin levels in comparison to unpregnant women. Betatrophin levels are positively and significantly associated with β cell function and lipid levels. Furthermore, lipids may contribute to
-
Original Article
Depressive Symptoms in Pregnancy: The Influence of Social, Psychological and Obstetric Aspects
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):293-300
06-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleDepressive Symptoms in Pregnancy: The Influence of Social, Psychological and Obstetric Aspects
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):293-300
06-01-2016Views118See moreAbstract
Purpose
To assess the prevalence of depressive symptoms and their association with social, psychological, behavioral and obstetric characteristics in pregnant women.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study. The sample consisted of 375 pregnant women who attended prenatal clinics in two public maternity hospitals located in the city of Goiania, Brazil. To testify the depressive symptoms, we used the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). A descriptive statistical analysis was performed using programs such as CDC EPI-INFO(tm), version 7.1.5, and Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS), version 21.0.
Results
the patients had probable depressive symptoms (15.47%) and possible depressive symptoms (25.33%). The bivariate analysis showed a significant association among "depressive symptoms" and the following variables: "single or divorced" (prevalence ratio, PR = 2.08; 95% confidence interval, CI = 1.26 to 3.44); "physical activity during pregnancy" (PR = 3.96; 95%CI = 1.28 to 12.31); exposure to "psychological/emotional" violence (PR = 4.74; 95%CI = 2.94 to 7.64); "prior mental problem" (PR = 2.66; 95%CI =1.49 to 4.73) and "obstetric complications during pregnancy" (PR = 2.53; 95%CI = 1.55 to 4.13). The multivariate analysis confirmed the association of these depressive symptoms with the variables "suffered psychological/emotional violence" (odds ratio, OR = 5.821; 95%CI = 2.939 to 11.528); "physical activity during pregnancy" (OR = 3.885; 95%CI = 1.060 to 14.231); "obstetric complications during pregnancy" (OR = 2.442; 95%CI = 1.233 to 4.834) and "single or divorced" (OR = 2.943; 95%CI = 1.326 to 6.533).
Conclusions
the prevalence of depressive symptoms among pregnant women is of 15.47%, and emotional violence is the main factor associated with gestational depression.
-
Original Article
Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Are Not Associated with the Clinical Under- or Overstaging of Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleMolecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Are Not Associated with the Clinical Under- or Overstaging of Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):239-245
05-01-2016Views143See moreAbstract
Purpose
to evaluate the agreement between the clinical and pathological stagings of breast cancer based on clinical and molecular features.
Methods
this was a cross-sectional study, in which clinical, epidemiological and pathological data were collected from 226 patients who underwent surgery at the Prof. Dr. José Aristodemo Pinotti Women's Hospital (CAISM/Unicamp) from January 2008 to September 2010. Patients were staged clinically and pathologically, and were classified as: understaged, when the clinical staging was lower than the pathological staging; correctly staged, when the clinical staging was the same as the pathological one; and overstaged, when the clinical staging was greater than the pathological staging.
Results
understaged patients were younger (52.2 years; p < 0.01) and more symptomatic at diagnosis (p = 0.04) when compared with correctly or overstaged patients. Clinicopathological surrogate subtype, menopausal status, parity, hormone replace therapy and histology were not associated with differences in staging. Women under 57 years of age were clinically understaged mainly due to underestimation of T ( tumor staging) (p < 0.001), as were the premenopausal women (p < 0.01). Patients whose diagnosis was made due to clinical complaints, and not by screening, were clinically understaged due to underestimation of N (lymph nodes staging) (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
the study shows that the clinicopathological surrogate subtype is not associated with differences in staging, while younger women diagnosed because of clinical complaints tend to have their breast tumors understaged during clinical evaluation.
-
Original Article
Quality of Life of Pregnant Women Living with HIV/AIDS
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):246-252
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleQuality of Life of Pregnant Women Living with HIV/AIDS
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):246-252
05-01-2016Views135See moreAbstract
Objective
to evaluate the quality of life of HIV positive (HIVþ) pregnant women using the HIV/AIDS Target Quality of Life (HAT-QoL) instrument.
Methods
cross-sectional study, conducted between May 2014 and November 2015 , with HIVþ pregnant women selected by convenience sampling. Sociodemographic and behavioral data were collected through interviews, and the HAT-QoL questionnaire was applied. Clinical and laboratorial data were collected from medical records.
