-
Original Article09-30-2019
Follow-up of Toxoplasmosis during Pregnancy: Ten-Year Experience in a University Hospital in Southern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):539-547
Abstract
Original ArticleFollow-up of Toxoplasmosis during Pregnancy: Ten-Year Experience in a University Hospital in Southern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):539-547
Views235See moreAbstract
Objective
To describe a population of pregnant women diagnosed with toxoplasmosis and their respective newborns, describing the hospital protocol for treatment and follow-up.
Methods
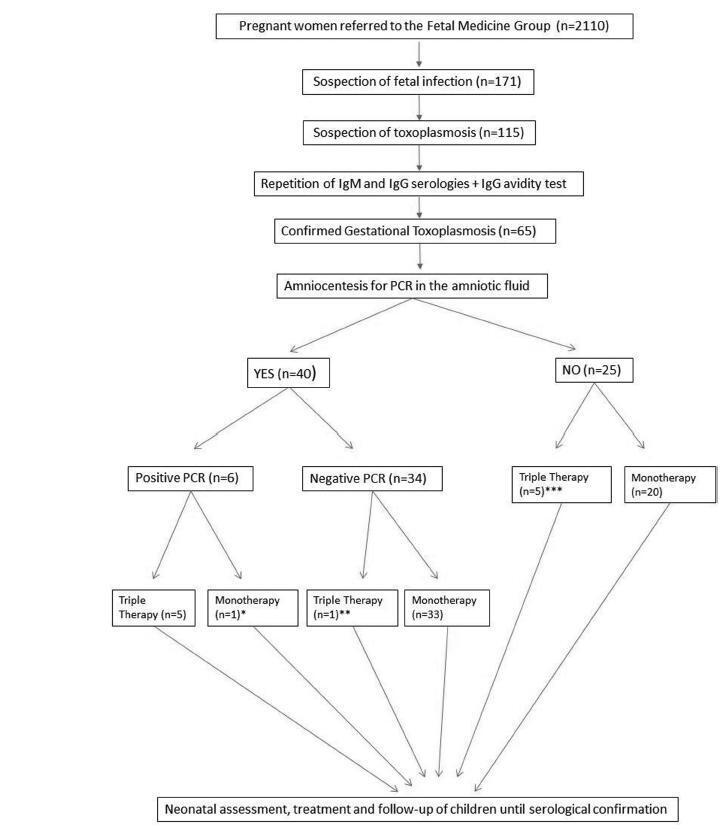
Retrospective cohort of pregnant women with acute toxoplasmosis infection and risk of transplacental transmission who were sent to the Fetal Medicine Group of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA) between - January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2016. All patients with confirmed disease were included. The diagnostic protocol and treatment were applied; a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of the amniotic fluid was used to diagnose toxoplasmosis and determine the treatment. The newborns were followed up at the pediatric outpatient clinic specializing in congenital infection. The patients who were not followed up or were not born in the HCPA were excluded.
Results
A total of 65 patients were confirmed to have gestational toxoplasmosis; 40 performed amniocentesis, and 6 (15%) were identified as having positive PCR in the amniotic fluid. In five of those cases, this result associated with the gestational age defined the triple therapy during pregnancy, and in one case, it defined the monotherapy (advanced gestational age). A total of 4 of these newborns were treated from birth with triple therapy for 10months, 1 was not treated (due to maternal refusal), and 1 progressed to death within the first 54 hours of life due to complications of congenital toxoplasmosis. Of the 34 remaining cases with a negative PCR, 33 were treated with monotherapy and 1 was treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings); of these children, 9 (26.5%) presented negative immunoglobulin G (IgG), 24 (70.6%) presented positive IgG (but none presented positive immunoglobulin M [IgM]), and 1 (2,9%) presented alterations compatible with congenital disease and started treatment with the triple therapy soon after birth. Out of the total sample of 60 patients, among the 25 who did not perform amniotic fluid PCR, 5 were treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings/prior treatment) and 20 patients were submitted to monotherapy; only two newborns underwent treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis. Among the 65 cases of gestational toxoplasmosis, 6 (9,2%) children had a diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis, and 2 patients with triple therapy felt severe adverse effects of the medications.
Conclusions
The present study suggests that research on PCR screening of the amniotic fluid may be useful to identify patients with a higher potential for fetal complications, who may benefit from the poly-antimicrobial treatment. Patients with negative PCR results must continue to prevent fetal infection with monotherapy, without risk of fetal or maternal impairment.
