-
Original Article07-01-2017
Effect of Obesity on Gestational and Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
Abstract
Original ArticleEffect of Obesity on Gestational and Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
Views145See moreAbstract
Purpose
To assess the impact of pre-pregnancy obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) on the gestational and perinatal outcomes.
Methods
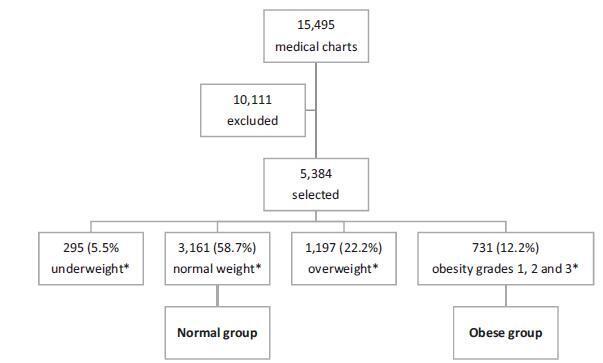
Retrospective cohort study of 731 pregnant women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 at the first prenatal care visit, comparing them with 3,161 women with a BMI between 18.5 kg/m2 and 24.9 kg/m2. Maternal and neonatal variables were assessed. Statistical analyses reporting the demographic features of the pregnant women (obese and normal) were performed with descriptive statistics followed by two-sided independent Student’s t tests for the continuous variables, and the chi-squared (χ2) test, or Fisher’s exact test, for the categorical variables. We performed a multiple linear regression analysis of newborn body weight based on the mother’s BMI, adjusted by maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertensive disorders, and cesarean deliveries to analyze the relationships among these variables. All analyses were performed with the R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) for Windows software, version 3.1.0. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Obesity was associated with older age [OR 9.8 (7.8-12.2); p < 0.01], hyperglycemic disorders [OR 6.5 (4.8-8.9); p < 0.01], hypertensive disorders [OR 7.6 (6.1-9.5); p < 0.01], caesarean deliveries [OR 2.5 (2.1-3.0); p < 0.01], fetal macrosomia [OR 2.9 (2.3-3.6); p < 0.01] and umbilical cord pH [OR 2.1 (1.4-2.9); p < 0.01). Conversely, no association was observed with the duration of labor, bleeding during labor, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes after birth, gestational age, stillbirth and early neonatal mortality, congenital malformations, and maternal and fetal injury.
Conclusion
We observed that pre-pregnancy obesity was associated with maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertension syndrome, cesarean deliveries, fetal macrosomia, and fetal acidosis.
-
Original Article07-01-2017
Evaluation of Quality of life, Physical Activity and Nutritional Profile of Postmenopausal Women with and without Vitamin D Deficiency
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):337-343
Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of Quality of life, Physical Activity and Nutritional Profile of Postmenopausal Women with and without Vitamin D Deficiency
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):337-343
Views243See moreAbstract
Introduction
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with various diseases. Prevalent in Brazil, it can result from inadequate lifestyle habits.
Objective
To demonstrate that postmenopausal women with vitamin D deficiency have worse quality of health, expressed as worse quality of life, lower levels of physical activity, and worse nutritional profile.
Methods
Postmenopausal women answered questionnaires about physical activity and quality of life, provided a 24-hour food record, and had serum vitamin D levels measured.
Results
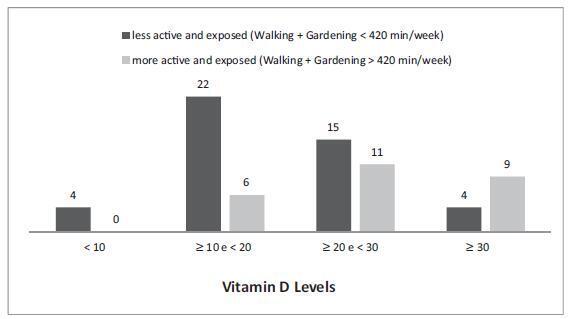
Among the more active women, those who perform a daily average of one hour of physical activity had vitamin D levels above 20 ng/mL (76.9%), and those, which expose themselves to sunlight, had vitamin D levels above 30 ng/mL (34.6%). Meanwhile the percentages for the women who are less physically active and less exposed to sunlight were 42.2% and 8.9% respectively. Being more active and more exposed to sunlight resulted in a lower fat percentage. Serum vitamin D levels were not correlated with quality of life.
