-
Original Article
Cervical Cancer Registered in Two Developed Regions from Brazil: Upper Limit of Reachable Results from Opportunistic Screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
06-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleCervical Cancer Registered in Two Developed Regions from Brazil: Upper Limit of Reachable Results from Opportunistic Screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):347-353
06-01-2018Views113Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to assess the time trends and pattern of cervical cancer diagnosed in the period from 2001 to 2012 by means of an opportunistic screening program from two developed regions in Brazil.
Methods
An observational study analyzing 3,364 cancer records (n = 1,646 from Campinas and n = 1,718 from Curitiba region) available in hospital-based cancer registries was done. An additional 1,836 records of CIN3/AIS from the region of Campinas was analyzed. The statistical analysis assessed the pooled data and the data by region considering the year of diagnosis, age-group, cancer stage, and histologic type. The Cochran-Armitage trend test was applied and p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
The total annual cervical cancer registered from2001 to 2012 showed a slight drop (273-244), with an age average of 49.5 y, 13 years over the average for CIN3/AIS (36.8 y). A total of 20.6% of the diagnoses (1.6% under 25 y) were done out of the official screening age-range. The biennial rate of diagnoses by age group for the region of Campinas showed an increase trend for the age groups under 25 y (p = 0.007) and 25 to 44 y (p = 0.003). Stage III was the most recorded for both regions, with an annual average of 43%, without any trend modification. There was an increasing trend for stage I diagnoses in the region of Campinas (p = 0.033). The proportion of glandular histologic types registered had an increased trend over time (p = 0.002), higher for the region of Campinas (21.1% versus 12.5% for the region of Curitiba).
Conclusion
The number, pattern and trends of cervical cancer cases registered had mild and slow modifications and reflect the limited effectivity of the opportunistic screening program, even in developed places.
Key-words Cervical cancerCervical intraepithelial neoplasiaEpidemiologypreventive medicinePublic healthSee more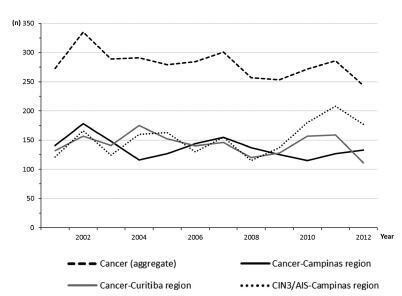
-
Original Article
The Effect on Performance Time and Quality of the Knots after Mono or Bimanual Training of Laparoscopic Intracorporeal Knot Tying according to the Gladiator Rule Technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):266-274
05-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleThe Effect on Performance Time and Quality of the Knots after Mono or Bimanual Training of Laparoscopic Intracorporeal Knot Tying according to the Gladiator Rule Technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):266-274
05-01-2018Views89Abstract
Objective
To assesswhether themonomanual or bimanual training of laparoscopic suture followingthe sametechniquemay interferewith theknots’ performancetimeand/or quality.
Methods
A prospective observational study involving 41 resident students of gynecology/ obstetrics and general surgery who attended a laparoscopic suture training for 2 days. The participants were divided into two groups. Group A performed the training using exclusively their dominant hand, and group B performed the training using both hands to tie the intracorporeal knot. All participants followed the same technique, called Romeo Gladiator Rule. At the end of the course, the participants were asked to perform three exercises to assess the time it took them to tie the knots, as well as the quality of the knots.
Results
A comparative analysis of the groups showed that there was no statistically significant difference (p = 0.334) between them regarding the length of time to tie one knot. However, when the time to tie 10 consecutive knots was compared, group A was faster than group B (p = 0.020). A comparison of the knot loosening average, in millimeters, revealed that the knots made by group B loosened less than those made by group A, but there was no statistically significant difference regarding the number of knots that became untied.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that the knots from group B showed better quality than those from group A, with lower loosening measures and more strength necessary to untie the knots. The study also demonstrated that group A was faster than B when the time to tie ten consecutive knots was compared.
Key-words laparoscopic trainingsuture trainingSee more -
Original Article
Cost-effectiveness of Carbetocin versus Oxytocin for Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage Resulting from Uterine Atony in Women at high-risk for bleeding in Colombia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):242-250
05-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleCost-effectiveness of Carbetocin versus Oxytocin for Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage Resulting from Uterine Atony in Women at high-risk for bleeding in Colombia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):242-250
05-01-2018Views219See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the cost-effectiveness of carbetocin versus oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) due to uterine atony after vaginal delivery/ cesarean section in women with risk factors for bleeding.