-
Original Article09-30-2019
Quality of Life Assessment by the Endometriosis Health Profile (EHP-30) Questionnaire Prior to Treatment for Ovarian Endometriosis in Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):548-554
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life Assessment by the Endometriosis Health Profile (EHP-30) Questionnaire Prior to Treatment for Ovarian Endometriosis in Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):548-554
Views241See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the existence of an association between ultrasound findings and epidemiological and clinical factors using results obtained from the EHP-30 questionnaire in women with ovarian endometriosis.
Methods
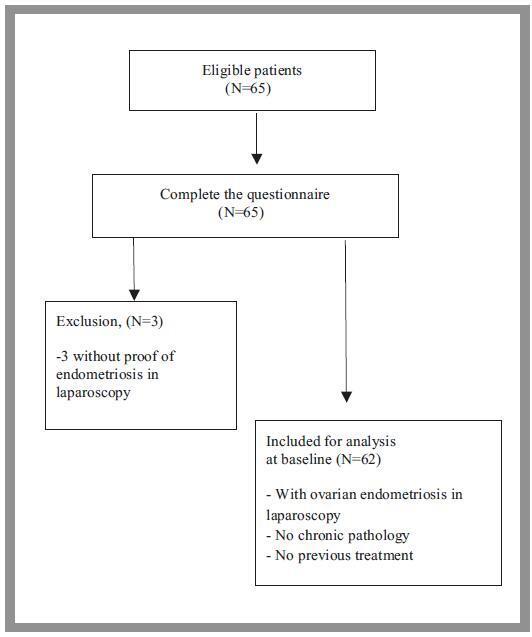
A cross-sectional observational study was performed between July 2012 and May 2015, in which patients with chronic pelvic pain suggestive of endometrioma, as indicated by the results from a transvaginal pelvic ultrasonography, completed the standardized Endometriosis Health Profile - 30 (EHP-30) questionnaire to access quality-of-life scores before beginning treatment for endometriosis. A total of 65 patients were included. The data was analyzed in the statistical program IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) for the comparison of data through linear multiple regression.
Results
The suitability of the linear regression model was confirmed by the histogram of the dependent variable and the residue distribution plot, confirming the trend of linearity as well as the homogeneous dispersion of the residues. The mean age of the patients was 39.7 ± 7.1 years old. Themajority was Caucasian (64.5%), had completed higher education (56.5%) and was nulligravida (40.3%). Infertility was present in 48.4% of the patients studied. Out of the total sample, 80.6% of the cases were symptomatic and complained mainly of acyclic pain, 79% of dysmenorrhea, and 61.3% of dyspareunia. This reflects the negative influence of endometriosis on the quality of life of patients with this disease.
Conclusion
Dyspareunia and acyclic pain were independent factors of correlation with high scores in the EHP-30 questionnaire, reflecting a worse quality of life.
-
Original Article09-30-2019
Prevalence of Sexual Dysfunctions and their Associated Factors in Pregnant Women in an Outpatient Prenatal Care Clinic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):555-563
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Sexual Dysfunctions and their Associated Factors in Pregnant Women in an Outpatient Prenatal Care Clinic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):555-563
Views243See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the prevalence of sexual dysfunction and its associated factors in pregnant women.
Methods
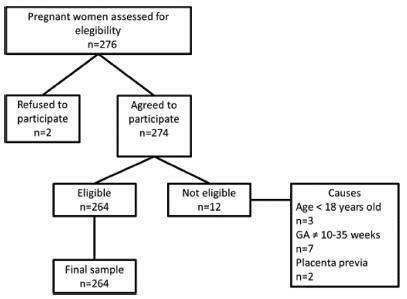
A descriptive, cross-sectional study including 262 pregnant women aged 18 years or older with gestational age between 10 and 35 weeks. Women with urinary tract infections and conditions of gestational risk were excluded. The Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) questionnaire was used. We performed a univariate descriptive analysis, and comparisons between the mean values of the sexual function domains were made using the Student t-test. The chi-squared test was used to determine the association between the independent and dependent variables. The prevalence ratios, with their respective 95% confidence intervals, were also estimated, and a multivariate analysis was performed.