Conclusion
Walking and gardening increased serum vitamin D levels and decreased the percentage of body fat. The limitations of the study prevented the impact of 25hidroxyvitamin D on the quality of life and nutritional aspects of the women from being evaluated.
-
Original Article07-01-2017
Definitive Contraception: Trends in a Ten-year Interval
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):344-349
Abstract
Original ArticleDefinitive Contraception: Trends in a Ten-year Interval
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):344-349
Views148See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the trends in definitive contraception in a ten-year interval comprising the years 2002 and 2012.
Method
Retrospective analysis of the tubal sterilization performed in our service in 2002 and2012,analyzingthedemographiccharacteristics,personalhistory,previouscontraceptive method, definite contraception technique, effectiveness and complications.
Results
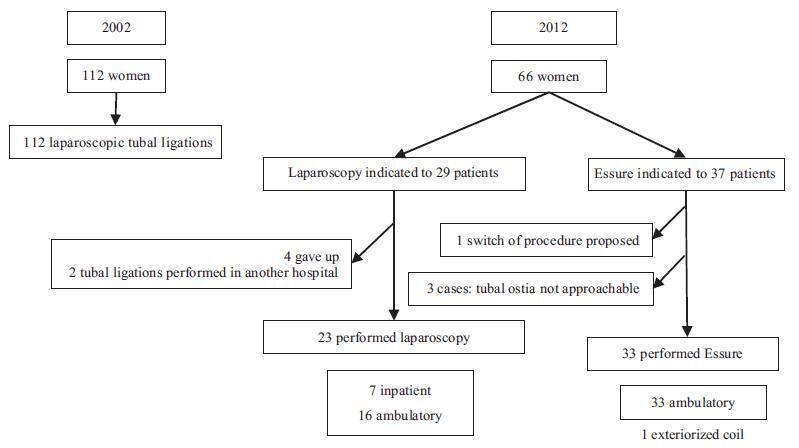
Definitive contraception was performed in 112 women in 2002 (group 1) and in 60 women in 2012 (group 2). The groups were homogeneous regarding age, parity, educational level and personal history. The number of women older than 40 years choosing a definitive method was more frequent in group 1, 49.1% (n = 55); for group 2, the rate was 34.8% (n = 23) (p = 0.04). The time between the last delivery and the procedure was 11.6±6.2 and 7.9±6.4 years (p = 0.014) in 2002 against 2012 respectively. In 2002, all patients performed tubal ligation by laparoscopic inpatient regime. In 2012, the bilateral placement of the Essure (Bayer Corporation, Whippany, NJ, US) device was suggested to 56.1% (n = 37) of the patients, while laparoscopy was suggested to 43.9% (n = 29) of them. All women who underwent laparoscopic sterilization had the procedure successfully completed using silastic rings. The overall bilateral device placement rate for the Essure was 91.6%, with only one complication reported. All Essure procedures were performed in an outpatient setting; for the laparoscopy, this rate was 79% (n = 15). No intentional pregnancies occurred until this date.
Conclusions
There is a trend in the decrease in definitive contraception over the years in our institution, maybe as a result of the development of long-acting reversible contraceptives. The hysteroscopic procedure has become a frequent option, as it is performed in an office setting without anesthesia, being a well-tolerated, minimal invasive method.