Results
twenty-seven pregnant women participated in the study. Their mean age was 27 years (standard deviation - SD: 7.3). The majority (59%) had up to 8 years of education, 52% identified themselves as white, 56% were unemployed, and 59% had a household income higher than the minimum wage. The mean infection time by the virus was 68.4 months (5.7 years). The majority (74%) were contaminated with HIV through sexual intercourse, and 67% declared not having a HIVþrelative. Regarding the use of condoms, 41% reported using them sporadically, and the same number did not have proper knowledge about them. Only 23 patients (85%) reported having been prescribed antiretrovirals. Fourteen (64%) had a CD4 count higher than 500 cells/mm3, and 13 pregnant women (59%) had an undetectable viral load. The scores from the quality of life questionnaire dimensions that were more affected are: infection "disclosure concerns" (mean: 39.8; SD: 27.1), followed by "financial concerns" (mean: 49.1; SD: 36), and "HIV acceptance" (mean: 49.1; SD: 35.8). The dimension with the best score was "medication concerns" (mean: 80.8; SD: 26.5).
Conclusion
quality of life has been increasingly used as a clinical outcome evaluation parameter. The results of this study contribute to the establishment of interventions based on the needs of HIVþ pregnant women.
-
Original Article
The Use of Long Acting Reversible Contraceptives and the Relationship between Discontinuation Rates due to Menopause and to Female and Male Sterilizations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):210-217
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleThe Use of Long Acting Reversible Contraceptives and the Relationship between Discontinuation Rates due to Menopause and to Female and Male Sterilizations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):210-217
05-01-2016Views148See moreAbstract
Introduction
Women require effective contraception until they reach menopause. The long acting reversible contraceptives (LARC) and the depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA, Depo-Provera(r), Pfizer, Puurs, Belgium) are great options and can replace possible sterilizations.
Purpose
To assess the relationship between the use of LARCs and DMPA and terminations ascribed to menopause and sterilizations in a Brazilian clinic.
Methods
We reviewed the records of women between 12 and 50 years of age attending the clinic that chose to use a LARC method or DMPA. Cumulative termination rates due to sterilization or because the woman had reached menopause were computed using single decrement life-table analysis over 32 years. We also examined all records of surgical sterilization at our hospital between the years 1980-2012.
Results
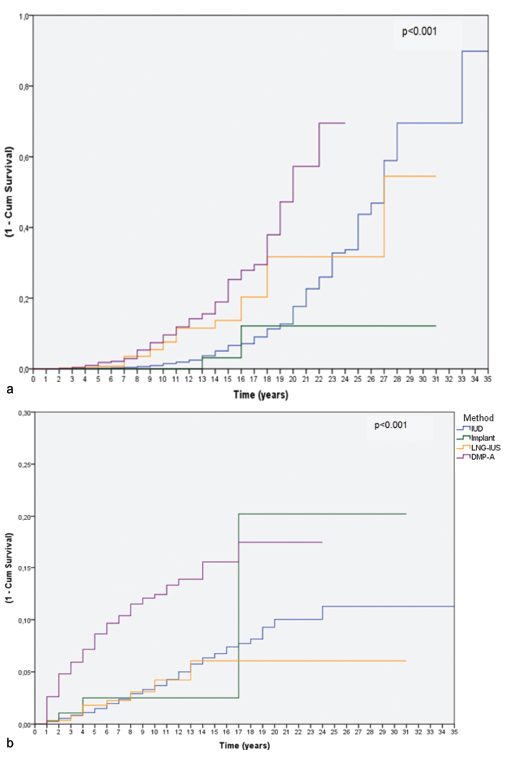
Three hundred thirty-two women had continuously used the same contraceptive until menopause, and 555 women had discontinued the method because they or their partners underwent sterilization. From year 20 to year 30 of use, levonorgestrel intrauterine-releasing system (LNG-IUS - Mirena(r), Bayer Oy, Turku, Finland; available since 1980), copper intrauterine device (IUD - available since 1980) and DMPA users showed a trend of cumulative higher discontinuation rates due to menopause when compared with the discontinuation rates due to sterilization. Over the study period, a steep decline in the use of sterilization occurred.
