-
Original Article04-09-2024
Screening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo32
Abstract
Original ArticleScreening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo32
Views522Abstract
Objective:
To ascertain how screening for preterm birth is performed among obstetricians working in public and private practice in a middle-income country.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of 265 obstetrician-gynecologists employed at public and private facilities. An online questionnaire was administered, with items designed to collect data on prematurity screening and prevention practices.
Results:
The mean age of respondents was 44.5 years; 78.5% were female, and 97.7% had completed a medical residency program. Universal screening (i.e., by ultrasound measurement of cervical length) was carried out by only 11.3% of respondents in public practice; 43% request transvaginal ultrasound if the manual exam is abnormal, and 74.6% request it in pregnant women with risk factors for preterm birth. Conversely, 60.7% of respondents in private practice performed universal screening. This difference in screening practices between public and private practice was highly significant (p < 0.001). Nearly all respondents (90.6%) reported prescribing vaginal progesterone for short cervix.
Conclusion:
In the setting of this study, universal ultrasound screening to prevent preterm birth was used by just over half of doctors in private practice. In public facilities, screening was even less common. Use of vaginal progesterone in cervical shortening was highly prevalent. There is an unmet need for formal protocols for screening and prevention of preterm birth in middle-income settings.
Key-words attitudes, practiceCervical length measurementgynecologistshealth knowledgeInfant, prematureobstetriciansPreterm birthPreventionScreeningsurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article04-09-2024
Gender affirming hormone therapy and transgender women fertility: Histologic predictors of germ cell presence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo33
Abstract
Original ArticleGender affirming hormone therapy and transgender women fertility: Histologic predictors of germ cell presence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo33
Views491Abstract
Objective:
Evaluate histological changes in testicular parameters after hormone treatment in transgender women.
Methods:
Cross-section study with patients who underwent gonadectomy at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre from 2011 to 2019. Hormone treatment type, route of administration, age at initiation and duration were recorded. Atrophy parameters were observed: testicular volume, tubular diameter, basal membrane length, presence of spermatogonia and spermatids (diploid and haploid spermatozoid precursors).
Results:
Eighty-six patients were included. Duration of hormone treatment is associated with testicular atrophy and spermatogenesis arrest. Other characteristics of hormone treatment such as age of initiation, route of administration and type of treatment were not associated with testicular histological changes. Testicular volume may predict spermatogenesis arrest. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio is an interesting predictor of germ cell presence.
Conclusion:
Cross-sex hormone treatment affects testicular germ cell presence. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio reduces inter variability of measurements and better exemplify how atrophic seminiferous tubules are. Fertility preservation should be addressed by healthcare providers in order to recognize gender affirming treatment impact on transgender health.
Key-words FertilityFertility preservationGonadal steroid hormonesHormone treatmentSpermatogenesisTransgender personsTransgender womenSee more -
Original Article04-09-2024
Bacteriological characteristics of primary breast abscesses in patients from the community in the era of microbial resistance
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo34
Abstract
Original ArticleBacteriological characteristics of primary breast abscesses in patients from the community in the era of microbial resistance
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo34
Views381See moreAbstract
Objective:
The aim of this study is to evaluate the etiological profile and antimicrobial resistance in breast abscess cultures from patients from the community, treated at a public hospital located in Porto Alegre, Brazil.
Methods:
This is an retrospective cross-sectional study that evaluated the medical records of patients with bacterial isolates in breast abscess secretion cultures and their antibiograms, from January 2010 to August 2022.
Results:
Based on 129 positive cultures from women from the community diagnosed with breast abscesses and treated at Fêmina Hospital, 99 (76.7%) of the patients had positive cultures for Staphylococcus sp, 91 (92%) of which were cases of Staphylococcus aureus. Regarding the resistance profile of S. aureus, 32% of the strains were resistant to clindamycin, 26% to oxacillin and 5% to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The antimicrobials vancomycin, linezolid and tigecycline did not show resistance for S. aureus.
Conclusion:
Staphylococcus aureus was the most common pathogen found in the breast abscess isolates during the study period. Oxacillin remains a good option for hospitalized patients. The use of sulfamethoxazole plus trimethoprim should be considered as a good option for use at home, due to its low bacterial resistance, effectiveness and low cost.
-
Original Article04-09-2024
Assessment of sexual and body esteem in postpartum women with or without perineal laceration: a cross-sectional study with cultural translation and validation of the Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo35
Abstract
Original ArticleAssessment of sexual and body esteem in postpartum women with or without perineal laceration: a cross-sectional study with cultural translation and validation of the Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo35
Views579See moreObjective:
We aimed to translate and determine cultural validity of the Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale (VSBE) for Brazilian Portuguese language in postpartum women who underwent vaginal delivery with or without perineal laceration and cesarean section.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study conducted virtually, with online data collection through a survey with 234 postpartum women of 975 that were invited. Clinical, sociodemographic, and psychometric variables from the VSBE questionnaire were analyzed (content validity index, internal consistency, test-retest reliability, construct/structural and discriminant validity). Multivariate analysis was performed to explore associated factors with the presence of perineal laceration.