-
Original Article07-01-2017
Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Cervical Cancer Screening among Riverside Women of the Brazilian Amazon
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):350-357
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Cervical Cancer Screening among Riverside Women of the Brazilian Amazon
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):350-357
Views307Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the overall and type-specific prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection among females living in riverside communities in the state of Pará, in the Eastern Brazilian Amazon. These communities are inhabited by low-income people, and are accessible only by small boats. Cervical cytology and risk factors for HPV infection were also assessed.
Methods
Cervical samples from 353 women of selected communities were collected both for Papanicolau (Pap) test and HPV detection. Conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time PCR were used to assess the overall and type-specific prevalence of HPV-16 and HPV-18, the main oncogenic types worldwide. Epidemiological questionnaires were used for the assessment of the risk factors for HPV infection.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 37 years (standard deviation [SD] ± 13.7). Most were married or with a fixed sexual partner (79%), and had a low educational level (80%) and family monthly income (< U$ 250; 53%). Overall, HPV prevalence was 16.4% (n = 58), with 8 cases of HPV-16 (2.3%) and 5 of HPV-18 (1.4%). Almost 70% of the women surveyed had never undergone the Pap test. Abnormal cytology results were found in 27.5% (n = 97) of the samples, with higher rates of HPV infection according to the severity of the lesions (p = 0.026).
Conclusions
The infections by HPV-16 and HPV-18 were not predominant in our study, despite the high prevalence of overall HPV infection. Nevertheless, the oncogenic potential of these types and the low coverage of the Pap test among women from riverside communities demonstrate a potential risk for the development of cervical lesions and their progression to cervical cancer, since the access to these communities is difficult and, in most cases, these women do not have access to primary care and public health services.
Key-words cervical cancer screeningEpidemiologyhuman papillomavirus 16human papillomavirus 18Sexually transmitted diseasesSee more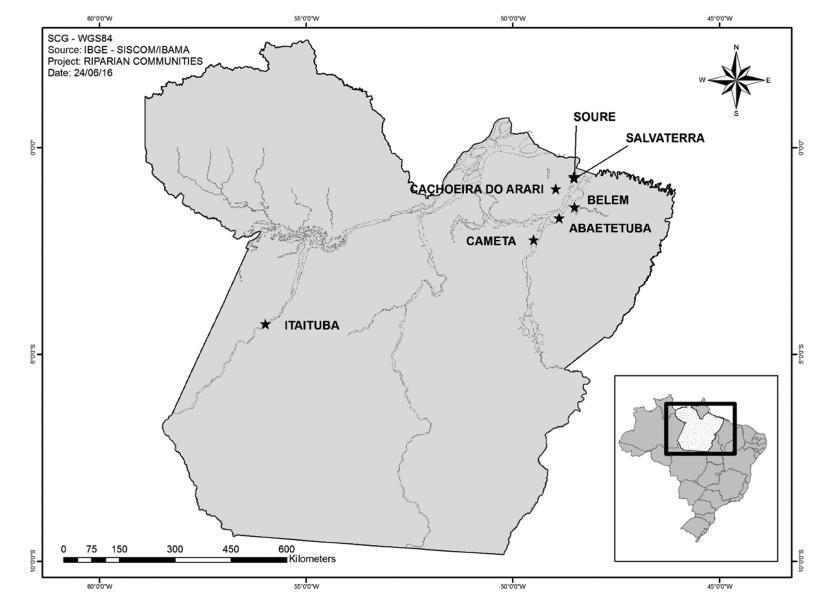
-
Original Article06-01-2017
Potential Drug Interactions and Drug Risk during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: An Observational Study in a Women’s Health Intensive Care Unit
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):258-264
Abstract
Original ArticlePotential Drug Interactions and Drug Risk during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: An Observational Study in a Women’s Health Intensive Care Unit
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):258-264
Views164See moreAbstract
Introduction
In the pregnancy-puerperal cycle, women may develop complications that require admission to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Thus, special attention to pharmacotherapy is necessary, particularly to potential drug interactions (PDIs) and to the effect of the drugs on the fetus and newborn.