Conclusion
Over the past 15 years of research we have observed a trend: women usually preferred to continue using LARC methods or DMPA until menopause rather than decide for sterilization, be it their own, or their partners'. The annual number of sterilizations dropped in the same period. The use of LARC methods and DMPA until menopause is an important option to avoid sterilization, which requires a surgical procedure with potential complications.
-
Original Article
Endometriosis, Ovarian Reserve and Live Birth Rate Following In Vitro Fertilization/Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):218-224
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleEndometriosis, Ovarian Reserve and Live Birth Rate Following In Vitro Fertilization/Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):218-224
05-01-2016Views101See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate whether women with endometriosis have different ovarian reserves and reproductive outcomes when compared with women without this diagnosis undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection ( IVF/ ICSI), and to compare the reproductive outcomes between women with and without the diagnosis considering the ovarian reserve assessed by antral follicle count ( AFC ).
Methods
This retrospective cohort study evaluated all women who underwent IVF/ ICSI in a university hospital in Brazil between January 2011 and December 2012. All patients were followed up until a negative pregnancy test or until the end of the pregnancy. The primary outcomes assessed were number of retrieved oocytes and live birth. Women were divided into two groups according to the diagnosis of endometriosis, and each group was divided again into a group that had AFC 6 (poor ovarian reserve) and another that had AFC 7 (normal ovarian reserve). Continuous variables with normal distribution were compared using unpaired t-test, and those without normal distribution, using Mann-Whitney test. Binary data were compared using either Fisher's exact test or Chi-square (2) test. The significance level was set as p < 0.05.
Results
787 women underwent IVF/ICSI (241 of which had endometriosis). Although the mean age has been similar between women with and without the diagnosis of endometriosis (33.8 4 versus 33.7 4.4 years, respectively), poor ovarian reserves were much more common in women with endometriosis (39.8 versus 22.7%). The chance of achieving live birth was similar between women with the diagnosis of endometriosis and those without it (19.1 versus 22.5%), and also when considering only women with a poor ovarian reserve (9.4 versus 8.9%) and only those with a normal ovarian reserve (25.5 versus 26.5%).
Conclusions
Women diagnosed with endometriosis are more likely to have a poor ovarian reserve; however, their chance of conceiving by IVF/ICSI is similar to the one observed in patients without endometriosis and with a comparable ovarian reserve.
-
Original Article
Incidence of Cervical Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Women with Positive and Negative HIV Status
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):231-238
05-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleIncidence of Cervical Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Women with Positive and Negative HIV Status
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):231-238
05-01-2016Views182Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the incidence and factors associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical infection by human papillomavirus (HPV) among HIV-positive and HIV-negative women.
Methods
A cohort of 103 HIV positive and 113 HIV negative women were monitored between October 2008 and February 2012, for at least one year. Procedures included cervical cytology, DNA/HPV detection by polymerase chain reaction, colposcopy with biopsy if necessary, followed by an interview for exposure characteristics data. CIN was based on the histopathological results.
Results
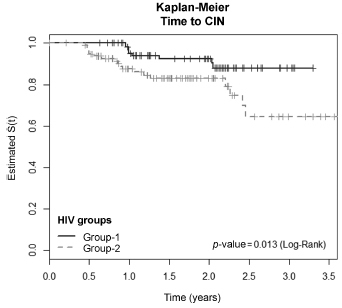
The incidence of CIN was of 8.8 and 4.6 cases/100 women-years in HIVpositive and HIV-negative women, respectively. HIV-positive women presented a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.8 for CIN and developed lesions earlier (0.86 year) than HIVnegative women (2 years) (p = 0.01). The risk of developing CIN decreased with age (HR = 0.9) and marital status (HR = 0.4). HPV patients presented a higher incidence of CIN when compared HIV-positive and HIV-negative women (p = 0.01). The incidence of HPV cervical infection was 18.1 and 11.4 cases/100 women-years in HIV-positive and HIV-negative women, respectively. Those HIV-positive presented earlier HPV infection (p = 0.002). The risk of developing HPV infection decreased with age and was higher among HIV-positive women. HPV 16 was the most common type in HIV-positive women, and also the type most closely associated with CIN in HIV-negative women.
Conclusions
HIV-positive women had a greater incidence of HPV and CIN, and in a shorter time interval. More rigorous and timely clinical control is required for this group.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaHIV infectionsHPV DNA probesPapillomavirus infectionsPolymerase chain reactionSee more