Results
A total of 64.9% of women reported a decrease in the frequency of sexual activity during pregnancy. Slightly more than half of the women (50.8%) were satisfied, and arousal was reported as excellent/good by 30.5% of them. The frequency of sexual difficulties/dysfunctions increased with pregnancy, rising from 5.7% to 58.8%, and pain during sexual intercourse was reported by 45.8% of them. Having higher education degree decreased the chance of being sexually dissatisfied by 50%. The total PSRI score showed a significant decrease from the prepregnancy period (mean score = 89.8, “excellent”) to the pregnancy period (mean score = 59.2, “good”).
Conclusion
The mean sexual function score during pregnancy was classified as good, although most pregnant women reported at least one type of alteration in the sexual function domains, and the report of dissatisfaction was more frequent in women with lower schooling.
-
Original Article09-16-2019
Putting Knowledge into Practice-The Challenge of Acquiring Healthy Habits during Pregnancy Colocando conhecimento em prática – O desafio de adquirir hábitos saudáveis durante a gravidez
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):469-475
Abstract
Original ArticlePutting Knowledge into Practice-The Challenge of Acquiring Healthy Habits during Pregnancy Colocando conhecimento em prática – O desafio de adquirir hábitos saudáveis durante a gravidez
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):469-475
Views181See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the knowledge concerning gestational weight gain (GWG), nutrition, and physical exercise (PE) in pregnant women, and how to put them into practice.
Methods
A cross-sectional study with 61 pregnant women above 26 weeks of gestation, at the Woman’s Hospital, CAISM, University of Campinas. Questionnaires regarding the knowledge of healthy habits (HH) during pregnancy, sociodemographic data, and previous obstetric outcomes were applied. An educational guide with advice on HH during pregnancy and in the postpartum period was offered.
Results
The average age of women was 28.7 ± 6.23 years, with 85% of them being married; 32% nulliparous; the average body mass index (BMI) before pregnancy was 25.4 ± 9.8 kg/m2, and themean number of years of schoolingwas 11.2 ± 3.8. Only 61%of the subjects had received any previous information about GWG during their antenatal care and were aware as to howmany pounds they should gain during pregnancy. Among the 61 women, 85% understood that they did not need to “eat for 2” and 99% knew that PE had benefits for their body and was safe for their baby. Half of the women practiced PE prior to pregnancy; however, only 31% continued the practice of PE during the pregnancy.
Conclusion
Despite understanding the need for HH during pregnancy, women still need encouragement to practice PE during pregnancy, as well as more information about GWG.
-
Original Article09-16-2019
Ultrasound Evaluation of the Cervix to Predict Failed Labor Induction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):476-484
Abstract
Original ArticleUltrasound Evaluation of the Cervix to Predict Failed Labor Induction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):476-484
Views222See moreAbstract
Objective
Labor induction does not always result in vaginal delivery, and can expose both the mother and the fetus to the risks inherent to the induction procedure or a possible cesarean section. Transvaginal sonography (TVS) of the cervix is a useful tool to predict prematurity; in the present study, this tool was used to evaluate postterm induction.
Methods
We evaluated the ultrasound characteristics of the cervix (cervical length, cervical funneling, internal os dilation, the presence or absence of the cervical gland area [CGA], and the morphological changes of the cervix as a result of applying fundal pressure) before the onset of labor induction among women with postterm pregnancy to identify the possible predictors of failed labor induction. The Bishop score (BS) was used for comparison purposes. Three groups were evaluated: successful versus unsuccessful induction; vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (excluding cases of acute fetal distress [AFD]); and vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (including cases of AFD). A fourth group including only the primiparous women from the three previous groups was also evaluated.
Results
Based on the studied characteristics and combinations of variables, a cervical length ≥ 3.0 cm and a BS ≤ 2 were the best predictors of induction failure.
Conclusion
Although TVS is useful for screening for induction failure, this tool should not be used as an indication for cesarean section.
-
Original Article09-16-2019
Intrauterine Device Insertion during Cesarean Section in Women without Prenatal Contraception Counseling: Lessons from a Country with High Cesarean Rates
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):485-492
Abstract
Original ArticleIntrauterine Device Insertion during Cesarean Section in Women without Prenatal Contraception Counseling: Lessons from a Country with High Cesarean Rates
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):485-492
Views136Abstract
Objective
Themoment of admission for deliverymay be inappropriate for offering an intrauterine device (IUD) to women without prenatal contraception counseling. However, in countries with high cesarean rates and deficient prenatal contraception counseling, this strategy may reduce unexpected pregnancies and repeated cesarean sections.