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine the profile of PDIs and the potential risk of drugs used during pregnancy and breastfeeding among patients admitted to the ICU.
Methods
We conducted an observational, cross-sectional and prospective study, including pregnant and breastfeeding women admitted to the ICU at the Women’s Hospital of a university in the city of Campinas, Brazil, for one year. Online databases were used to identify and classify the PDIs and the potential risk of the drugs used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Results
We evaluated 305 prescriptions of 58 women, 31 pregnant and 27 breastfeeding, and 284 (91%) prescriptions presented PDIs. A total of 175 different combinations of PDIs were identified in the prescriptions, and adverse effects caused by the simultaneous use of drugs were not actually observed in the clinical practice. A total of 26 (1.4%) PDIs were classified as contraindicated. We identified 15 (13.8%) drugs prescribed with risk D, and 2 (1.8%) with risk X for pregnant women, as well as 4 (4.9%) drugs prescribed with high risk for breastfeeding women.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that there is a high incidence of PDIs in prescriptions. Most drugs used by pregnant and breastfeeding women at the ICU did not present serious risks to their fetus and newborns, but sometimes drugs with risk D or X are necessary in the course of the treatment.
-
Original Article06-01-2017
Syphilis in Pregnancy and Congenital Syphilis: Reality in a Portuguese Central University Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):265-272
Abstract
Original ArticleSyphilis in Pregnancy and Congenital Syphilis: Reality in a Portuguese Central University Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):265-272
Views279See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate maternal-fetal surveillance and follow-up of infants at risk for congenital syphilis (CS).
Methods
Retrospective cohort study in a Portuguese Tertiary Referral Hospital. The main inclusion criterion was a positive syphilis serology. The study included all pregnant women that delivered in our hospital between January 2004 and December 2013. The neonates were classified according to their probability of infection based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines.
Results
Among the 27 pregnancies at risk for CS, 48.2% (n = 13) of the women had a diagnosis during the 1st trimester, and the median gestational age at the end of the treatment was 28 weeks. Inadequate treatment was noted in 44.4% (n = 12) of the women. Adverse pregnancy outcomes were observed in 30.8% of the cases (n = 8), 5 of which had been adequately treated. We found 2 (7.7%) cases with “proven or highly probable CS,” 10 (38.5%) with “possible CS,” 12 (46.1%) with “less likely CS,” and 2 (7.7%) with “unlikely CS.”Among the infants, the treatment was successful, except for 1 neurosyphilis case.
Conclusion
This study highlights many of the difficulties/concerns encountered in the maternal-neonatal management of syphilis. We highlight the importance of assuring the early detection of the infection as a way of guaranteeing the timely treatment, as well as a good compliance to the treatment and follow-up through a more efficient pregnant women surveillance network.
-
Original Article06-01-2017
Combined Effect of the PGR + 331C > T, CYP17A1 -34A > G and CYP19A1 1531G > A Polymorphisms on the Risk of Developing Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):273-281
Abstract
Original ArticleCombined Effect of the PGR + 331C > T, CYP17A1 -34A > G and CYP19A1 1531G > A Polymorphisms on the Risk of Developing Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):273-281
Views204See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate the magnitude of the association of the polymorphisms of the genes PGR, CYP17A1 and CYP19A1 in the development of endometriosis.
Methods
This is a retrospective case-control study involving 161 women with endometriosis (cases) and 179 controls. The polymorphisms were genotyped by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the TaqMan system. The association of the polymorphisms with endometriosis was evaluated using the multivariate logistic regression.