Methods
A decision treewas developed for vaginal delivery andanother one for cesarean, in which a sequential analysis of the results was obtained with the use of carbetocin and oxytocin for prevention of PPH and related consequences. A third-party payer perspective was used; only directmedical costs were considered. Incremental costs and effectiveness in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were evaluated for a one-year timehorizon. The costs were expressed in 2016 Colombian pesos (1 USD = 3,051 Col$).
Results
In the vaginal delivery model, the average cost of care for a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonic agents was Col$ 347,750 with carbetocin and Col$ 262,491 with oxytocin,while theQALYs were 0.9980 and 0.9979, respectively. The incremental costeffectiveness ratio is above the cost-effectiveness threshold adopted by Colombia. In the model developed for cesarean section, the average cost of a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonics was Col$ 461,750 with carbetocin, and Col$ 481,866 with oxytocin, and the QALYs were 0.9959 and 0.9926, respectively. Carbetocin has lower cost and is more effective, with a saving of Col$ 94,887 per avoided hemorrhagic event.
Conclusion
In case of elective cesarean delivery, carbetocin is a dominant alternative in the prevention of PPH compared with oxytocin; however, it presents higher costs than oxytocin, with similar effectiveness, in cases of vaginal delivery.
-
Original Article
A Long-term Estrogen Deficiency in Ovariectomized Mice is Associated with Disturbances in Fatty Acid Oxidation and Oxidative Stress
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):251-259
05-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleA Long-term Estrogen Deficiency in Ovariectomized Mice is Associated with Disturbances in Fatty Acid Oxidation and Oxidative Stress
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):251-259
05-01-2018Views185See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this work was to evaluate the changes caused by estrogen deficiency in lipid metabolism.
Methods
This study encompassed direct measurements of plasma biochemical analyses, liver lipid contents, and assessments of the mitochondrial β-oxidation capacity as well as an evaluation of the liver redox status in an animal model of estrogen deficiency.
Results
When compared with control mice, the livers of ovariectomized (OVX) mice presented considerable accretions in their lipid contents, which were accompanied by increased levels of lipid peroxidation in liver homogenates andmitochondria from OVX groups and decreased reduced glutathione (GSH) contents. In isolated mitochondria, estrogen deficiency inhibited mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids irrespective of their chain length. The liver mitochondrial and peroxisomal H2O2 generations in OVX mice were increased. Additionally, the activities of all antioxidant enzymes assessed were decreased.
Conclusion
These data provide one potential explanation for the increased susceptibility to metabolic diseases observed after menopause.
-
Original Article
Functioning in Women with Cervical Cancer in Brazil: the Perspective of Experts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):260-265
05-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleFunctioning in Women with Cervical Cancer in Brazil: the Perspective of Experts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):260-265
05-01-2018Views106Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to identify the perspective of the specialists about functioning in women with cervical cancer (CC).
Methods
A study was conducted with specialists using the Delphi methodology. The specialist contacts were found in oncology organizations and associations, as well as in a referral hospital in the treatment of CC. The questions that the experts answered covered the biopsychosocial domains of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF).
Results
Twenty-five specialists participated in the study. The experts’ responses generated 485 significant concepts. The categories that presented the highest frequencies of reporting by the specialists were health services, systems and policies; structure of the reproductive system; health professionals and sexual function.
Conclusion
Regarding the perception of the specialists, this study concluded that 24 categories of ICF are the most relevant in the context of functioning in women with CC. The results suggest that the biopsychosocial perspective was incorporated in the experts’ perceptions about the functioning phenomenon in women with CC in Brazil.
Key-words disability and healthhealth personnelinternational classification of functioningmedical oncologyUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
Tocolysis among Women with Preterm Birth: Associated Factors and Outcomes from a Multicenter Study in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
04-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleTocolysis among Women with Preterm Birth: Associated Factors and Outcomes from a Multicenter Study in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
04-01-2018Views177See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the use of tocolysis in cases of preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor in a Brazilian sample.