Results:
One-hundred fifty-eight women experienced vaginal delivery, of which 24.79% had an intact perineum, 33.33% had perineal laceration, and 9.4% underwent episiotomy; and 76 participants had cesarean sections. Women with perineal laceration were older, presented dyspareunia and previous surgeries than women without perineal laceration (p<0.05). For VSBE, a high internal consistency (Cronbach's α > 0.7) was observed, but it did not correlate with Body Attractiveness Questionnaire and Female Sexual Function Index; however, it correlated with the presence of women sutured for perineal laceration. Moreover, VSBE presented good structural validity with two loading factors after exploratory factor analysis. VSBE also demonstrated discriminant validity between the presence or absence of perineal laceration. The presence of urinary incontinence (UI) (OR=2.716[1.015-4.667];p=0.046) and a higher VSBE total score (OR=1.056[1.037-1.075];p<0.001) were the only factors associated with perineal laceration.
Conclusion:
Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale demonstrated appropriate translation and good internal consistency, discriminant/construct validity and reliability. Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale total score and presence of UI were associated with women that underwent perineal laceration.
-
Original Article03-15-2024
Outcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo20
Abstract
Original ArticleOutcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo20
Views376Abstract
Objective:
To present a series of cases with our initial experience and short-term outcomes of a modified vaginal mucosal flap urethroplasty.
Methods:
Patients diagnosed with urethral stricture and operated by the same operative technique between January 2012 and January 2018 were followed for at least 6 months. Uroflowmetry and clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Results:
Nineteen patients were included with an average age of 56.4 years, mean preoperative Qmax of 5.3 ml/s, and PVR of 101.4 mL. After 6 months of the procedure, the mean Qmax improved to 14.7 mL/s (p<0.05), PVR decreased to 47.3 mL (p<0.05), and 84.2% of all patients reported improvement in clinical self-reported symptoms. There was an improvement in symptoms such as voiding effort in 84.2% of patients, weak stream (89.5%), and recurrent urinary tract infection (85.7%). The success rate (absence of symptoms and normal Qmax with no significant PVR) of the procedure was 84.2%.
Conclusion:
The described technique was considered effective for the treatment of female urethra stricture, with a high clinical success rate and an objective improvement of Qmax and decrease in PVR after 6 months of the procedure.
Key-words Urethral strictureUrethroplastyUrinary bladder neck obstructionUrological surgical proceduresSee more -
Original Article03-14-2024
Nodular image in the appendix observed on ultrasound: endometriosis or neuroendocrine neoplasia?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo1
Abstract
Original ArticleNodular image in the appendix observed on ultrasound: endometriosis or neuroendocrine neoplasia?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo1
Views353See moreAbstract
Objective:
To evaluate the association between clinical and imaging with surgical and pathological findings in patients with suspected neuroendocrine tumor of appendix and/or appendix endometriosis.
Methods:
Retrospective descriptive study conducted at the Teaching and Research Institute of Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, in which medical records and databases of patients with suspected neuroendocrine tumor of appendix and/or endometriosis of appendix were analyzed by imaging.
Results:
Twenty-eight patients were included, all of which had some type of appendix alteration on the ultrasound examination. The pathological outcome of the appendix found 25 (89.3%) lesions compatible with endometriosis and three (10.7%) neuroendocrine tumors. The clinical findings of imaging and surgery were compared with the result of pathological anatomy by means of relative frequency.
Conclusion:
It was possible to observe a higher prevalence of appendix endometriosis when the patient presented more intense pain symptoms. The image observed on ultrasound obtained a high positive predictive value for appendicular endometriosis.
-
Original Article00-00-2024
Prevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
Views389See moreAbstract
Objective:
To analyze data of patients with symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse evaluated with PFDI20 and its subscales to report the prevalence of lower gastrointestinal symptoms and anal incontinence in the population of a public hospital and analyze its impact on quality of life.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of patients with symptomatic POP. Patients were evaluated with demographic data, POP-Q, pelvic floor ultrasonography, urological parameters, and pelvic floor symptoms (PFDI-20), and quality of life (P-QoL) surveys. Patients were classified as CRADI-8 "positive" for colorectal symptoms, with responses "moderate" in at least 3 and/or "severe" in at least 2 of the items in the CRADI-8 questionnaires.