Results
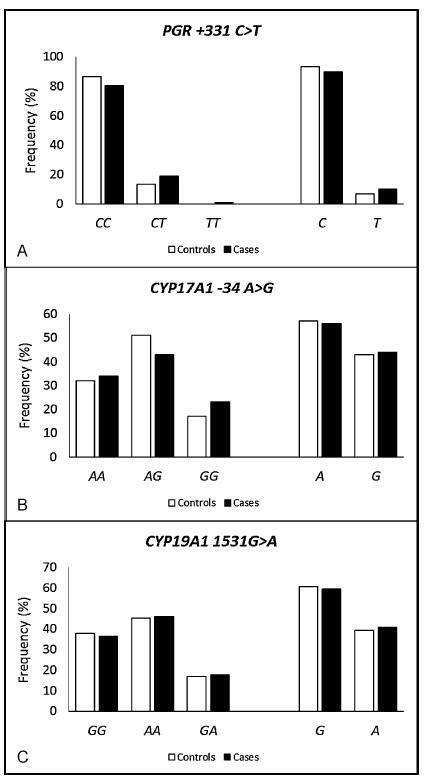
The endometriosis patients were significantly younger than the controls (36.0±7.3 versus 38.0±8.5 respectively, p = 0.023), and they had a lower body mass index (26.3±4.8 versus 27.9±5.7 respectively, p = 0.006), higher average duration of the menstrual flow (7.4±4.9 versus 6.1±4.4 days respectively, p = 0.03), and lower average time intervals between menstrual periods (25.2±9.6 versus 27.5±11.1 days respectively, p = 0.05). A higher prevalence of symptoms of dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, chronic pelvic pain, infertility and intestinal or urinary changes was observed in the case group when compared with the control group. The interval between the onset of symptoms and the definitive diagnosis of endometriosis was 5.2±6.9 years. When comparing both groups, significant differences were not observed in the allelic and genotypic frequencies of the polymorphisms PGR + 331C > T, CYP17A1 -34A > G and CYP19A1 1531G > A, even when considering the symptoms, classification and stage of the endometriosis. The combined genotype PGR + 331TT/CYP17A1 -34AA/CYP19A11531AA is positively associated with endometriosis (odds ratio [OR] = 1.72; 95% confidence interval [95%CI] = 1.09-2.72).
Conclusions
The combined analysis of the polymorphisms PGR-CYP17A1-CYP19A1 suggests a gene-gene interaction in the susceptibility to endometriosis. These results may contribute to the identification of biomarkers for the diagnosis and/or prognosis of the disease and of possible molecular targets for individualized treatments.
-
Original Article06-01-2017
What do Infertile Women Think about Oocyte Reception, Oocyte Donation, and Child Adoption?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):282-287
Abstract
Original ArticleWhat do Infertile Women Think about Oocyte Reception, Oocyte Donation, and Child Adoption?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):282-287
Views139See moreAbstract
Purpose
The views of infertile couples regarding oocyte donation by third parties and adoption are unknown, as these may be interpreted as a final closure of the available options for conception. This study aimed to determine the acceptance of oocyte donation, oocyte reception, and child adoption of infertile women who submitted to assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment
Methods
Sixty-nine women who were under treatment for infertility and submitted to ART procedures were included in this cross-sectional study. They were evaluated using semi-structured questionnaires administered during ovulation induction in a treatment cycle. Marital status, religion, years of schooling, occupation, type of infertility, age, duration of infertility, number of previous ART cycles, mean oocyte number per cycle, and mean number of embryos per cycle had no influence on a woman’s acceptance of oocyte donation or oocyte reception.
Results
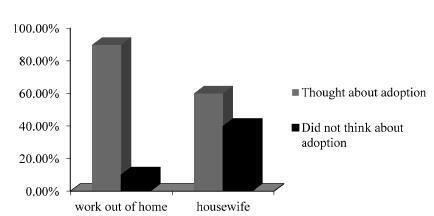
More than 90% of the patients thought that the subject of “adoption” should be brought up during their ART treatments, although they preferred to discuss this topic with psychologists, not doctors. Women with occupations were more willing to consider adoption.
Conclusion
The opinions of these patients on these issues seem to be based on personal concepts and ethical, religious, and moral values. Women preferred to discuss adoption with psychologists rather than doctors.