Methods
A sample of 1,491 women with preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor were assessed, considering treatment with tocolysis or expectant management, according to gestational age at birth (< 34 weeks and 34 to 36 þ 6 weeks) and drugs prescribed. The study took place in 20 Brazilian hospitals from April 2011 to July 2012. Bivariate analyses were conducted to evaluate associations with sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics and odds ratios with their respective 95% confidence intervals were estimated for maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Results
A total of 1,491 cases of preterm birth were considered. Tocolysis was performed in 342 cases (23%), 233 of which (68.1%) were delivered before 34 weeks. Within the expectant management group, 73% was late preterm and with more advanced labor at the time of admission. The most used drugs were calcium channel blockers (62.3%), followed by betamimetics (33%). Among the subjects in the tocolysis group, there were more neonatal and maternal complications (majority non-severe) and an occurrence of corticosteroid use that was 29 higher than in the expectant management group.
Conclusion
Tocolysis is favored in cases of earlier labor and also among thosewith less than 34 weeks of gestation, using preferably calcium channel blockers, with success in achieving increased corticosteroid use. Tocolysis, in general, was related to higher maternal and neonatal complication rates, which may be due to the baseline difference between cases at admission. However, these results should raise awareness to tocolysis use.
-
Original Article
Effectiveness of Metformin in the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Obese Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):180-187
04-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleEffectiveness of Metformin in the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Obese Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):180-187
04-01-2018Views184See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the effectiveness of metformin in the incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in obese pregnant women attending a public maternity hospital in Joinville, Santa Catarina, Brazil.
Methods
Randomized clinical trial including obese pregnant women with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2, divided into two groups (control and metformin). Both groups received guidance regarding diet and physical exercise. The participants were assessed at two moments, the first at enrollment (gestational age ≤ 20) and the second at gestational weeks 24-28. The outcomes assessed were BMI and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) diagnosis. The data distribution was assessed with the Friedman test. For all the analytical models, the p-values were considered significant when lower than 0.05. The absolute risk reduction was also estimated.
Results
Overall, 164 pregnant women were assessed and further divided into 82 participants per group. No significant difference was observed in BMI variation between the control and metformin groups (0.9 ± 1.2 versus 1.0 ± 0.9, respectively, p = 0.63). Gestational diabetes mellitus was diagnosed in 15.9% (n = 13) of the patients allocated to the metformin group and 19.5% (n = 16) of those in the control group (p = 0.683). The absolute risk reduction was 3.6 (95% confidence interval 8.0- 15.32) in the group treated with metformin, which was not significant.
Conclusion
Metformin was not effective in reducing BMI and preventing GDM in obese pregnant women.
-
Original Article
Association between Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):188-195
04-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleAssociation between Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):188-195
04-01-2018Views170Abstract
Objective
To analyze the association between the indirect methods of evaluating insulin resistance (IR) and blood pressure, anthropometric and biochemical parameters in a population of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients.
Methods
Cross-sectional study performed at the Hospital Universitário de Brasília (HUB, in the Portuguese acronym) involving PCOS patients diagnosed from January 2011 to January 2013. Four indirect methods, namely, fasting blood insulin level, fasting glucose/insulin ratio (G/I), homeostatic model-assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI), were used to obtain the IR diagnosis. The data were analyzed using the test of proportions, the Chisquare test, and Fisher exact test, when indicated.
Results
Out of the 83 patients assessed, aged 28.79 ± 5.85, IR was found in 51.81- 66.2% of them using the G/I ratio and the QUICKI, respectively. The test of proportions did not show a significant difference between the methods analyzed. The proportion of IR diagnoses was statistically higher in obese women than in women with normal body mass index (BMI). We observed a statistically significant association between all the methods for diagnosing IR and BMI, waist circumference (WC) and lipid accumulation product (LAP). With regards to arterial hypertension (AH), we observed a significant association according to three methods, with the exception of the ratio G/I.
Conclusion
Insulin resistance prevalence varied according to the diagnostic method employed,with no statistical difference between them. The proportion of IR diagnoses was statistically higher in obese women than in women with normal BMI.We observed a significant association between IR andWC, BMI, LAP, as well as dyslipidemia and AH in a high proportion of patients.
Key-words Body mass indexInsulin resistancelipid accumulation productPolycystic ovary syndromeWaist circumferenceSee more