Results:
One hundred thirteen patients were included. 42.5% (48) were considered positive for colorectal symptoms on CRADI-8. 53.4% presented anal incontinence. No significant differences were found in sociodemographic variables, POP-Q stage, ultrasound parameters, or urological parameters. Positive patients had a significantly worse result in PFDI-20, POPDI (48 vs 28; p<0.001), UDI6 (51 vs 24; p<0.001), and in the areas of social limitation (44.4 vs 22.2; p = 0.045), sleep- energy (61.5 vs 44.4; p = 0.08), and severity (56.8 vs 43.7, p=0.015) according to P-QoL.
Conclusion:
Moderate or severe colorectal symptoms are seen in 40% of patients with symptomatic POP in our unit. Full evaluation of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms should be performed routinely in urogynecology units.
-
Original Article00-00-2024
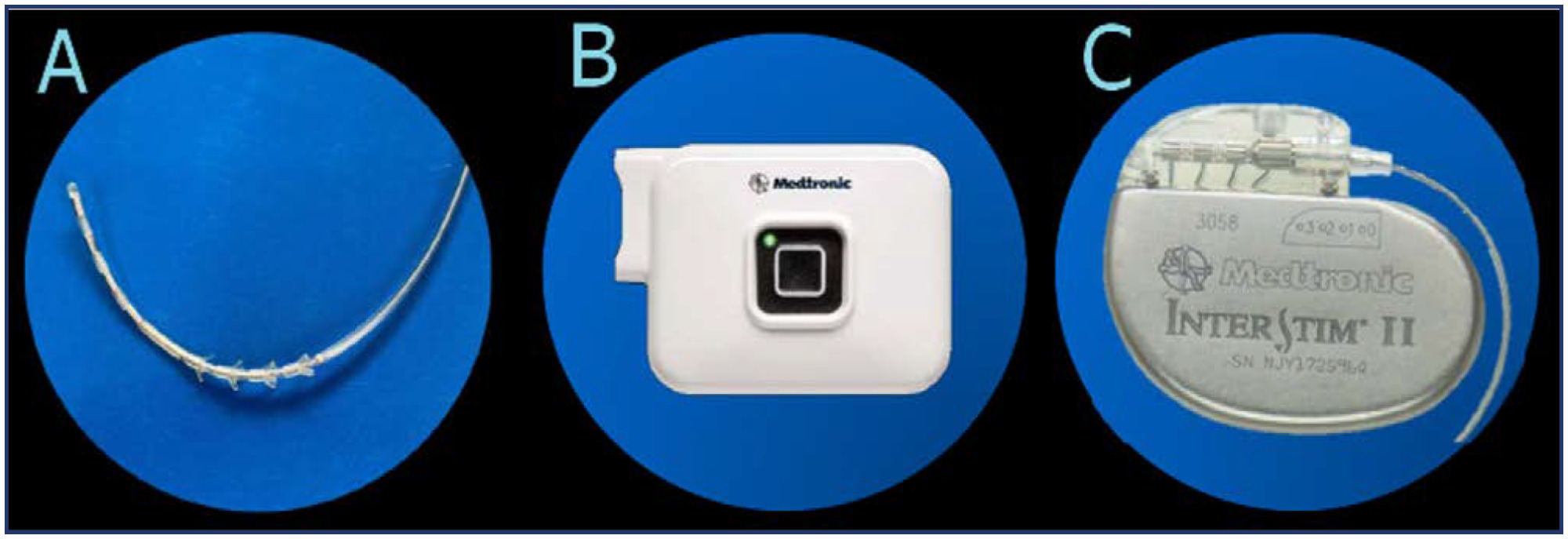
Sacral neuromodulation therapy for urinary and defecatory disorders: experience in a Latin American public hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo11
Abstract
Original ArticleSacral neuromodulation therapy for urinary and defecatory disorders: experience in a Latin American public hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo11
Views601Abstract
Objective:
To show the experience of a Latin American public hospital, with SNM in the management of either OAB, NOUR or FI, reporting feasibility, short to medium-term success rates, and complications.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort was conducted using data collected prospectively from patients with urogynecological conditions and referred from colorectal surgery and urology services between 2015 and 2022.
Results:
Advanced or basic trial phases were performed on 35 patients, 33 (94%) of which were successful and opted to move on Implantable Pulse Generator (GG) implantation. The average follow-up time after definitive implantation was 82 months (SD 59). Of the 33 patients undergoing, 27 (81%)reported an improvement of 50% or more in their symptoms at last follow-up. Moreover, 30 patients (90%) with a definitive implant reported subjective improvement, with an average PGI-I "much better" and 9 of them reporting to be "excellent" on PGI-I.
Conclusion:
SNM is a feasible and effective treatment for pelvic floor dysfunction. Its implementation requires highly trained groups and innovative leadership. At a nation-wide level, greater diffusion of this therapy among professionals is needed to achieve timely referral of patients who require it.
Key-words Electric stimulation therapyfecal incontinenceIncontinenceNon-obstructive urinary retentionoveractiveSacral neuromodulationUrinary bladderSee more