Methods
This was a prospective cohort study involving 100 women without prenatal contraception counseling. Postplacental IUD was offered after admission for delivery and placed during cesarean. The rates of IUD continuation, uterine perforation, and endometritis were assessed at 6 weeks and 6 months, and the proportion of women continuing with IUD at 6 months was assessed with respect to the number of previous cesareans.
Results
Ninety-seven women completed the follow-up. The rate of IUD continuation was 91% at 6 weeks and 83.5% at 6 months. The expulsion/removal rate in the first 6 weeks was not different from that between 6 weeks and 6 months (9 vs 9.1%, respectively). There were 2 cases of endometritis (2.1%), and no case of uterine perforation. Among 81 women continuing with intrauterine device after 6-months, 31% had undergone only the cesarean section in which the IUD was inserted, 44% had undergone 2 and 25% had undergone 3 or more cesarean sections.
Conclusion
Two thirds of the women who continued with IUD at 6 months had undergone 2 ormore cesarean sections. Since offering trial of labor is unusual after 2 or more previous cesareans, we believe that offering IUD after admission for delivery may reduce the risk of repeated cesarean sections and its inherent risks.
Key-words Cesarean sectionIntrauterine deviceintrauterine device continuationpostplacental intrauterine device insertionprenatal contraception counselingSee more -
Original Article09-16-2019
Assisted Reproductive Technologies in Latin America and Europe: a Comparative Analysis of Reported Databases for 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):493-499
Abstract
Original ArticleAssisted Reproductive Technologies in Latin America and Europe: a Comparative Analysis of Reported Databases for 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):493-499
Views181Abstract
Objective
To compare the Latin American and European assisted reproductive technology (ART) registries regarding data accessibility and quality, treatment utilization, effectiveness, safety, and quality of services.
Methods
We performed an ecological study using data from scientific publications of Latin American and European registries that report cycles initiated during 2013 (the most recent registries available until December of 2017). The summarized data are presented as frequencies, percentages, minimum-maximum values, and absolute numbers.
Results
Reporting clinics and cycle treatments were unevenly distributed between the participating countries for both registries, although access to ART is 15 times greater in Europe. In Latin America, individual services participate voluntarily reporting started cycles until cancellation, birth or miscarriage, while in Europe it varied among countries. It makes the data available from Latin America more uniform, although lesser representative when compared with European ones, given that reporting is compulsory formost countries. The cumulative live birth rate was better in Latin America. Female age, use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cycles with transfer of ≥ 3 embryos, as well as multiple pregnancy rates were greater in the Latin American Register of Assisted Reproduction (RLA, in the Portuguese acronym). Assisted reproductive technology complications, such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, hemorrhage, and infections were also higher in LatinAmerica, although they are extremely uncommon in both regions.
Conclusion
Both regions have points to improve in the quality of their reports. Latin America has produced a more uniform reporting, their clinical results are generally
Key-words Artificial inseminationassisted reproductive techniqueIn vitro fertilizationintracytoplasmic sperm injectionregistriesSee more -
Original Article09-16-2019
Effectiveness of Solution-Focused Group Counseling on the Mental Health of Midwifery Students
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):500-507
Abstract
Original ArticleEffectiveness of Solution-Focused Group Counseling on the Mental Health of Midwifery Students
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):500-507
Views293See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study was conducted with the objective of investigating the effectiveness of solution-focused group counseling (SFGC) on promoting the mental health of midwifery students.
Methods
The present study is an intervention-based study with a pretest, a post-test, and a control group. The statistical population included all of the midwifery students studying in the midwifery department of the Bam University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran, who filled out the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) in the screening phase. In the second phase, 40 individuals, having a low level of mental health based on the cutoff score of 23, were selected and randomly divided into 2 groups (intervention and control), each group with 20 participants. The intervention group participated in 5 sessions of 75 minutes for SFGC. Then, the post-test was held in both groups and the data analysis was conducted using the Mann-Whitney and the Kruskal-Wallis test with IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). The significance level was considered as p < 0.05.
Results
The findings showed that the mean of the post-test mental health scores of the intervention group (14.5 ± 50.35) and of the control group (23.6 ± 35.83) showed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001). Moreover, the comparison between the mean scores of the mental health subscales (physical symptoms, stress, social performance, and depression) showed a statistically significant difference in these groups, and SFGC improved physical symptoms, stress, social performance, and depression in the members of the intervention group.
Conclusion
Solution-focused group counseling may improve all levels of mental health. This type of counseling is recommended to be used to solve the psychological problemsand to improve the mental health of students, as well as of the staff of the health system.


